Abstract
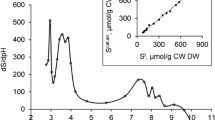
Fractions of acid invertase and acid phosphatase of the ericoid mycorrhizal fungus Hymenoscyphus ericae (Read) Korf & Kernan were compared by column chromatography and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Acid invertase levels were measured during the exponential phase after 14 days growth in pure culture. Most acid invertase was wall associated (50%) with 41% forming an extracellular fraction and 9% a soluble, cytoplasmic fraction. The wall-bound fraction was partially solubilized by 1 M NaCl, bulked with the extracellular fraction and separated by gel filtration into two acid invertase activity peaks. These peaks corresponded closely to two acid phosphatase activity peaks measured in the same eluates. Anion exchange chromatography under a continuous salt gradient separated the invertase and phosphatase isoforms from each other. Non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis demonstrated that the more active isoforms of each enzyme have different electrophoretic properties and are high mannose-type glycoproteins with a high affinity for the lectin, concanavalin A. The results are discussed in terms of the functional aspects of the two enzymes and their cytochemical localization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albersheim P, McNeil M, Darvill AG, Valent BS, Hahn MG, Robertsen BK, Aman P (1981) Structure and function of complex carbohydrates active in regulating the interactions of plants and their pests. In: Loewus FA, Ryan CA (eds) The phytochemistry of cell recognition and cell surface interactions. (Recent advances in phytochemistry, vol 15) Plenum Press, New York London, pp 1–272
Billett EE, Billett MA, Burnett JH (1977) Stimulation of maize invertase activity following infection by Ustilago maydis. Phytochemistry 16:1160–1163
Blum H, Beier H, Gross HJ (1987) Improved silver staining of plant proteins, RNA and DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis 8:93–99
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 62:248–254
Callow JA, Long DE, Lithgow ED (1980) Multiple molecular forms of invertase in maize smut infections. Physiol Plant Pathol 16:93–107
Chang PLY, Trevithick JR (1972a) Release of wall-bound invertases and trehalase in Neurospora crassa by hydrolytic enzymes. J Gen Microbiol 70:13–32
Chang PLY, Trevithick JR (1972b) Distribution of wall-bound invertase during the asexual life-cycle of Neurospora crassa. J Gen Microbiol 70:23–29
Dickerson AG (1972) A β-d-fructofuranosidase from Claviceps purpurea. Biochem J 129:263–272
Geissmann M, Frey T, Ruffner HP (1991) Occurrence and properties of acid invertase in cultures of Botrytis cinerea. Mycol Res 95:1321–1327
Gianinazzi-Pearson V, Bonfante-Fasolo P (1986) Variability in wall structure and mycorrhizal behaviour of ericoid mycorrhizal fungal isolates. In: Gianinazzi-Pearson V, Gianinazzi S (eds) Physiological and genetical aspects of mycorrhizae. INRA, Service des Publications, Versailles, pp 563–569
Gianinazzi-Pearson V, Dexheimer J, Gianinazzi S, Jeanmaire C (1984) Plasmalemma structure and function in endomycorrhizal symbioses. Z Pflanzenphysiol 1145:201–205
Gianinazzi-Pearson V, Bonfante-Fasolo P, Dexheimer J (1986) Ultrastructural studies of surface interactions during adhesion and infection by ericoid mycorrhizal fungi. In: Lugtenberg B (ed) Recognition in microbe-plant symbiotic and pathogenic interactions. (NATO ASI series, series H, vol 4) Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 273–282
Greenland AH, Lewis DH (1981) The acid invertase of the developing third leaf of oat. I. Changes in activity of invertase and concentrations of ethanol-soluble carbohydrates. New Phytol 88:265–277
Lemoine MC, Gianinazzi-Pearson V, Gianinazzi S, Straker CJ (1992) Occurrence and expression of acid phosphatase of Hymenoscyphus ericae (Read) Korf & Kernan, in isolation or associated with plant roots. Mycorrhiza 1:137–146
Mitchell DT, Read DJ (1981) Utilization of inorganic and organic phosphates by the mycorrhizal endophytes of Vaccinium macrocarpon and Rhododendron ponticum. Trans Br Mycol Soc 76:255–260
Pearson V, Read DJ (1975) The physiology of the mycorrhizal endophyte of Calluna vulgaris. Trans Br Mycol Soc 64:1–7
Smith SE, Smith FA (1990) Structure and function of the interfaces in biotrophic symbioses as they relate to nutrient transport. New Phytol 114:1–38
Straker CJ, Mitchell DT (1986) The activity and characterization of acid phosphatases in endomycorrhizal fungi of the Ericaceae. New Phytol 104:243–256
Straker CJ, Gianinazzi-Pearson V, Gianinazzi S, Cleyet-Marel JC, Bousquet N (1989) Electrophoretic and immunological studies on acid phosphatase from a mycorrhizal fungus of Erica hispidula L. New Phytol 111:215–221
Stribley DP, Read DJ (1974) The biology of mycorrhiza in the Ericaceae. III. Movement of carbon-14 from host to fungus. New Phytol 73:731–741
Vainstein MH, Peberdy JF (1991) Location of invertase in Aspergillus nidulans: release during hyphal wall digestion and secretion by protoplasts. Mycol Res 95:1270–1274
Williams AM, Maclean DJ, Scott KJ (1984) Cellular location and properties of invertase in mycelium of Puccinia graminis. New Phytol 98:451–463
Ziegler E, Albersheim P (1977) Extracellular invertases secreted by three races of plant pathogen are glycoproteins which possess different carbohydrate structures. Plant Physiol 59:1104–1110
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Straker, C.J., Schnippenkoetter, W.H. & Lemoine, MC. Analysis of acid invertase and comparison with acid phosphatase in the ericoid mycorrhizal fungus Hymenoscyphus ericae (Read) Korf and Kernan. Mycorrhiza 2, 63–67 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00203251
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00203251