Abstract
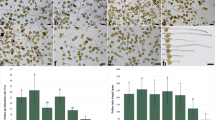
Spermidine applied for 18 h to intact maize seedlings through their roots reduces root growth 70%, and the effect is reversible. Histological observations of longitudinal sections of 0.4-cm root apical segments from 2-day-old maize seedlings grown for 18 h in 0.5 m CaSO4 solution with or without 1 mm spermidine contribute to the explanation of spermidine-dependent slow root growth. In the meristematic zone a strong reduction of the mitotic index and in the elongation zone an inhibition of cell elongation occur simultaneously. Cell shape analysis along the growth axis of the maize root apex expressed in terms of form factor (FCircle) values substantiates the dual effect of spermidine on mitotic activity and cell elongation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PA:
-
polyamine(s)
- Spm:
-
spermine
- Spd:
-
spermidine
References
Altmann A (1989) Polyamines and plant hormons. In: U Bacharach, JM Heimer (eds) The Physiology of polyamines. Vol 2. pp 121–145
Bacharach U, Shlomit R, Loebenstein G, Eilon G (1965) Antiviral action of oxidized spermine: Inactivation of plant viruses. Nature 208:1095–1096
Baluska F, Kubica S, Hauskrecht (1990) Postmitotic “isodiametric” cell growth in the maize root apex. Planta 181:269–274
Bueno M, Garrido D, Matilla A (1993) Gene expression induced by spermidine in isolated embryonic axes of chickpea seeds. Physiol Plant 87:381–388
Cona A, Federico R, Gramiccia M, Orsini S, Gradoni L (1991) The amino aldheydes produced by spermine and spermidine oxydation with maize polyamine oxidase have antileishmanial effect. Biotech Appl Biochem 14:54–59
de Agazio M, Federico R, Angelini R, De Cesare F, Grego S (1992) Spermidine pretreatment or root tip removal in maize seedlings: Effects on K+ uptake and tissue modifications. J Plant Physiol 140:741–746
Garmanik A, Frydman RR (1991) Cadaverine, an essential diamine for the normal root development of germinating soybean seed. Plant Physiol 97:778–785
Gatta L, Marchitelli C, Federico R (1992) Effect of polyamines and their oxidative products on maize and lentil root growth. Ann Bot (Italy) 50:43–48
Gaugas JM, Deweg DL (1978) Evidence for serum binding of oxidized spermine and its potent G1 phase inhibition of cell proliferation. Br J Cancer 39:548–557
Jackson MB, Hall KC (1993) Polyamine content and action in roots of Zea mays L. in relation to aerenchyma development. Ann Bot 72:569–575
Sacchi AG, Cocucci M (1992) Effect of deuterium oxide on growth, proton extrusion, potassium influx, and in vitro plasma membrane activities in maize root segments. Plant Physiol 100:1962–1967
Showalter AM (1993) Structure and function of plant cell wall proteins. Plant Cell 5:9–23
Smith TA (1985) Polyamines. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 36:117–143
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Agazio, M., Grego, S., Ciofi-Luzzatto, A. et al. Inhibition of maize primary root elongation by spermidine: Effect on cell shape and mitotic index. J Plant Growth Regul 14, 85–89 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00203118
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00203118