Abstract
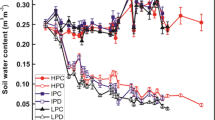
The response of gas exchange, leaf chlorophyll content, relative fluorescence to decreasing water potential and recovery was followed in European beech seedlings from two Italian populations, differing in their native precipitation amounts. A population from Sicily (southern Italy) was selected as representative of a xeric population while a population from central Italy, Abetone, represented a mesic one. Dry-matter partitioning, leaf area, hydraulic sufficiency and xylem embolism were evaluated in both well-watered control plants as well as in plants subjected to drought. With the onset of water stress, values of water potential, leaf relative water content, net photosynthesis, leaf conductance and leaf chlorophyll concentration decreased concurrently while relative fluorescence remained unchanged. The population from Sicily showed a delay in effects of the imposed drought. Within 5 days of rewatering, leaf conductance was not fully recovered while all of the other parameters recovered to control levels, in both populations. Total, shoot, stem and root dry weight tended to be higher in seedlings from Abetone, even though both populations had similar photosynthetic rates. The population from Sicily exhibited about 3% greater (even if not significant) allocation to roots than the population from Abetone. Seedlings from Abetone had higher, but not significant, leaf specific conductivity and per cent loss in hydraulic conductivity than seedlings from Sicily. Drought resulted in a reduction of hydraulic conductivity and hydraulic sufficiency in seedlings from both populations. Photosynthesis of water stressed plants from both populations appeared to be reduced primarily by carbon dioxide diffusion through stomata and perhaps secondarily by changes in chlorophyll concentration rather than by efficiency of photosystem II. The effect of hydraulic factors on gas exchange during drought and recovery was not clearly evident.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Abrams MD (1988) Comparative water relations of three successional hardwood species in central Wisconsin. Tree Physiol 4: 263–273
Abrams MD, Kloeppel BD, Kubiske ME (1992) Ecophysiological and morphological responses to shade and drought in two contrasting ecotypes of Prunus serotina. Tree Physiol 10: 343–355
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24: 1–15
Björkman O, Powles SB (1984) Inhibition of photosynthetic reactions under water stress: interaction with light level. Planta 161: 490–504
Borghetti M, Giannini R (1982) Indagini preliminari sulla variazione di alcuni caratteri in piantine di faggio di provenienza diversa. Ann Acc It Sci For XXXI: 119–134
Borghetti M, Leonardi S, Raschi A, Snyderman D, Tognetti R (1993) Ecotypic variation of xylem embolism, phenological traits, growth parameters and allozyme characteristics in Fagus sylvatica. Funct Ecol 7: 71–720
Eschrich W, Burchardt R, Essiamah S (1989) The induction of sun and shade leaves of European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.): anatomical studies. Trees 3: 1–10
Epron D, Dreyer E (1993) Photosynthesis of oak leaves under water stress: maintenance of high photochemical efficiency of photosystem II and occurrence of non-uniform CO2 assimilation. Tree Physiol 13: 107–117
Khalil AAM, Grace J (1992) Acclimation to drought in Acer pseudoplatanus L. (Sycamore) seedlings. J Exp Bot 43: 1591–1602
Michelozzi M, Johnson JD, Warrag EI (1995) Response of ethylene and chlorophyll in two Eucalyptus clones during drought. New For (in press)
Ni BR, Pallardy SG (1991) Response of gas exchange to water stress in seedlings of woody angiosperms. Tree Physiol 8: 1–9
Parker WC, Pallardy SG (1991) Gas exchange during a soil drying cycle in seedlings of four black walnut (Jugians nigra L.) families. Tree Physiol 9: 339–348
Schulze E-D (1986) Carbon dioxide and water vapor exchange in response to drought in the atmosphere and in the soil. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 37: 247–274
Shuway DL, Steiner KC, Kolb TE (1993) Variation in seedlings hydraulic architecture as a function of species and environment. Tree Physiol 12: 41–54
Sperry JS (1993) Winter xylem embolism and spring recovery in Betula cordifolia, Fagus grandifolia, Abies balsamea and Picea rubens. In: Borghetti M, Grace J, Raschi A (eds) Water transport in plants under climatic stress. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 86–98
Sperry JS, Pockman WT (1993) Limitation to transpiration by hydraulic conductance and xylem cavitation in Betula occidentalis. Plant Cell Environ 16: 279–287
Sperry JS, Donnelly JR, Tyree MT (1988a) A method for measuring hydraulic conductivity and embolism in xylem. Plant Cell Environ 11: 35–40
Sperry JS, Tyree MT, Donnelly JR (1988b) Seasonal occurrence of xylem embolism in sugar maple (Acer saccharum). Am J Bot 75: 1212–1218
Stickan W, Zhang X (1992) Seasonal changes in CO2 and H2O gas exchange of young European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.). Trees 6: 96–102
Tognetti R, Borghetti M (1994) Formation and seasonal occurrence of xylem embolism in Alnus cordata. Tree Physiol 14: 241–250
Tognetti R, Michelozzi M, Borghetti M (1994) Response to light of shade-grown beech seedlings objected to different watering regimes. Tree Physiol 14: 751–758
Trejo CL, Davies WJ (1991) Drought-induced closure of Phaseolus vulgaris L. stomata precedes leaf water deficits and any increase in xylem ABA concentration. J Exp Bot 42: 1507–1515
Tyree MT, Ewers FW (1991) The hydraulic architecture of trees and other woody plants. New Phytol 119: 345–360
Tyree MT, Yang S (1992) Hydraulic conductivity recovery versus water pressure in xylem of Acer saccharum. Plant Physiol 100: 669–676
Tyree MT, Alexander J, Machado J-L (1992) Loss of hydraulic conductivity due to water stress in intact juveniles of Quercus rubra and Populus deltoides. Tree Physiol 10: 411–415
Virzo De Santo A, Ligrone R, Alfani A, Fioretto A, Russo G (1984) CAM activity and day/night changes in the ultrastructure of stem chlorenchyma of Cissus quadrangularis L. as influenced by drought. Plant Cell Environ 7: 105–112
Weber JA, Gates DM (1990) Gas exchange in Quercus rubra (northern red oak) during a drought: analysis of relations among photosynthesis, transpiration, and leaf conductance. Tree Physiol 7: 215–225
Woodward FI (1987) Climate and plant distribution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Zhang J, Davies WJ (1989) Abscisic acid produced in dehydrating roots may enable the plant to measure the water status of the soil. Plant Cell Environ 12: 73–81
Zimmermann MH, Milburn JA (1982) Transport and storage of water. In: Lare OL, Nobel PS, Osmond CB, Ziegler H (eds) Physiological plant ecology, II; Encyclopedia of plant physiology new series, vol 12B. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 135–151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tognetti, R., Johnson, J.D. & Michelozzi, M. The response of European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) seedlings from two Italian populations to drought and recovery. Trees 9, 348–354 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00202499
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00202499