Abstract
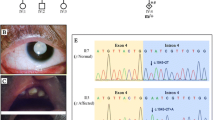
The molecular basis of null alleles was investigated by cDNA polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in seven Tay-Sachs patients. Although mRNAs were undetectable by Northern blot, cDNA-PCR amplification allowed us to get a sufficient amount of cDNA to characterize abnormal transcripts. In two French patients (one homozygote and one compound heterozygote with a 4-bp insertion in exon 11 of the second allele) suffering an infantile form of the disease, we detected abnormal RNAs with a 17-bp insertion due to a GT to AT transition at the donor site of intron 9, resulting in the activation of a cryptic donor site in the intron. This mutation has been found in 9 out of 82 Tay-Sachs chromosomes (11%) in association with alleles responsible from different clinical courses. In the other five patients we found the 4-bp insertion in exon 11 and two nonsense mutations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akli S, Chelly J, Mezard C, Gandy S, Kahn A, Poenaru L (1990) A “G” to “A” mutation at position -1 of a 5′ splice site in a late infantile form of Tay-Sachs disease. J Biol Chem 265:7324–7330
Akli S, Chelly J, Lacorte JM, Poenaru L, Kahn A (1991) Seven novel Tay-Sachs mutations detected by chemical mismatch cleavage of PCR-amplified cDNA fragments. Genomics 11:124–134
Arpaia E, Dumbrille-Ross A, Maler T, Neote K, Tropak M, Troxel C, Stirling JS, Bapat B, Lamhonwah AM, Mahuran DJ, Schuster SM, Clarke JTR, Lowden JA, Gravel RA (1988) Identification of an altered splice site in Ashkenazi Tay-Sachs disease. Nature 333:85–86
Chirgwin JM, Przybyla AE, Macdonald RJ, Rutter WJ (1979) Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry 18:5294–5299
Duncan BK, Miller JH (1980) Mutagenic deamination of cytosine residue in DNA. Nature 287:560–561
Hechtman P, Boulay B, Bayleran J, Kaplan F (1990) DNA diagnosis of Tay-Sachs disease: PCR amplification for detection of the French Canadian deletion allele (Abstract). Am J Hum Genet 43:3/A9
Myerowitz R, Costigan C (1988) The major defect in Ashkenazi Jews with Tay-Sachs disease is an insertion in the gene for the α-chain of β-hexosaminidase. J Biol Chem 263:18587–18589
Myerowitz R, Hogikyan ND (1987) A deletion involving Alu sequences in the β-hexosaminidase α-chain gene of French Canadians with Tay-Sachs disease. J Biol Chem 262:15386–15399
Nooman KE, Roninson IB (1988) mRNA phenotyping by enzymatic amplification of randomly primed cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res 16:10366
Proia RL, Soravia E (1987) Organisation of the gene encoding the human β-hexosaminidase α-chain. J Biol Chem 262:5677–5681
Robberson B, Cote G, Berget S (1990) Exon definition may facilitate splice site selection in RNAs with multiple exons. Mol Cell Biol 10:84–94
Shapiro MB, Senapathy P (1987) DNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res 15:7155–7174
Smith CWJ, Porro EB, Patton JG, Nadal-Ginard B (1989) Scanning from an independently specified branch point defines the 3′ splice site of mammalian introns. Nature 342:243–247
Tanaka A, Ohno K, Sandhoff K, Maire I, Kolodny E, Brown HA, Suzuki K (1990) GM2-gangliosidosis B1 variant: analysis of β-Hexosaminidase α gene abnormalities in seven patients. Am J Hum Genet 46:329–339
Winship PR (1989) An improved method for directly sequencing PCR amplified material using dimethyl sulphoxide. Nucleic Acids Res 17:1266
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akli, S., Chelly, J., Kahn, A. et al. A null allele frequent in non-Jewish Tay-Sachs patients. Hum Genet 90, 614–620 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00202478
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00202478