Abstract
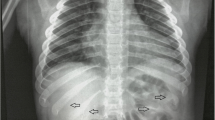
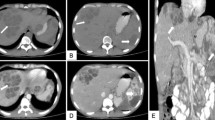
Objective. Melioidosis is a tropical infection caused by a gram-negative bacillus, Pseudomonas pseudomallei. The disease manifests initially as localized suppurative lesions and can progress to acute disseminated septicemia with 65–90% mortality if inadequately treated. Musculoskeletal involvement is common. The purpose of this study was to describe the clinical features and imaging appearances of musculoskeletal melioidosis.
Design. We retrospectively analyzed the clinical profiles and images of 26 patients diagnosed over a 6-year period as suffering from melioidosis.
Patients. The study group comprised 11 patients with musculoskeletal melioidosis and 15 patients with nonmusculoskeletal melioidosis.
Results and Conclusions. We found that musculoskeletal melioidosis mimicks other infections both clinically and radiologically. Clinical awareness is therefore crucial, as diagnosis can only be established by bacteriological and immunological studies. Prompt treatment with long-term combination antibiotics in high dosages and surgical drainage of abscesses improves survival.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borgmeier PJ, Kalovidouris AE. Septic arthritis of the sternomanubrial joint due to Pseudomonas pseudomallei. Arthritis Rheum 1980; 23: 1057–1059.
Diamond HS, Pastore R. Septic arthritis due to Pseudomonas pseudomallei. Arthritis Rheum 1967; 10: 459–465.
Saengnipanthkul S, Laupattarakasem W, Kowsuwon W, Mahaisavariya B. Isolated articular melioidosis. Clin Orthop 1991; 267: 182–185.
Kosuwon W, Saengnipanthkul S, Mahaisavariya B, Laupattarakase W, Kaen K. Musculoskeletal melioidosis. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1993; 75: 1811–1815.
Whitmore A, Krishnaswami CS. An account of the discovery of a hitherto undescribed infective disease occurring among the population of Rangoon. Indian Med Gaz 1912; 47: 262–267.
Patamasucon P, Schaad UB, Nelson JD. Melioidosis. J Pediatr 1982; 100: 175–182.
Koponen MA, Zlock D, Palmer DL, Merlin TL. Melioidosis: forgotten, but not gone! Arch Intern Med 1991; 151: 605–608.
McCormick JB, Sexton DJ, McMurray JG, Carey E, Hayes P, Feldman RA. Human-to-human transmission of Pseudomonas pseudomallei. Ann Intern Med 1975; 83: 512–513.
Osterras GR, Hardman JM, Bass JW, Wilson C. Neonatal melioidosis. Am J Dis Child 1971; 122: 446–448.
Ashdown LR. Nosocomial infection due to Pseudomonas pseudomallei: two cases and an epidemiologic study. Rev Infect Dis 1979; 1: 891–894.
Schlech WF III, Turchik JB, Westlake RE Jr, Klein GC, Band JD, Weaver RE. Laboratory-acquired infection with Pseudomonas pseudomallei (melioidosis). N Engl J Med 1981; 305: 1133–1135.
Guard RW, Khafagi FA, Brigden MC, Ashdown LR. Melioidosis in far north Queensland: a clinical and epidemiological review of twenty cases. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1984; 33: 467–473.
Mays EE, Ricketts EA. Melioidosis: recrudescence associated with bronchogenic carcinoma twenty-six years following initial geographic exposure. Chest 1975; 68: 261–263.
Puthucheary SD, Parasakthi N, Lee MK. Septicaemic melioidosis: a review of 50 cases from Malaysia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1992; 86: 683–685.
Rode JW, Webling DD. Melioidosis in the northern territory of Australia. Med JAust 1981; 1: 181–184.
Susaengrat W, Dhiensiri T, Sinavatana P, Sitprija V. Renal failure in melioidosis. Nephron 1987; 46: 167–169.
Tanphaichitra D. Tropical disease in the immuno-compromised host: melioidosis and pythiosis. Rev Infect Dis 1989; 2: S1629–1643.
Leelarasamee A, Bovornkitti S. Melioidosis: review and update. Rev Infect Dis 1989; 11: 413–425.
Boonma P, Sithikaesorn J, Bhuripanyo K, Patjanasoontorn B, Sookpranee M. Discriminant analysis among septicemic melioidosis and other bacterial septicemia. J Med Assoc Thai 1988; 73: 543–547.
Everett ED, Nelson RA. Pulmonary melioidosis: observations in thirty-nine cases. Am Rev Respir Dis 1975; 112: 331–340.
Yap EH, Chan YC, Ti TY, Thong TW, Tan AL, Yeo M, Ho LC, Singh M. Serodiagnosis of melioidosis in Singapore by the indirect hemagglutination test. Singapore Med J 1991; 32: 211–213.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pui, M.H., Tan, A.P.A. Musculoskeletal melioidosis: clinical and imaging features. Skeletal Radiol. 24, 499–503 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00202145
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00202145