Summary
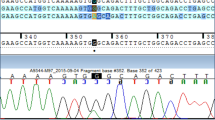
The steroid 21-hydroxylase enzyme (P450c21) is a member of the cytochrome P450 gene superfamily and is essential in the synthesis of cortisol and aldosterone. Defects in the P450c21B gene cause congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH), a common genetic disorder leading to virilization of newborn females. To avoid the standard cloning of mutant P450c21 genes from genomic libraries, we amplified the full-length genomic P450c21 genes by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The amplification was followed by cloning and sequencing of a defective P450c21B gene. The strategy described here is generally applicable, thus making a simple characterization of the complete P450c21B gene possible. The method was tested in one patient suffering from the simple virilizing form of CAH. The sequence of three independent clones originating from the defective P450c21B showed that Ile at position 172 in exon 4 was substituted by Asn. The identical mutation also has been found in other patients with CAH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amor M, Parker KL, Globerman H, New MI, White PC (1988) Mutation in the CYP21B gene (Ile-172 → Asn) causes steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:1600–1604
Carroll MC, Campbell RD, Porter RR (1985) Mapping of steroid 21-hydroxylase genes adjacent to complement component C4 genes in HLA, the major histocompatibility complex in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:521–525
Chiou SH, Hu MC, Chung B (1990) A missense mutation at Ile 172 → Asn or Arg 356 → Trp causes steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Biol Chem 265:3549–3552
Collier S, Sinnott PJ, Dyer PA, Price DA, Harris R, Strachan T (1989) Pulsed field gel electrophoresis identifies a high degree of variability in the number of tandem 21-hydroxylase and complement C4 gene repeats in 21-hydroxylase deficiency haplotypes. EMBO J 8:1393–1402
Donohoue PA, Dop C van, McLean RH, White PC, Jospe N, Migeon CJ (1986) Gene conversion in salt-losing congenital adrenal hyperplasia with absence of complement C4B protein. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 62:995–1002
Dunham I, Sargent CA, Dawkins RL, Campbell RD (1989) Direct observation of the gene organization of the complement C4 and steroid 21-hydroxylase loci by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. J Exp Med 169:1803–1816
Ennis PD, Zemmour J, Salter RD, Parham P (1990) Rapid doing of HLA-A. B cDNA by using the polymerase chain reaction: Frequency and nature of errors produced in amplification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:2833–2837
Globerman H, Amor M, Parker KL, New MI, Withe PC (1988) Non-sense mutation causing steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Invest 82:139–144
Harada F, Kimura A, Iwanaga T, Shimozawa Y, Yata J, Sasazuki T (1987) Gene conversion-like events cause steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:8091–8094
Higashi Y, Yoshioka H, Yamane M, Gotoh O, Fujii-Kuriyama Y (1986) Complete nucleotide sequence of two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes tandemly arranged in human chromosome: a pseudogene and a genuine gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:2841–2845
Higashi Y, Tanae A, Inoue H, Fujii-Kuriyama Y (1988a) Evidence for frequent gene conversion in the steroid 21-hydroxylase P450(C21) gene: implications for steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Am J Hum Genet 42:17–25
Higashi Y, Tanae A, Inoue H, Hiromasa T, Fujii-Kuriyama Y (1988b) Aberrant splicing and missense mutations cause steroid 21-hydroxylase (P450(c21)) deficiency in humans: possible gene conversion products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:7486–7490
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Miller WL, Morel Y (1989) The molecular genetics of steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Annu Rev Genet 23:371–391
Morel Y, Andre J, Uring-Lambert B, Hauptmann G, Betuel H, Tossi M, Forest MG, David M, Bertrand J, Miller WL (1989) Rearrangements and point mutations of P450c21 genes are distinguished by five restriction endonuclease haplotypes identified by a new probing strategy in 57 families with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Invest 83:527–536
Nebert DW, Adesnik M, Coon MJ, Estabrook RW, Gonzalez FJ, Guengerich FP, Gunsalus IC, Johnson EF, Kemper B, Levin W, Phillips IR, Sato R, Waterman MR (1987) The P450 gene superfamily: recommended nomenclature. DNA 6:1–11
Owerbach D, Crawford YM, Draznin MB (1990) Direct analysis of CYP21B genes in 21-hydroxylase deficiency using polymerase chain reaction amplification. Mol Endocrinol 4:125–131
Partanen J, Kere J, Wessberg S, Koskimies S (1989a) Determination of deletion sizes in the MHC-linked complement C4 and steroid 21-hydroxylase genes by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Genomics 5:345–349
Partanen J, Koskimies S, Sipilä I, Lipsanen V (1989b) Major-histocompatibility-complex gene markers and restriction-fragment analysis of steroid 21-hydroxylase (CYP21) and complement C4 genes in classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia patients in a single population. Am J Hum Genet 44:660–670
Rodrigues NR, Dunham I, Yu CY, Carroll MC, Porter RR, Campbell RD (1987) Molecular characterization of the HLAlinked steroid 21-hydroxylase B gene from an individual with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. EMBO J 6:1653–1661
Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S, Scharf SJ, Higuchi R, Horn GT, Mullis KB, Erlich HA (1988) Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239:487–491
Sinnott P, Collier S, Costigan C, Dyer PA, Harris R, Strachan T (1990) Genesis by meiotic cross over of a de novo deletion that contributes to steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:2107–2111
Speiser PW, New MI, White PC (1988) Molecular genetic analysis of non-classical steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency associated with HLA-B14, DR1. N Engl J Med 319:19–23
Tindall KR, Kunkel TA (1988) Fidelity of DNA synthesis by the Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase. Biochemistry 27:6008–6013
White PC (1987) Genetics of steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Recent Prog Horm Res 43:305–336
White PC, New MI, Dupont B (1984) HLA-linked congenital adrenal hyperplasia results from a defective gene encoding a cytochrome P450 specific for steroid 21-hydroxylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:7505–7509
White PC, Grossberger D, Onufer BJ, Chaplin DD, New MI, Dupont B, Strominger JL (1985) Two genes encoding steroid 21-hydroxylase are located near the genes encoding the fourth component for complement in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:1089–1093
White PC, New MI, Dupont B (1986) Structure of human steroid 21-hydroxylase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:5111–5115
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Partanen, J., Campbell, R.D. Substitution of Ile-172 to Asn in the steroid 21-hydroxylase B (P450c21B) gene in a Finnish patient with the simple virilizing form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Hum Genet 87, 716–720 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201731
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201731