Abstract
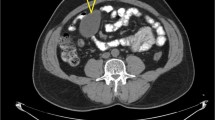
A large esophageal mucocele causing chest pain developed in a 26-year-old woman who had undergone esophageal bypass surgery and gastric interposition because of involvement by scleroderma. Computed tomographic (CT) scans showed the mucocele as an elongated mediastinal mass which spontaneously reduced in size during conservative management. The clinical and radiological features of this unusual postsurgical complication are herein reviewed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kamath MV, Ellison RG, Rubin JW, Moore HV, Pai GP. Esophageal mucocele: a complication of blind loop esophagus. Ann Thorac Surg 1987;43:263–269
Deaton WR, Bradshaw HH. The fate of an isolated segment of the esophagus. J Thorac Surg 1952;23:570–574
Glickstein MF, Gefter WB, Low D, Stephenson LW. Esophageal mucocele after surgical isolation of the esophagus. AJR 1987;149:729–730
Olsen CO, Hopkins RA, Postlethwait RW. Management of an infected mucocele occurring in a bypassed excluded esophageal segment. Ann Thorac Surg 1985;40:73–75
Mannell A, Epstein B. Exclusion of the esophagus: is this a dangerous manoeuvere? Br J Surg 1984;71:442–445
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Gelderen, W.F.C. Mucocele of the surgically isolated esophagus. Abdom Imaging 18, 13–14 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201692
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201692