Abstract
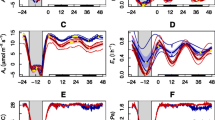
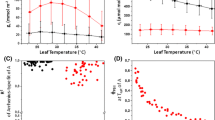
The role of the epidermis in the generation of the endogenous circadian rhythm of CO2 exchange in leaves of Bryophyllum fedtschenkoi has been examined. At 25° C the rhythm of CO2 output exhibited by whole leaves kept in continuous darkness and an initially CO2-free air stream also occurs in isolated pieces of mesophyll. The sensitivity to light of the rhythms in whole leaves and in isolated mesophyll appears to be identical. At 15° C, however, no rhythm is observed in isolated mesophyll tissue, despite there being a conspicuous rhythm in intact leaves. The rhythm of net CO2 assimilation in whole leaves kept in continuous light and a stream of normal air at either 25° C or at 15° C is abolished by removal of the epidermis, although at 15° C and under the higher of the two light levels used, there is an indication that rhythmicity may begin to reappear after the third day of the experiment. Thus, only under certain environmental conditions is the rhythm of CO2 exchange in Bryophyllum leaves independent of the epidermis. The results indicate that the rhythm of carbon dioxide fixation in continuous darkness and CO2-free air is generated primarily in the mesophyll cells, whereas the rhythm in continuous light and normal air is generated in the stomatal guard cells or in an interaction of these cells with the mesophyll cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PEPCase:
-
phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
References
Anderson, C.M., Wilkins, M.B. (1989a) Control of the circadian rhythm of carbon dioxide assimilation in Bryophyllum leaves by exposure to darkness and high carbon dioxide concentrations. Planta 177, 401–408
Anderson, C.M., Wilkins, M.B. (1989b) Period and phase control by temperature in the circadian rhythm of carbon dioxide fixation in illuminated leaves of Bryophyllum fedtschenkoi. Planta 177, 456–469
Anderson, C.M., Wilkins, M.B. (1989c) Phase resetting of the circadian rhythm of carbon dioxide assimilation in Bryophyllum leaves in relation to their malate content following brief exposure to high and low temperatures, darkness and 5% carbon dioxide. Planta 180, 61–73
Bennet-Clark, T.A. (1933) The rôle of organic acids in plant metabolism. New Phytol. 32, 128–161
Bollig, I.G., Wilkins, M.B. (1979) Inhibition of the circadian rhythm of CO2 metabolism in Bryophyllum leaves by cycloheximide and darkness. Planta 145, 105–112
Buchanan-Bollig, I. (1984) Circadian rhythms in Kalanchoë: effects of irradiance and temperature on gas exchange and carbon metabolism. Planta 160, 264–271
Buchanan-Bollig, I.G., Smith, J.A.C. (1984) Circadian rhythms in Crassulacean acid metabolism: phase relationships between gas exchange, leaf water relations and malate metabolism in Kalanchoë daigremontiana. Planta 161, 314–319
Buser-Suter, C., Wiemken, A., Matile, P. (1982) A malic acid permease in isolated vacuoles of a Crassulacean Acid Metabolism plant. Plant Physiol. 69, 456–459
Carter, P.J., Nimmo, H.G., Fewson, C.A., Wilkins, M.B. (1990) Bryophyllum fedtschenkoi protein phosphatase type 2A can dephosphorylate phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. FEBS Lett. 263, 233–236
Carter, P.J., Nimmo, H.G., Fewson, C.A., Wilkins, M.B. (1991) Circadian rhythms in the activity of a plant protein kinase. EMBO J. 10, 2063–2068
Friemert, V., Heininger, D., Kluge, M., Ziegler, H. (1988) Temperature effects on malic-acid efflux from the vacuoles and on the carboxylation pathways in Crassulacean-acid-metabolism plants. Planta 174, 453–461
Gorton, H.L., Williams, W.E., Binns, M.E., Gemell, C.N., Leheny, E.G., Shepherd, A.C. (1989) Circadian stomatal rhythms in epidermal peels from Vicia faba. Plant Physiol. 90, 1329–1334
Harris, P.J.C., Wilkins, M.B. (1976) Light induced changes in the period of the circadian rhythm of carbon dioxide output in Bryophyllum leaves. Planta 129, 253–258
Harris, P.J.C., Wilkins, M.B. (1978a) Evidence of phytochrome involvement in the entrainment of the circadian rhythm of CO2 metabolism in Bryophyllum. Planta 138, 271–278
Harris, P.J.C., Wilkins, M.B. (1978b) The circadian rhythm in Bryophyllum leaves: phase control by radiant energy. Planta 143, 323–328
Jones, R., Wilkins, M.B., Coggins, J.R., Fewson, C.A., Malcolm, A.D.B. (1978) Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from a crassulacean acid metabolism plant Bryophyllum fedtschenkoi. Purification and molecular properties. Biochem. J. 175, 391–406
Kluge, M. (1969) Veränderliche Markierungsmuster bei 14CO2-Fütterung von Bryophyllum tubiflorum zu verschiedenen Zeit-punkten der Hell/Dunkelperiode. I. Die 14CO2-Fixierung unter Belichtung. Planta 88, 113–129
Kottmeier, C.H., Schnabl, H. (1986) The Km-value of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase as an indicator of the swelling state of guard cell protoplasts. Plant Sci. 43, 213–217
Lüttge, U., Ball, E. (1978) Free-running oscillations of transpiration and CO2 exchange in CAM plants without a concomitant rhythm of malate levels. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 90, 69–77
Mansfield, T.A., Hetherington, A.M., Atkinson, C.J. (1990) Some current aspects of stomatal physiology. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol, 41, 55–75
Mayer, W., Moser, I., Bunning, E. (1973) Die Epidermis als Ort der Lichtperception für circadiane Laubblattbewegungen und photoperiodische Induktion. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 70, 66–73
Nimmo, G.A., Nimmo, H.G., Hamilton, I.D., Fewson, C.A., Wilkins M.B., (1986) Purification of the phosphorylated night form and the dephosphorylated day form of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from Bryophyllum fedtschenkoi. Biochem. J. 239, 213–220
Nimmo, G.A., Wilkins, M.B., Fewson, C.A., Nimmo, H.G. (1987) Persistent circadian rhythms in the phosphorylation state of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in Bryophyllum fedtschenkoi leaves and its sensitivity to inhibition by malate. Planta 170, 408–415
Nuernbergk, E.L. (1955a) Über den zeitlichen Verlauf der Photosynthese bei Gewächshaus pflanzen. Gartenbauwissen-schaft 19, 391–398
Nuernbergk, E.L. (1955b) Zur Technik der vergleichenden Messung der Photosynthese mittels des URAS und ihre Anwendung auf die Untersuchung periodischer Photosynthese-Kurven. Garten-bauwissenschaft 20, 58–91
Nuernbergk, E.L. (1961) Endogener Rhythmus und CO2-Stoff-wechsel bei Pflanzen mit diurnalem Säurerhythmus. Planta 56, 28–70
Ritz, D., Kluge, M. (1987) Circadian rhythmicity of CAM in continuous light: coincidences between gas exchange parameters, 14CO2 fixation patterns and PEP-carboxylase properties. J. Plant. Physiol. 131, 285–296
Ritz, D., Kluge, M., Veith, H.J. (1987) Effect of temperature and CO2 concentration on malate accumulation during CAM: evidence by 13C-mass-spectrometry. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 25, 391–399
Warren, D.M., Wilkins, M.B. (1961) An endogenous rhythm in the rate of dark fixation of carbon dioxide in leaves of Bryophyllum fedtschenkoi. Nature 191, 686–688
Wilkins, M.B. (1959) An endogenous rhythm in the rate of carbon dioxide output of Bryophyllum I. Some preliminary experiments. J. Exp. Bot. 10, 377–390
Wilkins, M.B. (1960) An endogenous rhythm in the rate of carbon dioxide output of Bryophyllum II. The effects of light and darkness on the phase and period of the rhythm. J. Exp. Bot. 11, 269–288
Wilkins, M.B. (1962) An endogenous rhythm in the rate of carbon dioxide output of Bryophyllum III. The effects of temperature on the phase and period of the rhythm. Proc. R. Soc. London 156, 220–241
Wilkins, M.B. (1973) An endogenous rhythm in the rate of carbon dioxide output of Bryophyllum IV. Action spectrum for the induction of phase shifts by visible radiation. J. Exp. Bot. 24, 488–496
Wilkins, M.B. (1983) The circadian rhythm of carbon dioxide metabolism in Bryophyllum: the mechanism of phase shift induction by thermal stimuli. Planta 157, 471–480
Wilkins, M.B. (1984) A rapid circadian rhythm of carbon dioxide metabolism in Bryophyllum fedtschenkoi. Planta 161, 381–384
Wilkins, M.B. (1989) On the mechanism of phase control by light in the rhythm of carbon dioxide output in leaves of Bryophyllum fedtschenkoi. J. Exp. Bot. 40, 1315–1321
Wilkins, M.B., Holowinsky, A. (1965) The occurrence of a circadian rhythm in a plant tissue culture. Plant Physiol. 40, 907–909
Willmer, C.M., Pallas, J.E., Black, C.C. (1973) Carbon dioxide metabolism in leaf epidermal tissue. Plant Physiol. 52, 448–452
Willmer, C.M. (1983) Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity and stomatal operation. Physiol. Vég. 21, 943–953
Willmer, C.M., Petropoulou, Y., Manetas, Y. (1990) No light activation and high malate sensitivity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in guard cell protoplasts of Cammelina communis L. J. Exp. Bot. 41, 1103–1107
Wolf, J. (1938) träge zur Kenntnis des Säurestoffwechsels sukkulenter Crassulaceen. III. Stoffliche Zusammenhänge zwischen gärfähigen Kohlenhydraten und organischen Säuren. Planta 28, 60–86
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilkins, M.B. The role of the epidermis in the generation of the circadian rhythm of carbon dioxide fixation in leaves of Bryophyllum fedtschenkoi . Planta 185, 425–431 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201067
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201067