Abstract
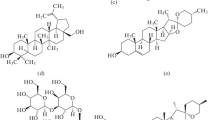
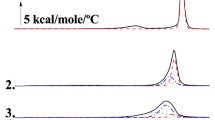
Two triterpenoids, iripallidal and iriflorental, known irone precursors, were shown to be solubilized by phosphatidylcholine (PC). Elution of liposomes (containing PC + iridals) on a Sephadex column showed that iridals and PC were always associated in the same fractions with comparable PC/iridal molecular ratios. Moreover, the physical parameters of dimyristoyl-PC membranes, measured by electron spin resonance were specifically modified by the presence of cycloiridals, indicating that they are integrated within liposomal membranes. These effects on fluidity and phase-transition patterns were compared with those of cholesterol. The secondary plant products, iridals, seem to have a structural role within cells comparable to that of sterols. Possible ecophysiological implications of iridals are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CNO:
-
25-doxyl, 27-nor-cholesterol
- DMPC:
-
dimyristoylphatidylcholine
- ESR:
-
electron spin resonance
- MLV:
-
multi-lamellar vesicle(s)
- PC:
-
phosphatidylcholine
References
Abe F, Chem RF, Yamauchi T (1991) Iridals from Belamcanda chinensis and Iris japonica. Phytochemistry 30: 3379–3382
Ames BN, Dubin DT (1960) The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem 235: 769–755
Berliner LJ, ed (1976) Spin labeling. Theory and applications. Academic Press, New York London
Bonfils JP, Sauvaire Y, Baissac Y, Marner FJ (1994) Iridal levels in Iris rhizomes: effects of wounding and dehydration. Phytochemistry 37: 701–705
Bonfils JP, Bonfils C, Larroque C, Surjus A, Gleize D, Sauvaire Y (1995a) Lipid composition of microsomes of Iris germanica rhizomes. Phytochemistry 38: 585–587
Bonfils JP, Bonfils C, Larroque C, Baccou JC, Sauvaire Y (1955b) 16-hydroxylation of iridal (triterpenoid from Iris species) mediated by cytochrome P450. Nat Prod Lett 6: 15–22
Cooke DT, Ros R, Burden RS, James CS (1993) A comparison of the influence of sterols on the specific activity of the H+-ATPases in isolated plasma membrane vesicles from oat, rye and rice. Physiol Plant 88: 397–402
Grunwald C (1974) Sterol molecular modifications influencing membrane permeability. Plant Physiol 54: 624–628
Hunter MIS, Hetherington AM, Crawford R (1983) Lipid peroxidation a factor in anoxia intolerance in Iris species. Phytochemistry 22: 1145–1147
Jaenicke L, Marner FJ (1986) The irones and their precursors. Prog Chem Org Nat Prod 50: 1–25
Jaenicke L, Marner FJ (1990) The irones and their origin. Pure Appl Chem 62: 1365–1368
Krick W, Marner FJ, Jaenicke L (1983) Isolation and structure determination of the precursors of α and γ irone and homologous compounds from I. pallida and I. florentina. Z Naturforsch 38c: 179–184
Marner FJ, Longerich I (1992) Isolation and structure determination of new iridals from Iris sibirica and Iris versicolor. Liebigs Ann Chem 269–272
Marner FJ, Krick W, Gellrich B, Jaenicke L, Winter W (1982) Irigermanal and iridogermanal. Two new triterpenoids from rhizomes of Iris germanica L. J Org Chem 47: 2531–2538
Marner FJ, Littek A, Arold R, Seferiadis K, Jaenicke L (1990) Isolation and structure determination of new spiro-bicyclic triterpenoids from Iris pseudacorus. Liebigs Ann Chem 563–567
Maurin L, Morin P, Bienvenue A (1987) A new paramagnetic analogue of cholesterol as a tool for studying molecular interactions of genuine cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta 900: 239–248
Maurin L, Bancel F, Morin P, Bienvenue A (1988) Interactions between a paramagnetic analogue of cholesterol and filipin. Biochim Biophys Acta 939: 102–110
Rohmer M, Bisseret P, Sutter B (1991) The hopanoids, bacterial triterpenoids, and the biosynthesis of isoprenic units in prokaryotes. In: Jucker E (ed) Progress in drug research. Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, Boston, Berlin, pp 271–285
Schroeder F, Barenholz Y, Gratton E, Thompson TE (1987) A fluorescence study of dehydroergosterol in phosphatidylcholine bilayer vesicles. Biochemistry 26: 2441–2448
Yeagle PL (1985) Cholesterol and cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 822: 267–287
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonfils, JP., Sauvaire, Y. & Maurin, L. Evidence of cycloiridals as membrane constituents: effects on fluidity patterns compared to those of cholesterol. Planta 200, 353–357 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00200303
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00200303