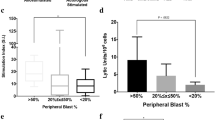
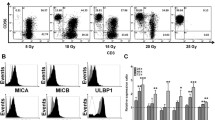
Summary
Peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) from chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients in remission were stimulated in vitro, in a 3-cell assay with autologous leukemic cells or autologous bone marrow (BM) cells alone, or each in combination with allogeneic PBL. The responder cells were used as effectors in a 4-h 51Cr release cytotoxicity assay using autologous targets such as leukemic cells, BM cells, phytohemagglutinin-induced lymphoblasts, and allogeneic K562 (erythroblastoid leukemic cell line) target cells. Sensitization of lymphocytes from CML patients with either autologous leukemic cells or BM cells generated cytotoxic cells (CTCs) capable of killing both the targets. These results suggested that in CML, the PBL may have been sensitized to myeloid maturation-related antigens in vivo, which, on secondary stimulation in vitro, may result in differentiation of CTCs cytotoxic to immature myeloid cells, either from autologous leukemic cells or autologous BM. The inability of PBL from patients with oral cancers to lyse autologous BM cells upon in vitro stimulation, supported this possibility. Clonogenic assays conducted to assess the colony forming potential of BM cells which had interacted with CTCs indicated that there was about 37% reduction in committed granulocyte stem cell colony formation without an appreciable change in committed granulocyte/monocyte stem cell units and clusters. Therefore, since the BM toxicity of the CTCs is not very high, these cells may have a potential clinical use in CML.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagby GC, Lawrence HJ, Neerhout RC (1983) T lymphocyte — mediated granulopoietic failure. N Engl J Med 309:1073
Balsari A, Fossatti G, Taramelli D, Tona G, Delia D, Giardini R, Parmiani G (1985) Allostimulation of patient lymphocytes generates both T and NK-like cells cytotoxic for autologous melanoma. Br J Cancer 52:73
Burgess AW, Wilson EC, Metcalf D (1977) Stimulation by human placental conditioned medium of haemopoietic colony forming human marrow cells. Blood 49:573
Dabholkar M, Advani S, Tatake R, Gangal S (1986) Natural and antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity in chronic myeloid leukemia patients in remission. Leuk Res 10:203
Damle NK, Khare AG, Advani SH, Gangal SG (1979) Leukemia associated in vitro cell mediated immunity in chronic myeloid leukemia patients in remission. Ind J Exp Biol 17:1376
DeVries J, Spitz H (1984) Cloned human cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) lines reactive with autologous melanoma cells. J Immunol 132:510
Grimm EA, Mazumdar A, Zhang HZ, Rosenberg SA (1982) Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. Lysis of natural killer-resistant fresh solid tumor cells by IL-2-activated autologous human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med 155:1823
Herin M, Lemoine C, Weynants P, Vessiere F, VanPel A, Knuth A, Devos R, Boon T (1987) Production of stable cytolytic T cell clones directed against autologous human melanoma. Int J Cancer 39:390
Herrman F, Schmidt RE, Ritz J, Griffin JD (1987) In vitro regulation of human hematopoiesis by natural killer cells: Analysis at a clonal level. Blood 69:246
Ichino Y, Ishikawa T (1984) Generation of human cytotoxic T lymphocytes against fresh autologous and allogeneic solid tumors by mixed lymphocyte tumor cell culture with T cell growth factors. Gann 75:436
Khare AG, Advani SH, Gangal SG (1981) In vitro generation of lymphocytoxicity to autochthonous leukemic cells in chronic myeloid leukemia. Br J Cancer 43:13
Kimura H, Yamaguchi Y, Fujisawa T (1984) Cytotoxicity of autologous and allogeneic lymphocytes against cultured human lung cancer cells: Optimal conditions for the production of cytotoxic lymphocytes. Gann 75:1006
Lee SK, Oliver RT (1978) Autologous leukemia specific T cell-mediated lymphocytotoxicity in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia. J Exp Med 147:912
Mazumdar A, Grimm EA, Rosenberg SA (1983) Characterization of the lysis of fresh solid tumor by autologous lymphocytes activated in vitro with phytohemagglutinin. J Immunol 130:958
Rao SGA, Nadkarni KS, Joshi KS, Kothari VC, Advani SH (1984) Normal responsiveness of granulocyte macrophage committed stem cells from patients with chronic myeloid leukemia to proliferation inhibition by prostaglandin E1. Ind J Exp Biol 22:340
Sondel PM, O'brien C, Porter L, Schlossman SF, Chess L (1976) Cell mediated destruction of human leukemic cells by MHC identical lymphocytes: Requirement for a proliferative trigger in vitro. J Immunol 117:2197
Vanky F, Stjernsward J (1979) In: Herberman RB, McIntire KR (eds) Immunodiagnosis of cancer, part II. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, p 998
Vanky F, Vose BM, Fopp M, Klein E (1979) Human tumor lymphocyte interaction in vitro. IV. Specificity of primary and secondary autologous lymphocyte mediated cytotoxicity. J Natl Cancer Inst 62:1407
Vanky F, Argov S, Klein E (1981) Tumor biopsy cells participating in systems in which cytotoxicity of lymphocytes is generated. Autologous and allogeneic studies. Int J Cancer 27:273
Vose BM (1980) Specific T cell mediated killing of autologous lung tumor cells. Cell Immunol 55:12
Vose BM, Bonnard GD (1982) Specific cytotoxicity against autologous tumor and proliferative response of human lymphocytes grown in interleukin-2. Int J Cancer 29:33
Vose BM, Bonnard GD (1982) Human tumor antigens defined by cytotoxicity and proliferative responses of cultured lymphoid cells. Nature 296:359
Vose BM, Vanky F, Klein E (1977) Lymphocyte cytotoxicity against autologous tumor biopsy cells in humans. Int J Cancer 20:512
Zarling JM, Bach FH (1978) Sensitization of lymphocytes against pooled allogeneic cells. I. Generation of cytotoxicity against autologous human lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Exp Med 147:1334
Zarling JM, Bach FH (1979) Continuous culture of T cells cytotoxic for autologous human leukemia cells. Nature 280:685
Zarling JM, Raich PC, McKeough M, Bach FH (1976) Generation of cytotoxic lymphocytes in vitro against autologous human leukemia cells. Nature 262:691
Zarling JM, Robins HI, Raich PC, Bach FH, Bach ML (1978) Generation of cytotoxic lymphocytes to autologous human leukemia cells by sensitization of pooled allogeneic normal cells. Nature 274:269
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Somasundaram, R., Rao, S.G.A., Advani, S.H. et al. In vitro generation of effector cells cytotoxic to autologous targets from chronic myeloid leukemia patients in remission. Cancer Immunol Immunother 27, 177–182 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00200024
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00200024