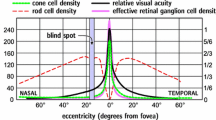
Abstract
The purpose of this paper is to outline a more general approach to visual acuity experiments than the classical methods borrowed from the optical sciences. A theory based on integral operators with symmetric kernels replaces the standard use of filters constructed from windowed sines and cosines. This more general approach allows greater latitude in the range of phenomena to be modelled. It also permits all the standard techniques used in Fourier expansion of a stimulus and response to be generalized to a space-variant system such as the human visual field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelson EH, Bergen JR (1991) The plenoptic function and the elements of early vision. In: Landy MS, Movshon JA (eds) Computational models of visual processing. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Cornsweet TN (1970) Visual perception. Academic, New York
Crameŕ H (1946) Mathematical methods of statistics. Princeton University Press, Princeton
De Valois RR, De Valois KK (1988) Spatial vision. Oxford University Press, New York
Dainty JC, Shaw R (1974) Image science. Academic, New York
Graham NVS (1989) Visual pattern analyzers. Oxford University Press, New York
Gonzalez RC, Wintz P (1987) Digital image processing. Addison-Wesley, New York
Koenderink JJ (1990) Solid shape. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Marr D (1982) Vision. Freedman, San Francisco
Mercer T (1909) Functions of positive and negative type and their connection with the theory of integral equations. Trans Lond Phil Soc (A) 209:415–446
Stewart AL, Pinkham RS (1991) A space-variant differential operator for visual sensitivity. Biol Cybern 64:373–379
Swanson WH, Wilson HR, Giese SC (1984) Contrast matching data predicted from contrast increment thresholds. Vision Res 24:63–75
Tricomi FG (1985) Integral equations. Dover, New York
Watt RJ (1988) Visual processing: computational psychophysical and cognitive research. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale
Watt RJ (1991) Understanding vision. Academic, New York
Young RA (1987) The Gaussian derivative model for spatial vision. I. Retinal mechanisms. Spatial Vision 2:273–293
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stewart, A.L., Pinkham, R.S. Space-variant models of visual acuity using self-adjoint integral operators. Biol. Cybern. 71, 161–167 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00197319
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00197319