Abstract
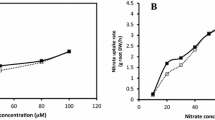
The effect of NH +4 on the regulation of NO −3 and NO −2 transport systems in roots of intact barley (Hordeum vulgareL.) seedlings grown in NO −3 or NO −2 was studied. Ammonium partially inhibited “induction” of both transport systems. The inhibition was less severe in NO −2 -fed than in NO −3 -fed seedlings, presumably due to lower uptake of NH +4 in the presence of NO −2 . In seedlings pretreated with NH +4 subsequent “induction” was inhibited only when NH +4 was also present during “induction”, even though pretreated roots accumulated high levels of NH +4 . This indicates that inhibition may be regulated by NH +4 concentration in the cytoplasm rather than its total accumulation in roots. L-Methionine sulfoximine did not relieve the inhibition by NH +4 , suggesting that inhibition is caused by NH +4 itself rather than by its assimilation product(s). Ammonium inhibited subsequent expression of NO −3 transport activity similarly in roots grown in 0.1, 1.0, or 10 mM NO −3 for 24 h (steady-state phase) or 4 d (decline phase), indicating that it has a direct, rather than general feedback effect. “Induction” of the NO −3 transport system was about twice as sensitive to NH +4 as compared to the NO −2 transport system. This may relate to higher turnover rates of membraneassociated NO −3 -transport proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Mes:
-
2(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid
- MSO:
-
L-methionine sulfoximine
References
Aslam M, Huffaker RC, Rains DW, Rao KP (1979) Influence of light and carbon dioxide concentration on nitrate assimilation by intact barley seedlings. Plant Physiol 63: 1205–1209
Aslam M, Travis RL, Huffaker RC (1992) Comparative kinetics and reciprocal inhibition of nitrate and nitrite uptake in roots of uninduced and induced barley (Hordeum vulgäre L.) seedlings. Plant Physiol 99: 1124–1133
Aslam M, Travis RL, Huffaker RC (1993) Comparative induction of nitrate and nitrite uptake and reduction systems by ambient nitrate and nitrite in intact roots of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) seedlings. Plant Physiol 102: 811–819
Aslam M, Travis RL, Huffaker RC (1994) Stimulation of nitrate and nitrite efflux by ammonium in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) seedlings. Plant Physiol 106: 1293–1301
Bloom AJ, Sukrapanna SS (1990) Effect of exposure to ammonium and transplant shock upon the induction of nitrate absorption. Plant Physiol 94: 85–90
Breteler H, Siegerist M (1984) Effect of ammonium on nitrate utilization by roots of dwarf bean. Plant Physiol 75: 1099–1103
Carlson RM (1978) Automated separation and conductimetric determination of ammonia and dissolved carbon dioxide. Anal Chem 50: 1528–1531
Cresswell RC, Syrett PJ (1982) The uptake of nitrite by the diatom Phaeodactylum: Interactions between NO −2 and NO −3 . J Exp Bot 33: 1111–1121
Goyal SS, Huffaker RC (1986a) A novel approach and a fully automated microcomputer-based system to study kinetics of NO −3 , NO −2 , and NH +4 transport simultaneously by intact wheat seedlings. Plant Cell Environ 9: 209–215
Goyal SS, Huffaker RC (1986b) The uptake of NO −3 , NO +4 , and NH +4 by intact wheat (Triticum aestivum) seedlings. I. Induction and kinetics of transport systems. Plant Physiol 82: 1051–1056
Haba P de la, Agüera E, Maldonado JM (1990) Differential effects of ammonium and tungsten on nitrate and nitrite uptake and reduction by sunflower plants. Plant Sci 70: 21–26
Hendriksen GH, Spanswick RM (1993) Investigation of the apparent induction of nitrate uptake in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) using NO −3 -selective microelectrodes. Plant Physiol 103: 885–892
Jackson WA, Fiesher D, Hageman RH (1973) Nitrate uptake by dark-grown corn seedlings. Some characteristics of apparent induction. Plant Physiol 51: 120–127
King BJ, Siddiqi MY, Ruth TJ, Warner RL, Glass ADM (1993) Feedback regulation of nitrate influx in barley roots by nitrate, nitrite, and ammonium. Plant Physiol 102: 1279–1286
Lainé P, Ourry A, Boucaud J (1995) Shoot control of nitrate uptake rates by roots of Brassica napus L. Effects of localized nitrate supply. Planta 196: 77–83
Lee RB, Drew MC (1989) Rapid, reversible inhibition of nitrate influx in barley by ammonium. J Exp Bot 40: 741–752
MacKown CT, McClure PR (1988) Development of accelerated net nitrate uptake. Effects of nitrate concentration exposure time. Plant Physiol 87: 162–166
MacKown CT, Jackson WA, Volk RJ (1982a) Restricted nitrate influx and reduction in corn seedlings exposed to ammonium. Plant Physiol 69: 353–359
MacKown CT, Volk RJ, Jackson WA (1982b) Nitrate assimilation by decapitated corn root systems: Effects of ammonium during induction. Plant Sci Lett 24: 295–302
Munn DA, Jackson WA (1978) Nitrate and ammonium uptake by rooted cuttings of sweet potato. Agron J 70: 312–316
Pan WL, Jackson WA, Moll RH (1985) Nitrate uptake and partitioning by corn root systems: Differential effects of ammonium among genotypes and stages of root development. Plant Physiol 77: 560–566
Rao KP, Rains DW (1976) Nitrate absorption by barley. 1. Kinetics and energetics. Plant Physiol 57: 55–58
Roberts JKM, Pang MKL (1992) Estimation of ammonium ion distribution between cytoplasm and vacuole using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Plant Physiol 100: 1571–1574
Rufty TW, Jackson WA, Raper CD (1982) Inhibition of nitrate assimilation in roots in the presence of ammonium: The moderating influence of potassium. J Exp Bot 33: 1122–1137
Schrader LE, Domska D, Jung PE, Peterson LA (1972) Uptake and assimilation of ammonium-N and nitrate-N and their influence on the growth of corn (Zea mays L). Argon J 64: 690–695
Smith FW, Thompson JF (1971) Regulation of nitrate reductase in excised barley roots. Plant Physiol 48: 219–223
Thayer JR, Huffaker RC (1980) Determination of nitrate and nitrite by high-pressure liquid chromatography: Comparison with other methods for nitrate determination. Anal Biochem 102: 110–119
Tompkins GA, Jackson WA, Volk RJ (1978) Accelerated nitrate uptake in wheat seedlings: Effects of ammonium and nitrite pretreatments and of 6-methylpurine and puromycine. Physiol Plant 43: 166–171
Ulrich WR (1983) Uptake and reduction of nitrate: Algae and fungi. In: Läuchli A, Bieleski RL (eds) Encyclopedia of plant physiology, NS, vol 15A: Inorganic plant nutrition. Springer, New York, pp 376–397
Ulrich WR (1987) Nitrate and ammonium uptake in green algae and higher plants: mechanism and relationship with nitrate metabolism. In: Ulrich WR, Aparicio PJ, Syrett PJ, Castillo F (eds) Inorganic nitrogen metabolism. Springer, New York, pp 32–38
Wang MY, Siddiqi MY, Ruth TJ, Glass ADM (1993) Ammonium uptake by rice roots. I. Fluxes and subcellular distribution of 13NH +4 . Plant Physiol 103: 1249–1258
Ward MR, Tischner R, Huffaker RC (1988) Inhibition of nitrate transport by anti-nitrate reductase IgG fragments and the idenification of plasma membrane associated nitrate reductase in roots of barley seedlings. Plant Physiol 88: 1141–1145
Warner RL, Huffaker RC (1989) Nitrate transport is independent of NADH and NAD(P)H nitrate reductases in barley seedlings. Plant Physiol 91: 947–953
Warncke DD, Barber SA (1973) Ammonium and nitrate uptake by corn (Zea mays L.) as influenced by nitrogen concentration and NH +4 NOJ ratio. Agron J 65: 950–953
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aslam, M., Travis, R.L., Rains, D.W. et al. Effect of ammonium on the regulation of nitrate and nitrite transport systems in roots of intact barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) seedlings. Planta 200, 58–63 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00196649
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00196649