Abstract
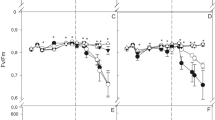
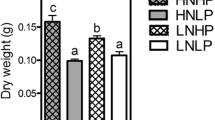
The effects of phosphorus nutrition on various aspects of photosynthetic metabolism have been examined for soybean plants (Glycine max) grown in growth chambers. Orthophosphate was supplied at two levels in 0.5-strength Hoagland's solution. At the end of the 19-d growth period, plants grown at 10 μM KH2PO4 (low-P plants) had undergone a 40% drop in net CO2 exchange (averaged over a 16-h light period), as compared with control plants grown with 200 μM KH2PO4. Low-P resulted in reductions in the initial activities of five, and in the total activities of seven, Calvin-cycle enzymes. Notable exceptions were the initial and total activities of chloroplastic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (EC 3.1.3.11) which were increased by 85 and 53%, respectively, by low-P. Low-P decreased leaf 3-phosphoglycerate (PGA) levels most (by 80%), ribulose-1,5-bis-phosphate (RuBP) less (by 47%) while triose-phosphate (TP) was not significantly changed. The results indicate that photosynthetic CO2-fixation in low-P plants was limited more by RuBP regeneration than by ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (EC 4.1.1.39) activity. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate regeneration in low-P plants did not appear to be limited by ATP and-or NADPH supply because ATP/ADP and NADPH/ NADP+ ratios were increased by 60 and 37%, respectively, by low-P, and because TP/PGA ratios were higher in low-P plants. Low-P may diminish RuBP regeneration, and hence photosynthesis, by reducing Calvin-cycle enzyme activity, in particular, the initial activity of ribulose-5-phosphate kinase (EC 2.7.1.19) (44% reduction), and by enhancing the flux of carbon into starch biosynthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AdN:
-
adenine nucleotides (ATP + ADP + AMP)
- Ci :
-
internal CO2 concentration
- NCE:
-
net carbon exchange rate
- NN:
-
nicotinamide nucleotides (NADPH +NADP+ + NADH + NAD+)
- PFD:
-
photosynthetically active photon flux density
- PGA:
-
3-phosphoglyceric acid
- RuBP:
-
ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate
- RuBPCase:
-
ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase
- TP:
-
triose phosphate
References
Abadia, J., Rao, I.M., Terry, N. (1987) Changes in leaf phosphate status have only small effects on the photochemical apparatus of sugar beet leaves. Plant Sci. 50, 49–55
Bonzon, M., Simon, P., Greppin, H., Wagner, E. (1983) Pyridine nucleotides and redox-charge evolution during the induction of flowering in spinach leaves. Planta 159, 254–260
Brooks, A. (1986) Effects of phosphorus nutrition on ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase activation, photosynthetic quantum yield and amounts of some Calvin-cycle metabolites in spinach leaves. Austr. J. Plant Physiol. 13, 221–237
Brooks, A., Woo, K.C., Wong, S.C. (1988) Effects of phosphorus nurition on the response of photosynthesis to CO2 and O2, activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase and amounts of ribulose bisphosphate and 3-phosphoglycerate in spinach leaves. Photosynth. Res. 15, 133–141
Dietz, K.J., Foyer, C. (1986) The relationship between phosphate status and photosynthesis in leaves. Reversibility of the effects of phosphate deficiency on photosynthesis. Planta 167, 376–381
Flügge, U.I., Freisl, M., Heldt, H.W. (1980) Balance between metabolite accumulation and transport in relation to photosynthesis by isolated spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 65, 574–577
Foyer, C., Spencer, C. (1986) The relationship between phosphate status and photosynthesis in leaves. Effects on intracellular orthophosphate distribution, photosynthesis and assimilate partitioning. Planta 167, 369–375
Fredeen, A.L., Rao, I.M., Terry, N. (1989) Influence of phosphorus nutrition on growth and carbon partitioning in Glycine max. Plant Physiol. 89, 225–230
Furbank, R.T., Foyer, C.H., Walker, D.A. (1987) Regulation of photosynthesis in isolated spinach chloroplasts during orthophosphate limitation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 87, 552–561
Giersch, C., Robinson, S.P. (1987) Regulation of photosynthetic carbon metabolism during phosphate limitation of photosynthesis in isolated spinach chloroplasts. Photosynth. Res. 14, 211–227
Heldt, H.W., Ja Chon, C., Lorimer, G.H. (1978) Phosphate requirement for the light activation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in intact spinach chlorplasts. FEBS Lett. 92, 234–240
Leegood, R.C., Walker, D.A., Foyer, C.H. (1985) Regulation of the Benson-Calvin cycle. In: Photosynthetic mechanisms and the environment, pp. 189–258, Barber, J., Baker, N.R., eds. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Maciejewska, U., Kacperska, A. (1987) Changes in the levels of oxidized and reduced pyridine nucleotides during cold acclimation of winter rape plants. Physiol. Plant. 69, 687–691
Muto, S., Miyachi, S. (1985) Roles of calmodulin dependent and independent NAD kinases in regulation of nicotinamide coenzyme levels of green plant cells. In: Molecular and cellular aspects of calcium in plant development, pp. 107–114, Trewavas, A.J., ed. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Rao, I.M., Terry, N. (1989) Leaf phosphate status, photosynthesis, and carbon partitioning in sugar beet. I. Changes in growth, gas exchange, and calvin cycle enzymes. Plant Physiol. 90, 814–819
Rao, I.M., Arulanatham, A.R., Terry, N. (1989a) Leaf phosphate status, photosynthesis and carbon partitioning in sugar beet. II. Diurnal changes in sugar phosphates, adenylates and nicotinamide nucleotides. Plant Physiol. 90, 820–826
Rao, I.M., Arulanantham, A.R., Terry, N. (1989b) Diurnal changes in adenylates and nicotinamide nucleotides in sugar beet leaves. Photosynth. Res. (in press)
Rao, I.M., Fredeen, A.L., Terry, N. (1990) Leaf phosphate status, photosynthesis and carbon partitioning in sugar beet. III. Diurnal changes in carbon partitioning and carbon export. Plant Physiol. 92, 29–36
Sicher, R.C., Kremer, D.F. (1988) Effects of phosphate deficiency on assimilate partitioning in barley seedlings. Plant Sci. 57, 9–17
Terry, N. (1980) Limiting factors in photosynthesis. I. Use of iron stress to control photochemical capacity in vivo Plant Physiol 65, 114–120
Terry, N., Ulrich, A. (1973) Effects of phosphorus deficiency on the photosynthesis and respiration of leaves of sugar beet. Plant Physiol. 51, 43–47
von Caemmerer, S., Edmondson, D.L. (1986) Relationship between steady-state ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity and some carbon reduction cycle intermediates in Raphanus sativus. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 13, 669–688
Woodrow, I.E., Berry, J.A. (1988) Enzymatic regulation of photosynthetic CO2 fixation in C3 plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 39, 533–594
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We are grateful to Dr. Joe Berry (Carnegie Institution of Washington, Stanford, California, USA) for his advice and helpful comments on the manuscript, Frank Murillo for his invaluable help in the preparation of graphics, and C. Carlson for his excellent technical assistance in gas-exchange measurements.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fredeen, A.L., Raab, T.K., Rao, I.M. et al. Effects of phosphorus nutrition on photosynthesis in Glycine max (L.) Merr.. Planta 181, 399–405 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195894
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195894