Summary
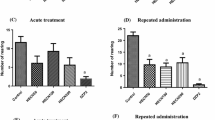
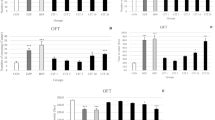
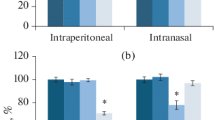
Effects of caerulein, a cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8) receptor agonist, on exploratory activity of mice were investigated. Exploratory and locomotor activity of animals were measured using elevated plus-maze and open field tests. The systemic administration of caerulein at nonsedative doses (100 ng/kg-1 µkg i. p.) resulted in a significant decrease in the exploratory activity of mice. This effect was completely blocked by proglumide, a CCK-8 antagonist (15 mg/kg i. p.), indicating the participation of CCK-8 receptors. Acute treatment with low doses (0.1–0.75 mg/kg i. p.) of diazepam did not attenuate the anxiogenic-like effect of caerulein, but at more high doses of diazepam the coadministration depressed locomotor activity in mice. After subchronic diazepam treatment (2.5 mg/kg once a day, 10 days, i.p.) tolerance was developed toward the sedative effect of diazepam, and 72 h after withdrawal of the drug the animals showed increased anxiety in the plus-maze test. 30 min after the last injection procedure the anxiogenic-like effect of caerulein (500 ng/kg i. p.) on exploration was absent in both diazepam or vehicle groups. However, 72 h after the last pretreatment injection caerulein (500 ng/kg i. p.) reduced significantly the exploratory activity in control group, whereas it was inactive after diazepam withdrawal. The results obtained in this study support the hypothesis that endogenous CCK-8 an CCK-8 receptors are involved in the neurochemistry of anxiety and the anxiolytic action of benzodiazepine tranquillizers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin HA, File SE (1988) Reversal of increased anxiety during benzodiazepine withdrawal: evidence for an anxiogenic endogenous ligand for the benzodiazepine receptor. Brain Res Bull 20: 603–606
Beinfeld MC (1983) Cholecystokinin in the central nervous system: a minireview. Neuropeptides 3: 411–427
Bouthillier A, De Montigny C (1988) Long-term benzodiazepine treatment reduces neuronal responsiveness to cholecystokinin: an electrophysiological study in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 151:135–138
Bradwejn J, De Montigny C (1984) Benzodiazepines antagonize cholecystokinin-induced activation of rat hippocampal neurones. Nature 312:363–364
Bradwejn J, De Montigny C (1985) Effects of PK 8165, a partial benzodiazepine receptor agonist, on cholecystokinin-induced activation of hippocampal pyramidal neurons: a microiontophoretic study in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 112:415–418
Crawley JN, Kiss JZ (1985) Tracing the sensory pathway from the gut to brain regions mediating the actions of cholecystokinin on feeding and exploration. Ann NY Acad Sci 448:586–588
Crawley JN (1988) Neuronal chlolecystokinin. ISI Atlas Pharmacol 2:84–90
Deupree D, Hsiao S (1987) Cholecystokinin octapeptide, proglumide, and conditioned taste avoidance in rats. Physiol Behav 41:125–128
File SE (1986) Aversive and appetitive properties of anxiogenic and anxiolytic agents. Behav Brain Res 21:189–194
File SE, Baldwin HA, Aranko K (1987) Anxiogenic effects in benzodiazepine withdrawal are linked to the development of tolerance. Brain Res Bull 19:607–610
Gentsch C, Lichtsteiner M, Feer H (1988) Competition for sucrosepellets in triads of male Wistar rats: the individuals' performances are differing but stable. Behav Brain Res 27:37–44
Harro J, Põld M, Vasar E, Allikmets L (1989) The role of brain cholecystokinin receptors in generation of anxiety states in mice and rats. In: Sudakov KV (ed) Systems Research in Physiology, vol. 5, Gordon & Breach, London (in press)
Hommer DW, Palkovits M, Crawley JN, Paul SM, Skirboll LR (1985) Cholecystokinin-induced excitation in the substantia nigra: evidence for peripheral and central components. J Neurosci 5:1387–1392
Kosaka T, Kosaka K, Tateishi K, Hamaoka Y, Yanaihara N, Wu J-Y, Hama K (1985) GABAergic neurons containing CCK-8-like and/or VIP-like immunoreactivities in the rat hippocampus and dentate gyrus. J Comp Neurol 239:420–430
Kubota K, Sugaya K, Matsuda I, Matsuoka Y, Itonaga M (1985) Caerulein antagonism by benzodiazepines in the food intake in mice. Jpn J Pharmacol 39:120–122
Kubota K, Sun F-Y, Sugaya K, Sunagane N (1986) Reversal of antinociceptive effect of caerulein by benzodiazepine. J Pharmacobio-Dyn 9:428–431
Lader M, File S (1987) The biological basis of benzodiazepine dependence. Psychol Med 17:539–547
Lister RG (1987) The use of a plus-maze to measure anxiety in the mouse. Psychopharmacology 92:180–185
Morley JE (1987) Behavioral effects of administered cholecystokinin. ISI Atlas Pharmacol 1:49–51
Moroji T, Hagino Y (1987) Bilateral subdiaphragmatic vagotomy does not prevent the behavioral effects of systematically administered ceruletide in mice. Neuropeptide 9:217–224
Pellow S, Chopin P, File SE, Briley M (1985) Validation of open: closed arm entries in an elevated plus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. J Neurosci Meth 14:149–167
Rägo L, Kiivet R-A, Harro J, Põld, M (1988) Behavioral differences in an elevated plus-maze: correlation between anxiety and decreased number of GABA and benzodiazepine receptors in mouse cerebral cortex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337: 675–678
Siegel RA, Düker E-M, Fuchs E, Pahnke U, Wuttke W (1985) Responsiveness of mesolimbic, mesocortical, septal and hippocampal cholecystokinin and substance P neuronal systems to stress, in the male rat. Neurochem Int 6:783–789
Siegel RA, Düker E-M, Pahnke U, Wuttke W (1987) Stress-induced changes in cholecystokinin and substance P concentrations in discrete regions of the rat hypothalamus. Neuroendocrinology 46:75–81
Sugaya K, Matsuda I, Kubota K (1985) Inhibition of hypothermic effect of cholecystokinin by benzodiazepines and a benzodi azepine antagonist, Ro 15–1788 in mice. Jpn J Pharmacol 39:277–280
Yaksh TL, Furui T, Kanawati IS, Go VLW (1987) Release of cholecystokinin from rat cerebral cortex in vivo: role of GABA and glutamate receptor systems. Brain Res 406:207–214
Zetler G (1980) Effects of cholecystokinin-like peptides on rearing activity and hexobarbital-induced sleep. Eur J Pharmacol 66:137–139
Zetler G (1985) Neuropharmacological profile of cholecystokininlike peptides. Ann NY Acad Sci 448:448–469
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to: J. Harro at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harro, J., Põld, M. & Vasar, E. Anxiogenic-like action of caerulein, a CCK-8 receptor agonist, in the mouse: influence of acute and subchronic diazepam treatment. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 341, 62–67 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195059
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195059