Abstract
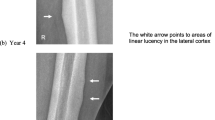
Aluminum-induced bone disease in uremic patients receiving dialysis was first described a little more than 10 years ago. The epidemic form of the disease was seen in centers where there was a high aluminum content in the water dialysate. Although this problem has been corrected, sporadic forms of the disease continue to be noted in dialyzed and nondialyzed patients. Multiple fractures are a radiological feature of aluminum-related bone disease. Fractures of the ribs and hips and vertebral crush fractures are the usual manifestations. We present four patients whose nontraumatic fractures involved large bones, without evidence of multiple fractures. In two of the patients symptoms were vague and subacute; a third patient with a subcapital fracture was ambulatory. Only in one patient (fractured dens) were symptoms acute enough to warrant immediate radiography. One of the patients had no symptoms pertaining to a fracture of C5 with retrolisthesis. Rib fractures are common in this condition but were seen in only one patient, in whom they were detected 8 years previously. Healing was not seen in any of the fractures. In patients receiving dialysis the presence of spontaneous fractures of large bones or cervical vertebrae, which may be clinically silent or vaguely symptomatic, should raise the possibility of aluminum-induced osteomalacia even if these fractures are solitary.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfrey AC (1984) Aluminum intoxication (editorial). N Engl J Med 310:1113
Andreoli SP, Bergstein JM, Sherrard DJ (1984) Aluminum intoxication from aluminum-containing phosphate binders in children with azotemia not undergoing hemodialysis. N Engl J Med 310:1079
Coburn JW, Norris KC, Nebeker HG (1986) Osteomalacia in bone disease arising from aluminum. Semin Nephr 6:68
Garrett P, McWade M, O'Callahan J (1986) Radiological assessment of aluminium related bone disease. Clin Radiol 37:63
Hodsman AB, Sherrard DJ, Wong EGC et al. (1981) Vitamin D resistant osteomalacia in hemodialysis patients lacking secondary hyperparathyroidism. Ann Intern Med 94:629
Kerr DNS, Ward MK, Arze RS, et al. (1986) Aluminum-induced dialysis osteodystrophy: the demise of “Newcastle bone disease”? Kidney Int 29 [Suppl]: S58
Kriegshauser JS, Swee RG, McCarthy JT, Hauser MF (1987) Aluminum toxicity in patients undergoing dialysis: radiographic findings and prediction of biopsy results. Radiology 164:399
Norris KC, Crooks PW, Nebeker HG, et al. (1985) Clinical and laboratory features of aluminum-related bone disease: differences between sporadic and “epidemic” forms of the syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis 6:342
Parkinson IS, Ward MK, Feest TG, Fawcett RWP, Kerr DNS (1979) Fracturing dialysis osteodystrophy and dialysis encephalopathy. An epidemiological survey. Lancet II:406
Phelps KR, Einhorn TA, Vigorita VJ, Lundin AP, Friedman EA (1986) Fracture healing with deferoxamine therapy in a patient with aluminum associated osteomalacia. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs 32:198
Sebes JI, Pinstein ML, Massie JD, et al. (1984) Radiographic manifestation of aluminum induced bone disease. AJR 142:424
Sundaram M (1989) Renal osteodystrophy. Skeletal Radiol 18:415
Ward MK, Feest TG, Ellis HA, et al. (1978) Osteomalacic dialysis osteodystrophy: evidence for a water-borne etiological agent, probably aluminum. Lancet 4:841
Windus DW, Stokes TJ, Julian BA, Fenves AZ (1987) Fatal Rhizopus infections in hemodialysis patients receiving deferoxamine. Ann Intern Med 107:678
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundaram, M., Dessner, D. & Ballal, S. Solitary, spontaneous cervical and large bone fractures in aluminum osteodystrophy. Skeletal Radiol. 20, 91–94 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193817
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193817