Abstract
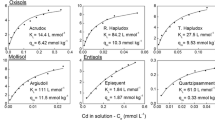
Previously presented evidence of Zn competition for Cd soil sorption sites has been confirmed by detailed studies of two Danish soils. Cadmium distribution between soil and solute decreases for increasing Zn solute concentrations. A Langmuir model accounting for both Cd and Zn sorption onto the same sorption sites was supported by independent experimental data on Cd and Zn distribution. The competition of Zn is governed by the product of the Zn soil sorption stability constant and the actual Zn solute concentration. Cadmium distribution coefficients may be significantly influenced by Zn at Zn solute concentrations above 100 μg Zn dm−3. This may have implications for interpreting Cd plant uptake and leaching.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christensen, T. H.: 1984,Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 21, 105.
Christensen, T. H.: 1985,Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 26, 265.
Christensen, T. H.: 1987,Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 34, 293 (this issue).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christensen, T.H. Cadmium soil sorption at low concentrations: VI. A model for zinc competition. Water Air Soil Pollut 34, 305–314 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193778
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193778