Summary
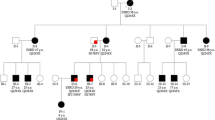
We describe a large three generation family with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (PKD). Ultrasonographic screening of 60 family members revealed 20 individuals, whose age ranged from ten to eighty years, with one or several cysts in only one kidney and 7 individuals with cysts in both kidneys. Transmission of unilateral cysts seems to be autosomal dominant, although there are some generation gaps. Linkage studies with several markers of the PKD1 locus on the short arm of chromosome 16 showed no linkage with the disease. Lod scores for linkage between the disease and the most informative marker 3′HVR were computed using different penetrance models and several hypotheses concerning the clinical status of individuals with unilateral renal cysts. Results varied from Z = 1.31 to Z =-21.47 (θ = 0). Smith's test of heterogeneity gave a conditional probability of non-linkage between 0.9 and 1.0. We conclude that this family presents a form of autosomal dominant PKD with reduced penetrance and no linkage to the PKD1 locus on the short arm of chromosome 16. Other hypotheses, such as the existence of two distinct hereditary diseases in this large family, or neomutation in one branch of the family associated with a high frequency of isolated renal cysts, are also considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman LV (1968) Surgical pathology, 4th edn. Mosby, StLouis, Mo
Bachner L, Albouze G, Ferran C, Vinet MC, Julier C, Grünfeld JP, Kaplan JC (1987) Family studies of adult dominant polycystic kidney diseae (PKD1 locus) using the highly polymorphic probe 3′HVR at HBA locus. Independent locus for the neonatal recessive disease? (abstract). (9th International Workshop on Human Gene Mapping) Cytogenet Cell Genet 46:574
Bachner L, Vinet MC, Albouze G, Julier C, LeMerrer M, Kaplan J, Mathieu M, Piussan C, Grunfeld JP, Kaplan JC (1989a) Linkage analysis in 15 French families with various clinical forms of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) (abstract). (10th International Workshop on Human Gene Mapping) Cytogenet Cell Genet 51:955
Bachner L, Vinet MC, Lacaver, Sraer JD, Chevet D, Julier C, Kaplan JC (1989b) Linkage analysis of a French family with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) non allelic to PKD1 locus (abstract). (10th International Workshop on Human Gene Mapping) Cytogenet Cell Genet 51:955
Bear JC, McManamon P, Morgan J (1984) Age at clinical onset and at ultrasonographic detection of adult polycystic kidney disease: data for genetic counselling. Am J Med Genet 18:45–53
Bear JC, Parfrey PS, Morgan J, Cramer BC, McManamon PJ, Gault MH, Churchill DN, Singh M, Hewitt R, Somlo S, Reeders S (1989) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: ultrasonographic detection and prognosis of PKD1 and PKD2 forms. Am J Hum Genet 45:39
Breuning MN, Saris JJ, Wapenaar MC, DenDunnen JT, Ommen GJP van, Callen DF, Sutherland D, Buys HCM, Pearson PL (1987a) New probes close to the gene for adult polycystic kidney disease (PKD1) on 16p (abstract). (9th International Workshop on Human Gene Mapping) Cytogenet Cell Genet 46:586
Breuning MH, Reeders ST, Brunner H, Ijdo JW, Saris JJ, Verwest A, Ommen GJB van, Pearson PL (1987b) Improved early diagnosis of adult polycystic kidney disease with flanking DNA markers. Lancet II:1359–1361
Breuning MH, et al (1989) Map of 12 polymorphic loci on the short arm of chromosome 16 close to the gene for polycystic kidney disease (PKD1) (abstract). (10th International Workshop on Human Gene Mapping) Cytogenet Cell Genet 51:969
Brissenden JE, Roscoe JM, Silverman M (1989) Linkage heterogeneity in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Am J Hum Genet 45:132
Jarman AP, Higgs DR (1988) A new hypervariable marker for the human α globin gene cluster. Am J Hum Genet 43:249–256
Kimberling WJ, Fain PA, Kenyon JB, Goldgar DBS, Sujansky E, Gabow PA (1988) Linkage heterogeneity of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 319:913–918
Lathrop GM, Lalouel JM (1984) Easy calculations of lod-scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet 29:235–239
Lazarou LP, Davies F, Sarfarazi M, Coles GA, Harper PS (1987) Adult polycystic kidney disease and linked RFLPs at the α-globin locus: a genetic study in the South Wales population. J Med Genet 24:466–473
Milutinovic J, Fialkow PJ, Phillips LA, Agodoa LY, Bryant JI, Denney JD, Rudd TG (1980) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: early diagnosis and data for genetic counselling. Lancet I:1203–1205
Milutinovic J, Fialkow PJ, Agodoa LY, Phillips LA, Rudd TG, Bryant JI (1984) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: sympoms and clinical findings. Q J Med 212:511–522
Morton NE (1956) The detection and estimation of linkage between the genes for elliptocytosis and the Rh blood type. Am J Hum Genet 8:80–96
Nakamura Y, Martin C, Krapcho K, O'Connel P, Leppert M, Lathrop J, Lalouel JM, White R (1988) Isolaltion and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence (pCMM65) on chromosome 16 (D16S84). Nucleic Acids Res 16:3122
Ott J (1985) Analysis of human linkage. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Pieke SA, Kimberling WJ, Kenyon JB, Gabow P (1989) Genetic heterogeneity of polycystic kiney disease: an estimate of the proportion of families unlinked to chromosome 16. Am J Hum Genet 45:58
Porch P, Noes HN, Stapleton FB (1986) Unilateral presentation of adult-type polycystic kidney disease in children. J Urol 135:782–785
Reeders ST, Breuning MH, Davies KE, Nicholls RD, Jarman AP, Higgs DR, Pearson PL, Weatherall DJ (1985) A highly polymorphic DNA marker linked to adult polycystic kidney disease on chromosome 16. Nature 317:542–544
Reeders ST, Breuning MH, Ryynanen MA, Wright AF, Davies KE, King AW, Watson ML, Weatherall DJ (1987) A study of genetic linkage heterogeneity in adult polycystic kidney disease. Hum Genet 76:348–351
Reeders ST, Keith T, Green P, Germinio GG, Barton NJ, Lehmann OJ, Brown VA, Phipps P, Morgan J, Bear JC, Parfrey P (1988) Regional localization of the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease locus. Genomics 3:150–155
Reeders ST, Germino GG, Gillespie GAJ (1989) Mapping the locus of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: diagnostic application. Clin Chem 35:13–16
Romeo G, Costa G, Catizone L, Germino GG, Weatherhall DJ, Devoto M, Roncuzzi L, Zuchelli P, Keith T, Reeders ST (1988) A second genetic locus for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet II:8–11
Ryynanen M, Dolata MM, Lampainen E, Reeders ST (1987) Localisation of a mutation producing autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease without renal failure. J Med Genet 24:462–465
Sedman A, Bell P, Manco-Johnson M, Schrier R, Warady BA, Heard EO, Butler-Simon N, Gabow P (1987) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in childhood: a longitudinal study. Kidney Int 31:1000–1005
Smith CAB (1963) Testing for heterogeneity of recombination fraction values in human genetics. Ann Hum Genet 11:461–468
Strand WR, Rushton HG, Markle BM, Kapur S (1989) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in infants: asymmetric disease mimicking a unilateral renal mass. J Urol 141:1151–1153
Tada S, Yamagishi J, Kobayashi H, Hata Y, Kobari T (1983) The incidence of simple renal cysts by computed tomography. Clin Radiol 34:437–439
Taitz LS, Brown CB, Blank CE, Steiner GM (1987) Screening for polycystic kidney disease: importance of clinical presentation in the newborn. Arch Dis Child 62:45
Vinet MC, Dode C, Pascal O, Monnier N, Rochette J, Bachner L (1989) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and α−4.2 thalassemia in a Caucasian family. Hum Genet 83:55–57
Wolff E, Nakamura Y, O'Connell P, Leppert M, Lathrop GM, Lalouel JM, White R (1988) Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence (pEKMDA2–1) on chromosome 16 (D16S83). Nucleic Acids Res 16:9885
Xiao GH, Grzeschik K-H, Scherer G (1988) Anonymous genomic DNA sequences detecting restriction fragment length polymorphisms on human chromosomes (abstract). (9th International Workshop on Human Gene Mapping) Cytogenet Cell Genet 46:721
Zerres K, Völpel MC, Weiss H (1984) Cystic kidneys: genetics, pathologic anatomy, clinical picture, and prenatal diagnosis. Hum Genet 68:104–135
Zerres K, Albrecht R, Waldherr R (1985) Acquired cystic kidney disease — a possible pitfall in genetic counseling. Hum Genet 71:267–269
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bachner, L., Vinet, M.C., Lacave, R. et al. Linkage study of a large family with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease with reduced expression. Hum Genet 85, 221–227 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193200
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193200