Abstract
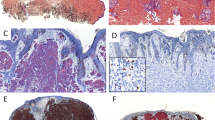
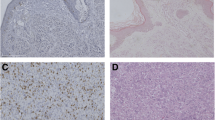
The clinical course of malignant melanomas is frequently unpredictable, although a number of prognostically useful variables can be identified. There is a need for additional markers of prognostic value. In a series of 60 malignant cutaneous melanomas, we analysed the immunohistochemical expression of c-myc proto-oncogene, heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) and HLA-DR molecules in order to investigate their prognostic significance. C-myc, HSP70 and HLA-DR were expressed in 43.3%, 56.6% and 38.3% of all melanoma cases, respectively. Advanced Clark levels (Clark III–V) were significantly associated with c-myc expression rate (P<0.05), HSP70 detection (P<0.01) and HLA-DR positivity (P<0.01). Increased Breslow thickness (>1.5 mm) was related to HLA-DR expression (P<0.05). High mitotic rate was closely associated with c-myc positivity (P<0.05), while HSP70 and HLA-DR expression separately correlated to clinical stage of the disease (P<0.05). The evaluation of these variables may be of immunological and prognostic significance. They were found to be associated with melanocyte subpopulations of the vertical growth phase which are arguably characterized by an increased invasive potential.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albino AP, Shea CR, McNutt NS (1992) Oncogenes in melanomas. J Dermatol 19:83–86
Andersen SN, Rognum TO, Lund E (1993) Strong HLA-DR expression in large bowel carcinomas is associated with good prognosis. Br J Cancer 68(1):80–85
Balaban GB, Herlyn M, Clark WH Jr, Nowell PC (1986) Karyotypic evolution in human malignant melanoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 19:113–122
Banerjee S, Ganapathi R, Ghosh L, Yu CL (1992) Down regulation of ras and myc expression associated with mdr-1 over-expression in adriamycin-resistant tumor cells. Cell Mol Biol 38(6):561–570
Beckmann RP, Lovett M, Welch WJ (1992) Examining the function and regulation of HSP70 in cells subjected to metabolic stress. J Cell Biol 117(6):1137–1150
Blachere NE, Udono H, Janetski S (1993) Heat shock protein vaccines against cancer. J Immunother 14(4):352–356
Brandtzaeg P, Sollid LM (1988) Lymphoepithelial interactions in the mucosal immune system. Gut 29:1116–1130
Breslow A (1970) Thickness, cross-sectional areas and depth of invasion in the prognosis of cutaneous melanoma. Am Surg 172:902–908
Brocker EB, Suter L, Sorg C (1984) HLA-DR antigen expression in primary melanomas of the skin. J Invest Dermatol 82:244–247
Brocker EB, Zwadlo G, Holzmann B, Macher E, Sorg C (1988) Inflammatory cell infiltrates in human melanoma at different stages of tumor progression. J Cancer 41:562–567
Chen L, Linsley PS, Hellstrom KE (1993) Costimulation of T cells for tumor immunity. Immunol Today 14:483–486
Ciocca DR, Clark GM, Tandon AK (1993) Heat shock protein HSP70 in patients with axillary lymph node-negative breast cancer: prognostic implications. J Natl Cancer Inst 85(7):570–574
Clark WH Jr (1967) A classification of malignant melanoma in man correlated with histogenesis and biologic behavior. In: Advances in the biology of the skin, vol VIII. Pergamon Press, New York, pp 621–647
Cooper R, Wanebo H, Hagar W (1985) Regression in thin malignant melanoma. Arch Dermatol 121
De Nagel DC, Pierce SK (1992) A case for chaperones in antigen processing. Immunol Today 13(3):86–89
Elder DE (1984) Prognostic guides to melanomas. In: Mackie RM (ed) Clinics in oncology. WB Saunders, London, pp 457–475
Elder DE, Murphy GF (1991) Melanocytic tumors of the skin. Atlas of tumor pathology, AFIP, Bethesda
Fumagalli S, Doneda L, Nomura N, Larizza L (1993) Expression of the c-ski proto-oncogene in human melanoma cell lines. Melanoma Res 3:23–27
Gioufas AG, Moutsopoulos GM (1991) Stress proteins. In: Gioufas AG, Moutsopoulos GM: Immunology, 1st edn, Athens, pp 141–148
Gordon L, Peacocke M, Gilchrest BA (1992) Induction of c-fos but not c-myc in S-91 cells by melanization signals. J Dermatol Sci 3(1):35–41
Gress TM, Muller-Pillasch F, Weber C (1994) Differential expression of heat shock proteins in pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Res 54(2):547–551
Hilton DA, West KP (1990) An evaluation of the prognostic significance of HLA-DR expression in gastric carcinoma. Cancer 66:1154–1157
Jaattela M (1993) Overexpression of major heat shock protein HSP70 inhibits tumor necrosis factor-induced activation of phospholipase A2. J Immunol 151(8):4286–4294
Jaattela M, Wissing D (1993) Heat shock proteins protect cells from monocyte cytotoxicity: possible mechanism of self protection. J Exp Med 177(1):231–236
Kang SM, Beverly B, Tran SC, Brorson K, Schwartz RH, Lenard M (1992) Transactivation by AP-1 is a molecular target of T cell clonal anergy. Science 257:1134–1138
Male D, Champion B, Cooke A (1987) Advanced immunology. Gower Medical, London
Meade-Tollin LC, Pipes BL, Anderson SJ, Seftor EA, Hendrix MJ (1990) A comparison of levels of intrinsic single strand breaks/alkali labile sites associated with human melanoma cell invasion. Cancer Lett 53:45–54
McGovern VJ (1973) The classification of malignant melanoma and its histological repeating. Cancer 32(6):1446–1457
Mihm MC, Murphy GF, Kanfuan N (1988) Pathobiology and recognition of malignant melanoma. Williams and Wilkins
Nakamura K, Rokutan K, Marni N (1991) Induction of heat shock proteins and their implication in protection against ethanol-induced damage in cultured guinea pig gastric mucosal cells. Gastroenterol 101(1):161–169
Nacopoulou L, Azaris P, Papacharalampous N, Davaris P (1981) Prognostic significance of histologic host response in cancer of the large bowel. Cancer 47:930–936
Nowell PC (1976) The clonal evolution of tumor cell populations. Science 194:23–28
Paul (1991) Oncogenesis. In: MacSween A (ed) Recent advances in histopathology. Churchill, Linvingstone, California, vol 13
Peltenburg LT, Steegenga WT, Kruse KM, Schrier PI (1992) C-myc-induced natural killer cell sensitivity of human melanoma cells is reversed by HLA-B27 transfection. Eur J Immunol 22(10):2737–2740
Peris K, Cerroni L, Chimenti S, Soyer HP, Kerl H, Hofler H (1991) Proto-oncogene expression in dermal naevi and melanomas. Arch Dermatol Res 283:500–505
Pitot HC (1993) The molecular biology of carcinogenesis. Cancer 72(3):962–970
Roit IM, Brostoff J, Male D (1993) Immunology, 3rd ed, Mosby, Saint-Louis
Runger TM, Klein CE, Beeker JC, Brucker EB (1994) The role genetic instability, adhesion, cell motility, and immune escape mechanisms in melanoma progression. Curr Opin Oncol 6:188–296
Sarmyn M, Yaar M, Holbrock N, Gilchrest BA (1991) Immediate and delayed molecular response of human keratinocytes to solar-stimulated irradiation. Lab Invest 65(4):471–478
Schiaffonati L, Pappalardo C, Tacchini L (1991) Expression of the HSP70 gene family in rat hepatoma cell lines of different growth rates. Exp Cell Res 196(2):330–336
Tauchi K, Tsutsumi Y, Hori S, Yoshimura S, Osamura RY, Watanabe K (1991) Expression of heat shock protein 70 and c-myc protein in human breast cancer: an immunohistochemical study. J Clin Oncol 21(4):256–263
VanBuskirk AM, DeNagel DC, Guagliardi LE et al. (1991) Cellular and subcellular distribution of PBP 72/74, a peptide-binding protein that plays a role in antigen processing. J Immunol 146(2):500–506
Udono H, Srivastava PK (1993) Heat shock protein 70 associated peptides elicit specific cancer immunity. J Exp Med 178(4):1391–1396
Yougel RA, Elliot TJ (1989) Stress proteins, infection and immune surveillance. Cell 59:5–8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lazaris, A.C., Theodoropoulos, G.E., Aroni, K. et al. Immunohistochemical expression of C-myc oncogene, heat shock protein 70 and HLA-DR molecules in malignant cutaneous melanoma. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 426, 461–467 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193169
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193169