Abstract
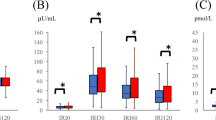
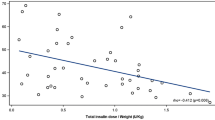
To investigate the effects of antihypertensive treatment with the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor lisinopril on insulin sensitivity and related metabolic variables, the insulin sensitivity index (SI), determined with the Minimal Model Method of Bergman, fasting plasma insulin and glucose concentrations, serum total triglyceride and lipoprotein cholesterol fractions, and blood pressure were assessed in 24 lean, non-diabetic patients with essential hypertension. Following a double-blind, randomised crossover design, these parameters were measured after a 4-week run-in period, after 8 weeks of lisinopril or placebo, and after an additional 8 weeks on placebo or lisinopril, respectively. Furthermore, the level of physical fitness was estimated using the Conconi bicycle ergometer test. SI was low in this study population (5.6 vs 13.3 · 10−4·min−1·mU−1·1−1 in normal lean control subjects). It did not differ between the placebo run-in phase, the lisinopril phase, and the placebo crossover phase (5.8, 5.5, and 5.4·10−4·min−1·mU−1·1−1, respectively). Moreover, during the administration of lisinopril, no significant changes occurred in fasting plasma insulin and glucose, areas under the glucose and insulin curves, glucose disappearance rate, serum total triglycerides, and cholesterol or lipoprotein cholesterol fractions. Heart rate at rest, body weight, and anaerobic threshold remained stable throughout the study. Compliance assessed by pill-counting exceeded 90% at all visits. These findings demonstrate that the ACE inhibitor lisinopril is neutral with regard to insulin sensitivity, plasma insulin and glucose, and lipoprotein metabolism in patients with essential hypertension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reaven GM (1988) Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 37:1595–1607
Ferranini E, Buzzigoli G, Bonadonna R, et al. (1987) Insulin resistance in essential hypertension. N Engl J Med 317:350–357
Weidmann P, de Courten M, Böhlen L (1993) Insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia and hypertension. J Hypertens 11 [Suppl 5]:S27-S38
Ferrari P, Weidmann P, Shaw S, et al. (1991) Altered insulin sensitivity, hyperinsulinemia and dyslipidemia in hypertension-prone humans. Am J Med 91:589–596
Allemann Y, Horber FF, Colombo M, et al. (1993) Insulin sensitivity and body fat distribution in normotensive offspring of hypertensive parents. Lancet 341: 327–331
Castelli WP (1984) Epidemiology of coronary heart disease: the Framingham Study. Am J Med 76 [Suppl 2A]:4–12
De Fronzo RA, Ferrannini E (1991) Insulin resistance, a multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care 14:173–94
Laws A, Reaven GM (1993) Insulin resistance and risk factors for coronary heart disease. Clin Endocrinol Metab 7:1063–1078
Gambardella S, Frontoni S, Pellegrinotti M, Testa G, Spallone V, Menzinger G (1993) Carbohydrate metabolism in hypertension: influence of treatment. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 22:S87-S97
Collins R, Peto R, MacMahon S, et al. (1990) Blood pressure, stroke and coronary heart disease. Part 2, short-term reduction in blood pressure: overview of randomized drug trials in their epidemiological context. Lancet:827–838
Ferrari P, Rosman J, Weidmann P (1991) Antihypertensive agents, serum lipoproteins and glucose metabolism. Am J Cardiol 67:262–35B
Pollare T, Lithell H, Berne C (1989) A comparison of the effects of hydrochlorothiazide and captopril on glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with hypertension. N Engl J Med 321:868–873
Paolisso G, Gambardella A, Verza M, D'Amore A, Sgambato S, Varricchio M (1992) ACE inhibition improves insulin-sensitivity in aged insulin-resistant hypertensive patients. J Hum Hypertens 6:175–179
Kawai K, Suzuki S, Murayama Y, Watanabe Y, Yamashita K (1992) Comparison of the effects of nilvadipine and captopril on glucose and lipid metabolism in NIDDM patients with hypertension. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 16:137–143
Santoro D, Natali A, Palombo C, et al. (1992) Effects of chronic angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition on glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in essential hypertension. Hypertension 20:181–191
Allemann Y, Baumann S, Jost M, et al. (1992) Insulin sensitivity in normotensive subjects during angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition with fosinopril. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 42:275–280
Nuttall FQ, Gannon MC, Wald JL, Ahmed M (1985) Plasma glucose and insulin profiles in normal subjects ingesting diets of varying carbohydrate, fat, and protein content. J Am Coll Nutr 4:437–450
Bergman RN, Prager R, Volund A, Olefsky JM (1987) Equivalence of the insulin sensitivity index in man derived by the minimal model method and the euglycemic glucose clamp. J Clin Invest 79:790–800
Yang YJ, Youn JH, Bergman RN (1987) Modified protocols improve insulin sensitivity estimation using the minimal model. Am J Physiol 253:E595-E602
Conconi F (1982) Determination of the anaerobic threshold by a noninvasive field test in runners. J Appl Physiol 52:869–873
Böhlen L, de Courten M, Hafezi F, Shaw S, Riesen W, Weidmann P (1994) Insulin sensitivity and atrial natriuretic factor during beta-modulation with celiprolol in normal subjects. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 23:877–833
Weidmann P, Beretta-Piccoli C, Ziegler WH, Keusch G, Glück Z (1978) Age versus urinary sodium for judging renin, aldosterone and catecholamine levels. Studies in normal subjects and patients with essential hypertension. Kidney Int 14:619–628
US Department of Health, Education and Welfare (1974) Manual of laboratory operations. Lipid research clinics program. Lipid and lipoprotein analysis (publication No. NIH-75–628). US Department of Health, Education and Welfare, Washington
Saxenhofer H, Weidmann P, Riesen W, et al. (1990) Therapeutic efficacy of the HMG-CoA-reductase inhibitor pravastatin in hyperlipoproteinaemia type II. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 41:109–112
Oksa A, Gajdos M, Fedelesova V, Spustova V, Dzurik R (1994) Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors on glucose and lipid metabolism in essential hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 23:79–86
Torlone E, Rambotti AM, Periello G, et al. (1991) ACE-inhibition increases hepatic and extrahepatic sensitivity to insulin in patients with Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus and arterial hypertension. Diabetologia 34:119–125
Santoro D, Natali A, Galvan AQ, Masoni A, Gazzetti P, Ferrannini E (1991) Glucose tolerance and insulin secretion in essential hypertension after treatment with an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor. J Hypertens Suppl 9:S406-S407
Shionoiri H, Sugimoto K, Minamisawa K, et al. (1990) Glucose and lipid metabolism during long-term treatment with cilazapril in hypertensive patients with or without impaired glucose metabolism. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 15:933–938
Andronico G, Angileri G, Piazza G, Cerasola G (1991) Metabolic effects of enalapril and nifedipine in diabetic hypertensives. J Hypertens Suppl 9:S408-S409
Ludvik B, Kueenburg E, Brunnbauer M, Schernthaner G, Prager R (1991) The effects of ramipril on glucose tolerance, insulin secretion, and insulin sensitivity in patients with hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 18:S157-S159
Bak JF, Gerdes LU, Sorensen NS, Pedersen O (1992) Effects of perindopril on insulin sensitivity and plasma lipid profile in hypertensive non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Am J Med 92:69S–72S
Bergemann R, Wohler D, Weidmann P, Betzin J, Nawrath T (1992) Verbesserte Glucoseeinstellung und Albuminurie bei Diabetikert unter ACE-Hemmer-Behandlung: eine Metaanalyse publizierter Studien aus den Jahren 1985 bis 1990. Schweiz Med Wschr 122:1369–1376
Houston MC (1992) Exercise and hypertension. Maximizing the benefits in patients receiving drug therapy. Postgrad Med 92:139–144
Abrams JJ, Ginsberg H, Grundy SM (1982) Metabolism of cholesterol and plasma triglycerides in nonketotic diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 31:903–910
Taskinen MR, Kuusi T, Helve E, Nikkilä EA, Yki-Järvinen H (1988) Insulin therapy induces antiatherogenic changes of serum lipoproteins in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Arteriosclerosis 8:168–177
Whelton A, Dunne B, Jr, Glazer N, et al. (1992) Twenty-four hour blood pressure effect of once-daily lisinopril, enalapril, and placebo in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 6:325–331
Huckell VF, Belanger LG, Kazimirski M, Subramanian T, Cox AJ (1993) Lisinopril in the treatment of hypertension: a Canadian postmarketing surveillance study. Clin Ther 15:407–422
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thürig, C., Böhlen, L., Schneider, M. et al. Lisinopril is neutral to insulin sensitivity and serum lipoproteins in essential hypertensive patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 49, 21–26 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192353
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192353