Abstract
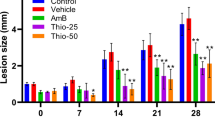
Reports in the literature indicate the use of animal models for testing newer anti-leishmanial drugs in vivo. However, in certain established cell lines and macrophages in vitro models have the advantage over the in vivo system of simplicity and speed with which the results can be obtained. A simple in vitro system using peritoneal exudate macrophages of BALB/c mice infected with Leishmania donovani promastigotes has been tested for its use in determining the efficacy of several new drugs. Two well-established drugs, amphotericin B and sodium stibogluconate, as expected, could kill the intracellular parasites effectively. Two relatively new drugs not routinely used against leishmania, rifampicin and metronidazole at concentrations of 20 μg/ml and 10 μg/ml, respectively, were also able to kill the intracellular leishmania parasites effectively. Critical factors for drug testing in vitro have been elucidated: the most important being the temperature of incubation after infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mukhopadhyay A, Chaudhary G, Arora SK, Sehgal S, Basu SK (1989) Receptor-mediated drug delivery to macrophages in chemotherapy of leishmaniasis. Science 244:705–707
Beach DH, Goad LJ, Holz GG Jr (1988) Effects of anti-mycotic azoles on growth and sterol biosynthesis of Leishmania promastigotes. Mol Biochem Parasitol 31:149–162
Berenes RL, Marr JJ (1979) Growth of L. donovani amastigotes in a continuous macrophagelike cell culture. J Protozool 26:453–456
Berman JD (1988) Inhibition of leishmanial protein kinase by anti-leishmanial drugs. Am J Trop Med Hyg 38:298–303
Berman JD, Webster HK (1982) In vitro effects of mycophenolic acid and allopurinol against L. tropica in human macrophages. Antimicrobial Agent Chemother 21:887–891
Berman JD, Wyler DJ (1980) An in vitro model for investigation of chemotherapeutic agents in leishmaniasis. J Infect Dis 142:83–86
Cenini P, Bolognesi A, Stirpe F (1988) Ribosome inactivating proteins from plants inhibit ribosome activity of Trypanosoma and Leishmania. J Protozool 35:384–387
Chakraborty AK, Majumdar HK (1988) Mode of action of pentavalent antimonials: specific inhibition of type-I DNA topoisomerase of Leishmania donovani. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 152:605–611
Even-paz Z, Weinrauch L, Livshin R, El On J, Greenblatt CL (1982) Rifampicin treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Int J Dermatol 21:110–112
Jalees S, Jaleel S, Topa PK, Hussain QZ, (1982) An easily prepared two-phase medium for cultivation of L. donovani. J Commun Dis 14:111–117
Kinnanom KE, Steck EA, Loizeaux PS, Chapman WL, Waits VB, Hanson WL (1980) Leishmaniasis: in search of a new chemotherapeutic agents. Am J Vet Res 41:405–407
Konigk E, Rasoul SA (1978) Catabolism of adenine 5′-monophosphate in promastigotes of L. tropica. Trop Med Parasitol 28:319–322
Manson Bahr PEC (1959) East African kala azar with special reference to the pathology, prophylaxis of treatment. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 53:123–137
Marr JJ, Berens RL, (1978) Purine metabolism in L. donovani and L. braziliensis. J Protozool 25:14A
Martinez S, Looker DL, Berens RL, Marr JJ (1988) The synergistic action of pyrazolopyrimi-dines and pentavalent antimony against Leishmania donovani and L. braziliensis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 39:250–255
Martinez S, Looker DL, Marr JJ (1988) A tissue culture system for the growth of several species of leishmania: growth kinetics and drug sensitivity. Am J Trop Med Hyg 38:304–307
Mattock NM, Peters W (1975) The experimental chemotherapy of Leishmaniasis II. The activity in tissue culture of some antiparasitic and antimicrobial compounds in clinical use. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 69:359–371
Murray HW, Berman JD, Wright SD (1988) Immunochemotherapy of intracellular Leishmania donovani infection: gamma-interferon plus pentavalent antimony. J Infect Dis 157:973–978
Navin TR, Pearson RD (1987) Inhibition of L. donovani growth by streptomycin and tobramycin. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 20:141–142
Peters W (1983) Chemotherapy of leishmania — Present status, problems and prospects. In: Anand N, Sen AB (eds) Chemotherapy and immunology of malaria, filariasis and leishmaniasis, vol. 22. McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, pp 243–254
Sanyal RK, Arora RR (1979) Assessment of drug therapy of kala azar in current in Bihar. J Commun Dis 11:198–202
Stauber LA, Franchino EM, Grun J (1958) An eight-day method for screening compounds against visceral leishmaniasis, in the hamsters. J Protozool 5:269–273
Steck EA (1974) The Leishmaniasis. Prog Drug Res 18:289–351
Trotter ER, Peters W, Robinson BL (1980) The experimental chemotherapy of Leishmaniasis VI. The development of rodent models for infection. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 74:127–138
Wijers DJB (1971) A ten-Years' study of kala azar in Tharaka (Meru Distt, Kenya). II. Relapses. East Afr Med J 48:551–558
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, S.K., Sinha, R. & Sehgal, S. Use of in vitro method to assess different brands of anti-leishmanial drugs. Med Microbiol Immunol 180, 21–27 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00191697
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00191697