Abstract
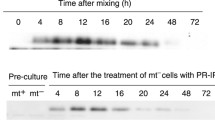
A sex pheromone, protoplast-release-inducing protein (PR-IP), of the Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex is known to induce the release of protoplasts from mating-type minus (Mt−) cells during sexual reproduction and to have two subunit polypeptides of 19 and 42 kDa. Here, we describe the regulation mechanism for the release of the PR-IP. The sex pheromone was fractionated to yield subunits of 19 and 42 kDa, respectively, and each subunit was treated with V8 protease and with CNBr. By reference to the partial amino-acid sequences of the digested polypeptides, oligo nucleotides were synthesized and used as primers for the combined reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Amplified fragments of DNA, of 130 bp in the case of the 19-kDa subunit and of 330 bp in the case of the 42-kDa subunit, were obtained, sequenced, and used as probes to identify the respective transcripts. From the results of Northern hybridization, the sizes of transcripts were estimated to be 1.2 kb for the 19-kDa subunit and 1.4 kb for the 42-kDa subunit. These transcripts appeared transiently only when mating-type plus (mt+) cells were treated with another sex pheromone (PR-IP Inducer) for more than 4 h in the light. By immunoblotting with anti-42-kDa-subunit antiserum, it was shown that PR-IP accumulated gradually in the medium but not in the mt+ cells after treatment with PR-IP Inducer in the light. We suggest that PR-IP is synthesized de novo and secreted from mt+ cells only after the perception of PRIP Inducer that has been released from mt− cells in the light during the sexual reproduction of Closterium. An analysis by genomic Southern hybridization revealed that probes for the 19-kDa and 42-kDa peptides hybridized to 6.8-kb and 5.1-kb DNA fragments, respectively, after the digestion of the genome with EcoRI. These hybridized DNA fragments were obtained not only from the genome of mt+ cells but also from the genome of mr cells, in which no transcripts for PR-IP could be detected by Northern hybridization. On the basis of these results, we discuss the possibility that the expression of the gene for the two subunits of PR-IP might be critically dependent upon the action of putative sex-determining genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- kDa:
-
kilodalton
- mt+ :
-
mating-type plus
- mt− :
-
mating-type minus
- PR-IP:
-
protoplast-release-inducing protein
- PVDF:
-
polyvinylidine difluoride
- RT-PCR:
-
reverse transcriptionpolymerase chain reaction
References
Al-Hasani, H., Jaenicke, L. (1992) Characterization of the sex-inducer glycoprotein of Volvox carteri f. weismannia. Sex. Plant Reprod. 5, 8–12
Brook, A.J. (1981) The Biology of Desmids. University of California Press, Berkeley and Los Angeles
Buchanan, M.J., Imam, S.H., Eskue, W.A., Snell, W.J. (1989) Activation of the cell wall degrading protease, lysin, during sexual signalling in Chlamydomonas: the enzyme is stored as an inactive, higher relative molecular mass precursor in the periplasm. J. Cell Biol. 108, 199–207
Cleveland, D.W., Fischer, S.G., Kirschner, M.W., Laemmli, U.K. (1977) Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J. Biol. Chem. 252, 1102–1106
Coecel, P.F.M., de Jong, W. (1986) Vigorous chemotactic attraction as a sexual response in Closterium ehrenbergii Meneghini (Desmidiaceae, Chlorophyta). Phycologia 25, 405–408
Cook, P.A. (1963) Variation in vegetative and sexual morphology among the small urved species of Closterium. Phycologia 3, 1–18
Dubois-Tylski, T. (1973) La conjugation en culture'n vitro'chez Closterium rostratum. Eur. Bull. Soc. Bot. Fr. 120, 33–41
Edge, A.S.B., Faltynek, C.R., Hof, L., Reichert, L.E., Weber, P. (1981) Deglycosylation of glycoproteins by trifluoromethanesulfonic acid. Anal. Biochem. 118, 131–137
Gershoni, J.M., Palade, G.E. (1982) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels to a positively charged membrane filter. Anal. Biochem. 124, 396–405
Hamada, J., Yoshizawa-Katoh, T., Tsunewaki, K. (1982) Genetic study on mating type genes by a new type of tetrad analysis in Closterium ehrenbergii. Bot. Mag. Tokyo 95, 101–108
Hogetsu, T., Yokoyama, M. (1979) Light, a nitrogen-depleted medium and cell-cell interaction in the conjugation process of Closterium ehrenbergii Meneghini. Plant Cell Physiol. 20, 811–817
Ichimura, T. (1971) Sexual cell division and conjugation-papilla formation in sexual reproduction of Closterium strigosum. In: Proc. of the 7th Int. Seaweed Symp, pp. 208–214, Nishizawa, K., ed. University of Tokyo Press, Tokyo
Ichimura, T. (1983) Hybrid inviability and predominant survival of mating type minus progeny in laboratory crosses between two closely related mating groups of Closterium ehrenbergii. Evolution 37, 252–260
Ichimura, T., Kasai, F. (1987) Time-lapse analysis of sexual isolation between two closely related mating groups of the Closterium ehrenbergii species complex (Chlorophyta). J. Phycol. 23, 523–534
Karlson, P., Luscher, M. (1959) ‘Peromones’: A new term for a class of biologically active substances. Nature 183, 55–56
Kasai, F., Ichimura, T. (1990) A sex determining mechanism in the Closterium ehrenbergii (Chlorophyta) species complex. J. Phycol. 26, 195–201
Kato, A., Sasaki, K. (1983) Effect of tunicamycin on sexual reproduction in heterothallic strains of Closterium. J. Fac. Sci. Hokkaido Univ. Ser. V 13, 1–6
Kato, A., Sasaki, K. (1985) Sexual interaction in heterothallic strains of Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale. Plant Physiol. 77, 556–559
Kato, A., Obokata, J., Sasaki, K. (1981) Mating type interaction in Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale: mating induced protoplast release. Plant Cell Physiol. 22, 1215–1222
Kato, A., Takagi, T., Sasaki, K. (1983) Light conditions for sexual reproduction in heterothallic strains of Closterium. Plant Cell Physiol. 24, 93–100
Laemmli, U.K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685
Lippert, B.E. (1967) Sexual reproduction in Closterium moniliferum and C. ehrenbergii. J. Phycol. 3, 182–198
Mages, H.-W, Tschochner, H., Sumper, M. (1988) The sexual inducer of Volvox carteri. Primary structure deduced from cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett. 234, 407–410
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E.F., Sambrook, J. (1982) Molecular Cloning. A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Prescott, A., Martin, C. (1987) A rapid method for the quantitative assessment of levels of specific mRNAs in plants. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 4, 219–224
Schnell, D.J., Blobel, G., Pain, D. (1990) The chloroplast import receptor is an integral membrane protein of chloroplast envelope contact sites. J. Cell Biol. 111, 1825–1838
Sekimoto, H., Satoh, S., Fujii, T. (1990) Biochemical and physiological properties of a protein inducing protoplast release during conjugation in the Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex. Planta 182, 348–354
Sekimoto, H., Fujii, T. (1992) Analysis of gametic protoplast-release in Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex (Chlorophyta). J. Phycol. 28, 615–619
Sekimoto, H., Satoh, S., Fujii, T. (1993a) Analysis of binding of biotinylated protoplast-release-inducing protein that induces release of gametic protoplasts in the Closterium peracerosumstrigosum-littorale complex. Planta 189, 468–474
Sekimoto, H., Inoki, Y., Fujii, T. (1993b) Detection and evaluation of an inducer of diffusible mating pheromone of heterothallic Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex. Plant Cell Physiol. 34, 991–996
Snell, W.J. (1985) Cell-cell interactions in Chlamydomonas. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 36, 287–315
Snell, W.J., Eskue, W.A., Buchanan, M.J. (1989) Regulated secretion of a serine protease that activates an extracellular matrix-d grading metalloprotease during fertilization in Chlamydomonas. J. Cell. Biol. 109, 1689–1694
Starr, R.C., Jaenicke, L. (1974) Purification and characterization of the hormone initiating sexual morphogenesis in Volvox carteri f. nagariensis lyengar. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 71, 1050–1054
Sumper, M., Berg, E., Wenzl, S., Godl, K. (1993) How a sex pheromone might act at a concentration below 10−16 M. EMBO J. 12, 831–836
Tschochner, H., Lottspeich, F., Sumper, M. (1987) The sexual inducer of Volvox carteri: purification, chemical characterization and identification of its gene. EMBO J. 6, 2203–2207
Watanabe, M.M., Ichimura, T. (1982) Biosystematic studies of the Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex IV. Hybrid breakdown between two closely related groups, Group II-A and Group II-B. Bot. Mag. Tokyo 95, 241–247
Weisshaar, B., Gilles, R., Moka, R., Jaenicke, L. (1984) A high frequency mutation starts sexual reproduction in Volvox carteri. Z. Naturforsch. 39c, 1159–1162
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Recipient of a Fellowship for Japanese Junior Scientists from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education (Japan) to H. S.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sekimoto, H., Sone, Y. & Fujii, T. Regulation of expression of the genes for a sex pheromone by an inducer of the sex pheromone in the Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex. Planta 193, 137–144 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00191617
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00191617