Abstract
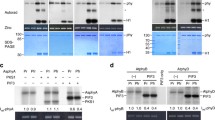
In the moss Ceratodon purpureus a phytochrome gene encodes a phytochrome type (PhyCer) which has a C-terminal domain homologous to the catalytic domain of eukaryotic protein kinases (PKs). PhyCer exhibits sequence conservation to serine/ threonine as well to tyrosine kinases. Since PhyCer is expressed very weakly in moss cells, to investigate the proposed PK activity of PhyCer, we overexpressed PhyCer transiently in fibroblast cells. For this purpose we made a chimeric receptor, EC-R, which consists of the extracellular, the membrane-spanning and the juxtamembrane domains of the human epidermal growth-factor receptor (EGF-R) linked to the PK catalytic domain of PhyCer (CerKin). The expression of EC-R in transiently transfected cells was confirmed with antibodies directed against the extracellular domain of EGF-R or against CerKin. Both EGF-R and EC-R were immunoprecipitated from lysates of overexpressing cells with antibodies against the extracellular domain of EGF-R. Phosphorylation experiments were performed with the immunoprecipitates and the phosphorylation products were subjected to phosphoamino acid analysis. Phosphorylation products specifically obtained with EC-R-transfected cells exhibit phosphorylation on serine and threonine residues. In EC-R transfected cells the endogenous EGF-R showed enhanced phosphorylation of serine and threonine residues compared to EGF-R immuno-precipitated from control cells. Although CerKin is closest to the catalytic domain of a protein tyrosine kinase from Dictyostelium discoideum, EC-R does not appear to phosphorylate tyrosine residues in vitro. From our data we conclude that PhyCer carries an active PK domain capable of phosphorylating serine and threonine residues.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CerKin:
-
protein kinase catalytic domain of PhyCer
- EC-R:
-
chimeric receptor consisting of the extracellular, the membrane spanning and the juxtamembrane domains of the human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R) linked to the protein kinase catalytic domain of PhyCer
- EGF-R:
-
epidermal growth factor receptor
- mAb:
-
monoclonal antibody
- PhyCer:
-
phytochrome gene in Ceratodon encoding a phytochrome type which has a C-terminal domain homologous to the catalytic domain of eucaryotic protein kinases
- PK:
-
protein kinase
- PVDF:
-
polyvinyl difluoride
- Ser:
-
serine
- Thr:
-
threonine
- Tyr:
-
tyrosine
References
Algarra P, Linder S, Thümmler F (1993) Biochemical evidence that phytochrome of the moss Ceratodon purpureus is a light-regulated protein kinase. FEES Lett 315: 69–73
Chen C, Okayama H (1987) High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol 7: 2745–2752
Clack T, Mathews S, Sharrock RA (1994) The phytochrome apoprotein family in Arabidopsis is encoded by five genes: the sequences and expression of PHYD and PHYE. Plant Mol Biol 25: 413–427
Duclos B, Marcandier S, Cozzone AJ (1991) Chemical properties and separation of phosphoamino acids by thin-layer chromatography and/or electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol 201: 10–20
Fendly BM, Winget M, Hudziak R, Lipari MT, Napier MA, Ullrich A (1990) Characterization of murine monoclonal antibodies reactive to either human epidermal growth factor receptor or HER2/neu gene product. Cancer Res 20: 1550–1558
Furuya M (1993) Phytochromes-Their molecular species, gene families, and functions. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 44: 617–645
Herbst R, Lammers R, Schlessinger J, Ullrich A (1991) Substrate phosphorylation specificity of the human c-kit receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem 266: 19908–19916
Honegger AM, Kris RM, Ullrich A, Schlessinger J (1989) Evidence that autophosphorylation of solubilized receptors for epidermal growth factor is mediated by intermolecular cross-phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 925–929
Kendrick RE, Kronenberg GHM (1994) Photomorphogenesis in plants (2nd edn). Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Boston, London
Knecht DA, Dimond RL (1984) Visualization of antigenic proteins on Western blots. Anal Biochem 136: 180–184
Lindberg RA, Quinn AM, Hunter T (1992) Dual-specificity of protein kinases; will any hydroxyl do? TIBS 17: 114–119
Quail PH (1991) Phytochrome: a light-activated molecular switch that regulates plant gene expression. Annu Rev Genet 25: 389–409
Rüdiger W, Thümmler F (1991) Phytochrome, the visual pigment of plants. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng 30: 1216–1228
Thümmler F, Dufner M, Kreisl P, Dittrich P (1992) Molecular cloning of a novel phytochrome gene of the moss Ceratodon purpureus which encodes a putative light-regulated protein kinase. Plant Mol Biol 20: 1003–1017
Thümmler F, Algarra P, Fobo GM (1995) Sequence similarities of phytochrome to protein kinases: implication for the structure, function and evolution of the phytochrome gene family. FEBS Lett 357: 149–155
Ullrich A, Schlessinger J (1990) Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell 61: 203–212
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dr. Patricia Algarra was supported by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, Germany. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), Bonn, Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thümmler, F., Herbst, R., Algarra, P. et al. Analysis of the protein kinase activity of moss phytochrome expressed in fibroblast cell culture. Planta 197, 592–596 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00191565
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00191565