Summary
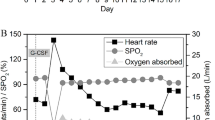
Recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (rhGM-CSF) was given to an intensive-care patient with polytrauma in a life-threatening situation with acquired agranulocytosis and sepsis. Mature granulocytes reappeared in the blood 2 days after initiation of rhGM-CSF therapy; granulocyte precursors peaked at 43% after 5 days. Bone marrow examination performed 7 days after the beginning of rhGM-CSF therapy revealed complete regeneration of granulopoiesis. The functional analysis of these blood leukocytes in vitro showed regular production of reactive oxygen radicals. Clinically, the patient recovered without any serious side effects due to the rhGM-CSF therapy. These results suggest that rhGM-CSF accelerates granulocyte recovery from acquired agranulocytosis with the presence of their functional activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- rhGM-CSF:
-
Recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor
- rhG-CSF:
-
recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
- HBSS:
-
Hank's balanced salt solution
- MNC:
-
mononuclear cells
- PMN:
-
polymorphonuclear neutrophils
- CL:
-
chemiluminescence
References
Blair AL, Cree IA, Beck JS, Hastings MJG (1988) Measurement of phagocyte chemiluminescence in a microtiter plate format. J Immunol Methods 112:163–168
Bone RC (1991) Let's agree on terminology: definitions of sepsis. Crit Care Med 19:973–976
Bonilla MA, Gillio AP, Ruggeiro M, Kernan NA, Brochstein JA, Abbond M, Fumagalli L, Vincent M, Gabrilove JL, Welte K, Souza LM, O'Reilly R (1989) Effects of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on neutropenia in patients with congenital agranulocytosis. New Engl J Med 320:1574–1580
Breiheim G, Stendahl O, Dahlgren C (1984) Intra- and extracellular events in luminol-dependent chemiluminescence of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun 45:1–6
Chaimongkol B, Nanthachit N, Navarawong V, Siriloiratama P (1989) Drug-induced agranulocytosis. J Med Assoc Thai 72:666–672
Dunker D, Ullmann U (1986) Influence of various antimicrobial agents on the chemiluminescence of phagocytosing human granulocytes. Chemotherapy 32:18–25
Ferrante A, Thong YH (1978) A rapid one-step procedure for purification of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leukocytes from human blood using a modification of the hypaque-ficoll technique. J Immunol Methods 24:389–393
Ganser A, Ottmann OG, Erdmann H, Schulz G, Hoelzer D (1989) The effect of recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on neutropenia and related morbidity in chronic severe neutropenia. Ann Intern Med 111:887–892
Glasser L, Fiederlein RL (1987) Functional differentiation of normal human neutrophils. Blood 69:937–944
Lieschke GJ, Burgess AW (1992) Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor I. N Engl J Med 327:28–35
Lord BI, Gurney H, Chang J, Thatcher N, Crowther D, Dexter TM (1992) Haemopoetic cell kinetics in humans treated with rhGM-CSF. Int J Cancer 50:26–31
Ruvidic R, Jelic S (1972) Haematological aspects of drug-induced agranulocytosis. Scand J Haematol 9:18–27
Vincent PC (1986) Drug-induced aplastic anaemia and agranulocytosis. Incidence and mechanisms. Drugs 31:52–63
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gross-Weege, W., Weiss, M., Wernet, P. et al. Instant therapy of acquired agranulocytosis and sepsis by recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in a polytrauma patient. Clin Investig 71, 791–794 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00190320
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00190320