Abstract
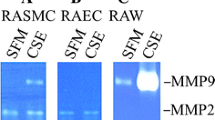
In the present study, we investigated the effect of ambient pressure on [3H]-thymidine incorporation and on the production of matrix metalloproteinase 1 (tissue collagenase/proMMP-1) using human aortic endothelial cells immortalized with simian virus 40 (SE-1). Incubation of cells at ambient pressures of 50 and 100 mmHg for 24 h slightly increased [3H]-thymidine incorporation when directly compared with normal culture conditions. The amount of [3H]-thymidine incorporated in SE-1 reached a maximum at 150 mmHg, while a further increase in pressure to 200 mmHg decreased incorporation. The same ambient pressure slightly stimulated human aortic intimal smooth muscle cells (SMC) to increase [3H]-thymidine incorporation but not medial SMC. Immunoblot analysis also showed that ambient pressure, ranging from 50 to 200 mmHg, like 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate stimulated SE-1 to produce proMMP-1, an effect not seen with either intimal or medial SMC. The amount of proMMP-1 produced also reached a maximum level at 150 mmHg. We postulate that human endothelial cells are ambient pressure sensitive and that relatively lower ambient pressures play an important role in the growth of endothelial cells, while higher pressures injure endothelial cells, resulting in the initiation of atherosclerosis. This cell line may prove useful in the investigation of both the physiological and pathological roles of blood pressure on endothelial cell function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angel P, Baumann I, Stein B, Delius H, Rahmsdorf HJ, Herrlich P (1987) 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate induction of the human collagenase gene is mediated by an inducible enhancer element located in the 5′-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol 7:2256–2266
Angel P, Imagawa M, Chiu R, Stein B, Imbra RJ, Rahmsdorf HJ, Jonat C, Herrlich P, Karin M (1987b) Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell 49:729–739
Ando J, Nomura H, Kamiya A (1987) The effect of fluid shear stress on the migration and proliferation of cultured endothelial cells. Microvasc Res 33:62–70
Ando J, Komatsuda T, Kamiya A (1988) Cytoplasmic calcium response to fluid shear stress in cultured vascular endothelial cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 24:871–877
Blumberg PM (1988) Protein kinase C as the receptor for the phorbol ester tumor promoters: Sixth Rhoads Memorial Award Lecture. Cancer Res 48:1–8
Buga GM, Gold ME, Fukuto JM, Ignarro LJ (1991) Shear stress-induced release of nitric oxide from endothelial cells grown on beads. Hypertension 17:187–193
Chiu R, Boyle WJ, Meek J, Smeal T, Hunter T, Karin M (1988) The c-fos protein interacts with c-jun/AP-1 to simulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell 54:541–552
Diamond SL, Eskin SG, McIntire LV (1989) Fluid flow stimulates tissue plasminogen activator secretion by cultured human endothelial cells. Science 243:1483–1485
Ekblom P, Lehtonen E, Saxén L, Timpl R (1981) Shift in collagen type as an early response to induction of the metanephric mesenchyme. J Cell Biol 89:276–283
Espey LL (1987) The distribution of collagenous connective tissue in rat ovarian follicles. Biol Rep 14:502–506
Frangos JA, Eskin SG, McIntire LV, Ives CL (1985) Flow effects on prostacyclin production by cultured human endothelial cells. Science 227:1477–1479
Graves LM, Bornfeldt KE, Raines EW, Potts BC, Macdonald SG, Ross R, Krebs EG (1993) Protein kinase A antagonizes platelet-derived growth factor-induced signaling by mitogenactivated protein kinase in human arterial smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10300–10304
Gross J, Lapiere CM (1962) Collagenolytic activity in amphibian tissues: a tissue culture assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 48:1014–1022
Gross JL, Moscatelli D, Rifkin DB (1983) Increased capillary endothelial cells protease activity in response to angiogenic stimuli in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:2623–2627
Heath JK, Atkinson SJ, Meikle MC, Reynolds JJ (1984) Mouse osteoblasts synthesize collagenase in response to bone resorbing agents. Biochem Biophys Acta 802:151–154
Hiraoka K, Sasaguri Y, Komiya S, Inoue A, Morimatsu M (1992) Cell proliferation-related production of matrix metalloproteinases 1 (tissue collagenase) and 3 (stromelysin) by cultured human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Biochem Int 27:1083–1091
Kaibuchi K, Tsuda T, Kikuchi A, Tanimoto T, Yamashita T, Takai Y (1986) Possible involvement of protein kinase C and calcium ion in growth factor-induced expression of c-myc oncogene in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 261:1187–1192
Kato S, Sasaguri Y, Morimatsu M (1993) Down-regulation in the production of matrix metalloproteinase 1 by human aortic intimal smooth muscle cells. Biochem Mol Biol Int 31:239–248
Kikkawa U, Takai Y, Tanaka Y, Miyabe R, Nishizuka Y (1993) Protein kinase C as a possible receptor protein of tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem 258:11442–11445
Liotta LA (1986) Tumor invasion and metastases: role of the extracellular matrix. Rhoads Memorial Award Lecture. Cancer Res 46:1–7
Murahashi M, Sasaguri Y, Ohuchida M, Kakita N, Morimatsu M (1992) Immortalization of human aortic smooth muscle cells with origin-minus simian virus 40 DNA. Biotech Appl Biochem 16:152–160
Nakanishi Y, Sugiura F, Kishi J, Yayakawa T (1986) Collagenase inhibitor stimulates cleft formation during early morphogenesis of mouse salivary gland. Dev Biol 113:201–206
Okada Y, Nagase H, Harris ED Jr (1986) A metalloproteinase from human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts that digests connective tissue matrix components. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem 261:14245–14255
Okada Y, Takeuch N, Tomita K, Nakanishi I, Nagase H (1989) Immunolocalization of matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin) in rheumatoid synovioblasts (B cells): correlation with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 48:645–653
Ooshima A (1981) Collagen alpha B chain: increased proportion in human atherosclerosis. Science 213:666–668
Reich R, Tsafriri A, Mechanic GL (1985) The involvement of collagenolysis in ovulation in the rat. Endocrinology 116:522–527
Ross R (1993) The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature 362:801–808
Ross R, Raines EW, Bowen-Pope DF (1986) The biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell 46:155–169
Sasaguri Y, Yanagi H, Nagase H, Nakano R, Fukuda S, Morimatsu M (1991) Collagenase production by immortalized human aortic endothelial cells infected with simian virus 40. Virchows Arch [B] 60:91–97
Sasaguri Y, Murahashi N, Sugama K, Kato S, Hiraoka K, Satoh T, Isomoto H, Morimatsu M (1994) Development-related changes in matrix metalloproteinase expression in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Lab Invest (in press)
Satoh T, Sugama K, Matsuo A, Kato S, Ito S, Hatanaka M, Sasaguri Y (1994) Histamine as an activator of cell growth and extracellular matrix reconstruction for human vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis (in press)
Schüle R, Rangaraja P, Yang N, Kliewer S, Ransone LJ, Bolado J, Verma IM, Evans RM (1991) Retinoic acid is a negative regulator of AP-1 responsive genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:6092–6096
Shima I, Sasaguri Y, Kusukawa J, Nakano R, Yamana H, Fujita H, Kakegawa T, Morimatsu M (1993) Production of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (92-kDa gelatinase) by human oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma in response to epidermal growth factor. Br J Cancer 67:721–727
Strähle U, Schmidt A, Kelsey G, Stewart F, Cole TJ, Schmid W, Schülz G (1992) At least three promoters direct expression of the mouse glucocorticoid receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:6731–6735
Tokunaga O, Watanabe T (1987) Properties of endothelial cell and smooth muscle cell cultured in ambient pressure. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 23:528–534
Welgus HG, Jeffrey JJ, Eisen AZ (1981) The collagen substrate specificity of human skin fibroblast collagenase. J Biol Chem 256:9511–9515
Woessner JF Jr (1962) Collagen breakdown and non-collagen protein in the rat uterus during post-partum involution. Biochem J 83:304–314
Woessner JF Jr, Cahill DR (1974) Collagen breakdown in relation to tooth eruption and resorption in the dog. Arch Oral Biol 19:1195–1201
Yanagi H, Sasaguri Y, Sugama K, Morimatsu M, Nagase H (1992) Production of tissue collagenase (matrix metalloproteinase 1) by human aortic smooth muscle cells in response to platelet-derived growth factor. Atherosclerosis 91:207–216
Yang-Yen HF, Chambard JC, Sun YL, Smeal T, Schmidt TJ, Drouin J, Karin M (1990) Transcriptional interference between c-jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell 62:1205–1215
Yoshizumi M, Kurihara H, Sugiyama T, Takaku F, Yanagisawa M, Masaki T, Yazaki Y (1989) Hemodynamic shear stress stimulates endothelin production by cultured endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 161:859–864
Zarins CK, Giddens DP, Bharadvaj BK, Sottiurai VS, Mabon RF, Glagov S (1983) Carotid bifurcation atherosclerosis: quantitative correlation of plaque localization with flow velocity profiles and wall shear stress. Circ Res 53:502–514
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kato, S., Azagami, S., Morimastu, M. et al. Ambient pressure stimulates immortalized human aortic endothelial cells to increase DNA synthesis and matrix metalloproteinase 1 (tissue collagenase) production. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 425, 385–390 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00189576
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00189576