Abstract
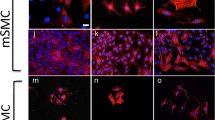
The initial phase of smooth muscle differentiation in the vascular system of the mouse embryo was observed immunohistochemically with monoclonal antibody against α-smooth muscle actin. Few smooth muscle cells were detected in the vascular system of the 9.5-day embryo, where only the dorsal aorta and umbilical artery showed signs of smooth muscle differentiation. In the 10.5-day embryo, smooth muscle cells were observed in the dorsal aorta, ventral aorta, omphalomesenteric artery and vein, umbilical artery and vein, internal carotid artery, aortic arches III and IV, and subclavian artery. The extent of smooth muscle differentiation varied among these vessels and among regions of a vessel. At 11.5 days of gestation, smooth muscle cells appeared in the basilar artery, vertebral artery, aortic arches VI, intersomitic artery, ductus venosus, and caudal artery. Smooth muscle cells were absent from the venous system characteristic of the embryo at the stages examined. Alpha-smooth muscle actin-positive cells were also observed in allantoic mesoderm in the placenta at 9.5 days, when the umbilical vessels were not surrounded by smooth muscle cells. Vascular smooth muscle cells appear to arise independently from mesenchyme at multiple sites in the vascular system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert EN (1972) Developing elastic tissue. An electron microscopic study. Am J Anat 69:89–102
Coffin JD, Poole TJ (1988) Embryonic vascular development: immunohistochemical identification of the origin and subsequent morphogenesis of the major vessel primordia in quail embryos. Development 102:735–748
Duband JL, Gimona M, Scatena M, Sartore S, Small JV (1993) Calponin and SM22 as differentiation markers of smooth muscle: spatiotemporal distribution during avian embryonic development. Differentiation 55:1–11
Feinberg RN, Sherer GK, Auerbach R (eds) (1991) The development of the vascular system. Karger, Basel
Frid MG, Shekhonin BV, Koteliansky VE, Glukhova MA (1992) Phenotypic changes of human smooth muscle cells during development: late expression of heavy caldesmon and calponin. Dev Biol 153:185–193
Gabbiani G, Schmid E, Winter S, Chaponnier C, Chastonay C de, Vandekerckhove J, Weber K, Franke WW (1981) Vascular smooth muscle cells differ from other smooth muscle cells: predominance of vimentin filaments and a specific α-type actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:298–302
Hirakow R, Hiruma T (1981) Scanning electron microscopic study on the development of primitive blood vessels in chick embryos at the early somite stage. Anat Embryol 163:299–306
Hughes AFW (1942) The histogenesis of the arteries of the chick embryo. J Anat 77:266–287
Karrer HE, Cox J (1960) Electron microscope study of developing chick embryo aorta. J ultrastruct Res 4:420–454
Kuro-o M, Nagai R, Tsuchimochi H, Katoh H, Yazaki Y, Ohkubo A, Takaku F (1989) Developmentally regulated expression of vascular smooth muscle myosin heavy chain isoforms. J Biol Chem 264:18272–18275
Kuro-o M, Nagai R, Nakahara K, Katoh H, Tsai RC, Tsuchimochi H, Yazaki Y, Ohkubo A, Takaku F (1991) cDNA cloning of a myosin heavy chain isoform in embryonic smooth muscle and its expression during vascular development and in arteriosclerosis. J Biol Chem 266:3768–3773
Leslie K, Mitchell J, Woodcock-Mitchell J, Low R (1990) Alpha smooth muscle actin expression in developing and adult human lung. Differentiation 44:143–149
McHugh KM (1995) Molecular analysis of smooth muscle development in the mouse. Dev Dyn 204:278–290
Miano JM, Cserjesi P, Ligon KL, Periasamy M, Olson EN (1994) Smooth muscle myosin heavy chain exclusively marks the smooth muscle lineage during mouse embryogenesis. Circ Res 75:803–812
Mikawa T, Fischman DA (1992) Retroviral analysis of cardiac morphogenesis: discontinuous formation of coronary vessels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:9504–9508
Nakamura H (1988) Electron microscopic study of the prenatal development of the thoracic aorta in the rat. Am J Anat 181:406–418
Ruzicka DL, Schwartz RJ (1988) Sequential activation of α-actin genes during avian cardiogenesis: Vascular smooth muscle α-actin gene transcripts mark the onset of cardiomyocyte differentiation. J Cell Biol 107:2575–2586
Sabin FR (1917) Origin and development of the primitive vessels of the chick and of the pig. Carnegie Contrib Embryol 6:61–124
Sappino AP, Schürch W, Gabbiani G (1990) Biology of disease. Differentiation repertoire of fibroblastic cells: expression of cytoskeletal proteins as marker of phenotypic modulations. Lab Invest 63:144–161
Sawtell N, Lessard J (1989) Cellular distribution of smooth muscle actins during mammalian embryogenesis: expression of the α-vascular but not the γ-enteric isoform in differentiating striated myocytes. J Cell Biol 109:2929–2937
Skalli O, Ropraz P, Trzeciak A, Benzonana G, Gillessen D, Gabbiani G (1986) A monoclonal antibody against α-smooth muscle actin: a new probe for smooth muscle differentiation. J Cell Biol 103:2787–2796
Taylor WR, Delafontaine P, Griendling KK, Nerem RM, Alexander RW (1990) Pressure induces insulin-like growth factor I secretion by endothelial cells. Hypertension 16:334
Vandekerckhove J, Weber K (1978) At least six different actins are expressed in a higher mammal: an analysis based on the amino acid sequence of the amino-terminal tryptic peptide. J Ml Biol 122:783–802
Woodcock-Mitchell J, Mitchell JJ, Low RB, Kieny M, Sengel P, Rubbia L, Skalli O, Jackson B, Gabbiani G (1988) α-smooth muscle actin is transiently expressed in embryonic rat cardiac and skeletal muscles. Differentiation 39:161–166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, Y., Imanaka, T. & Takano, T. Spatial and temporal pattern of smooth muscle cell differentiation during development of the vascular system in the mouse embryo. Anat Embryol 194, 515–526 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185997
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185997