Abstract
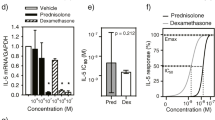
Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) is an important hematopoietic growth factor which has been shown to induce proliferation and activation of inflammatory cells, and may play a role in allergic diseases and experimental allergic reactions. Since little is known about the involvement of cytokines in allergic inflammation in the lung, we investigated whether human lung fragments produce GM-CSF in vitro. The present studies demonstrate that human lung fragments produce GM-CSF in vitro and that glucocorticoids are potent inhibitors of this cytokine production. Human lung was cut into fragments, rinsed, and cultured in 60-mm tissue culture plates containing 50 mg of tissue in RPMI 1640 with antibiotics in the presence or absence of a variety of steroids for 18 h. Lung fragments were rinsed and then incubated for an additional 4 h. Supernatants were harvested and analyzed for GM-CSF activity using the GM-CSF/interleukin (IL)-3 responsive M-07e human luekemic cell line. Steroids alone had no effect on M-07e proliferation. Human lung fragments produced 32.1 ± 11.8 ng of GM-CSF equivalents per gram wet weight of tissue during the 4 h incubation (mean ± S.E.M., n = 5, range 9.2–74.2). While specific antisera against human GM-CSF neutralized 96.8 ± 2.8% (n = 5) of the activity, anti-IL-3 antibody had no effect, suggesting most or all of this activity was GM-CSF. Treatment of lung fragments in vitro for 18 h with hydrocortisone (HC) inhibited the production of GM-CSF dose-dependently. Maximal inhibition of GM-CSF production was 72.8 ± 4.0% at a concentration of 10−6 m hydrocortisone (n = 5), and the molar concentration of HC that inhibited of GM-CSF production by lung tissue by 50% (IC50) was approximately 4.5 × 10−7 m. Kinetic studies revealed that a 6 h preincubation with the drug was required for 50% inhibition of GM-CSF production. HC and other glucocorticoids, at a concentration of 0.1 µm, demonstrated significant inhibition of GM-CSF release. Based on the rank order of potency of several glucocorticoids, and the fact that nonglucocorticoid steroids including testosterone and β-estradiol (0.1 µm) had no effect, we suggest that this is a specific receptor-mediated effect. We conclude that human lung produces GM-CSF in vitro and that antiinflammatory steroids are potent and effective inhibitors of the production of this cytokine. This may contribute to the therapeutic efficacy of these drugs in pulmonary diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avanzi GC, Brizzi MF, Giannotti J, Ciarletta A, Yang Y-C, Pegoraro L, Clark SG (1990) M-07e human leukemic factor-dependent cell line provides a rapid and sensitive bioassay for the human cytokines GM-CSF and IL-3. J Cell Physiol 145:458–464
Ballard PL, Carter JP, Graham BS, Baxter JD (1975) A radioreceptor assay for evaluation of the plasma glucocorticoid activity of natural and synthetic steroids in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 41:290–304
Bochner BS, Landy SD, Plant M, Dinarello CA, Schleimer RP (1987) Interleukin-1 production by human lung tissue. I. Identification and characterization. J Immunol 139:2297–2302
Bochner BS, Rutledge BK, Schleimer RP (1987) Interleukin-1 production by human lung tissue. II. Inhibition by antiinflammatory steroids. J Immunol 139:2303–2307
Broide DH, Firestein GS (1991) Endobronchial allergen challenge in asthma. Demonstration of cellular source of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor by in situ hybridization. J clin Invest 88:1048–1053
Broudy VC, Kaushansky K, Harlan JM, Adamson JW (1987) Interleukin-1 stimulates human endothelial cells to produce granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol 139:464–469
Churchill L, Friedman B, Schleimer RP, Proud D (1992) Production of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor by cultured human tracheal epithelial cells. Immunology 75:189–195
Cox G, Vanceri C, Ohtoshi T, Gauldie J, Dolovich J, Jordana M, Denburg J (1990) Human bronchial epithelial cell derived granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) prolongs survival of human eosinophils in vitro. (abstract) J Allergy Clin Immunol 85:233
Cox G, Ohtoshi T, Vancheri C, Denburg JA, Dolovich J, Gauldie J, Jordana M (1991) Promotion of eosinophil survival by human bronchial epithelial cells and its modulation by steroids. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 4:525–531
Culpepper JA, Lee F (1985) Regulation of IL-3 expression by glucocorticoids in cloned murine T-lymphocytes. J Immunol 135:3191–3197
Dausse JP, Duval D, Meyer P, Gaignault JC, Marchordeau C, Raynaud JP (1977) The relationship between glucocorticoid structure and effects upon thymocytes. Mol Pharmacol 13:948–955
Ebisawa M, Bochner BS, Lichtenstein LM, Bickel C, Klunk D, Schleimer RP (1992) Effect of cytokines on eosinophil transendothelial migration (abstract). J Allergy Clin Immunol 89:296
Fujisawa T, Abu-Ghazaleh R, Kita H, Sanderson CJ, Gleich GJ (1990) Regulatory effect of cytokines on eosinophil degranulation. J Immunol 144:642–646
Guba SC, Stella G, Turka LA, June CH, Thompson CB, Emerson SG (1989) Regulation of interleukin-3 gene induction in normal human T cells. J Clin Invest 84:1701–1706
Guyre PM, Girard MT, P. M. Morganelli, Manganiello PD (1988) Glucocorticoid effects on the production and actions of immune cytokines. J Steroid Biochem 30:89–93
Hamilton JA, Piccoli DS, Cebon J, Layton JE, Rathanswani P, McColl SR, Leizer T (1992) Cytokine regulation of colony-stimulating factor (CSF) production in cultured human synovial fibroblasts. II. Similarities and differences in the control of interleukin-1 induction of granulocyte-macrophage CSF and granulocyte-CSF production. Blood 79:1413–1319
Kato M, Liu MC, Stealey BA, Friedman B, Lichtenstein LM, Permutt S, Schleimer RP (1992) Production of granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor in human airways during allergen-induced late-phase reactions in atopic subjects. Lymph Cytokine Res 11:287–292
Kelley J (1990) Cytokines of the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis 141:765–788
Lamas AM, Marcotte GV, Schleimer RP (1989) Human endothelial cells prolong eosinophil survival. Regulation by cytokines and glucocorticoids. J Immunol 142:3978–3984
Lee SW, Tsou A-P, Chan H, Thomas J, Petrie K, Eugui EM, Allison AC (1988) Glucocorticoids selectively inhibit the transcription of the interleukin-1β gene and decrease the stability of interleukin-1β mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:1204–1208
Lopez AF, Williamson DJ, Gamble JR, Begley CG, Harlan JM, Klebanoff SJ, Waltersdorph A, Wong G, Clark SC, Vadas MA (1986) Recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulates in vitro mature human neutrophil and eosinophil function, surface receptor expression, and survival. J Clin Invest 78:1220–1228
Marini M, Soloperto M, Mezzetti M, Fasoli A, Mattoli S (1991) Interleukin-1 binds to specific receptors on human bronchial epithelial cells and upregulates granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor synthesis and release. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 4:519–524
Marini M, Vittori E, Hollemborg J, Mattoli S (1992) Expression of the potent inflammatory cytokines, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-6 and interleukin-8, in bronchial epithelial cells of patients with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 89:1001–1009
Massey W, Friedman B, Kato M, Cooper, P, Kagey-Sobotka A, Lichtentein LM, Schleimer RP (1993) Appearance of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor activity at allergen-challenged cutaneous late-phase reaction sites. J Immunol 150:1084–1092
Metcalf D, et al. (1986) The molecular biology and functions of the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulation factors. Blood 67:257–267
Owen WF Jr., Rothenberg ME, Silberstein DS, Gasson JC, Stevens RL, Austen KF (1987) Regulation of human eosinophil viability, density, and function by granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor in the presence of 3T3 fibroblasts. J Exp Med 166:129–141
Schleimer RP (1990) Effects of glucocorticoids on inflammatory cells relevant to their therapeutic applications in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis 141:559–569
Schleimer RP, Davidson DA, Lichtenstein LM, Adkinson NF Jr. (1986) Selective inhibition of arachidonic acid metabolite release from human lung tissue by antiinflammatory steroids. J Immunol 136:3006–3011
Schleimer RP, Benenati SV, Friedman B, Bochner BS (1991) Do cytokines play a role in leukocyte recruitment and activation in the lungs? Am Rev Respir Dis 143:1169–1174
Sedgwick JB, Calhoun WJ, Busse WW (1991) Functional and density comparison of blood and airway eosinophils following segmental antigen challenge (abstract). Am Rev Respir Dis 143:A42
Silberstein DS, Owen WF Jr., Gasson JC, DiPersio JF, Golde DW, Bina JC, Soberman R, Austen KF, David JR (1986) Enhancement of human eosinophil cytotoxicity and leukotriene synthesis by biosynthetic (recombinant) granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol 137:3290–3294
Tobler A, Marti H-P, Gimmi C, Cachelin AB, Saurer S, Fey MF (1991) Dexamethasone and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, but not cyclosporine A, inhibit production of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in human fibroblasts. Blood 77:1912–1918
Vacca A, Martinotti S, Screpanti I, Maroder M, Felli MP, Farina AR, Gismondi A, Santoni A, Frati L, Gulino A (1990) Transcriptional regulation of the interleukin-2 gene by glucocorticoid hormones. Role of steroid receptor and antigen-responsive 5′-flanking sequences. J Biol Chem 265:8075–8080
Warringa RAJ, Koenderman L, Kok PTM, Kreukniet J, Bruijnzeel PLB (1991) Modulation and induction of eosinophil chemotaxis by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-3. Blood 77:2694–2700
Yang YC, Ciarlette A, Norton CR, Turner KJ, Fenton GM, Alderman EM, Clark SC. (1987) Expression of the human interleukin-3 gene by activated peripheral blood lymphocytes. In: Gale RP, Golde DW (eds) Recent advances in leukemia and lymphoma. Alan R. Liss, New York, p. 265
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: R. P. Schleimer
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kato, M., Schleimer, R.P. Antiinflammatory steroids inhibit granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor production by human lung tissue. Lung 172, 113–124 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185082
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185082