Summary
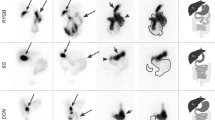
In an experimental study on 65 rats the influence of different Roux-Y biliary anastomoses on the enterohepatic bile acid circulation was investigated. Long (10 cm) and short (3 cm) isoperistaltic and long (10 cm) anisoperistaltic Roux-Y loops were studied and compared to sham-operated controls. 75-SeHCAT a y-labeled synthetic bile acid was used for assessment of enterohepatic circulation. Hepatic excretion and enteric bile flow was investigated by 99m-Tc-HIDA. Intestinal transit time was evaluated by 51-Cr-EDTA an inert marker of intestinal contents. Animals with biliary anastomoses showed an increased retention of the synthetic bile acid 75-SeHCAT compared to the controls. Highest retention values were found in animals with anisoperistaltic loops (t1/2 = 98.6 h). Isoperistaltic loops showed uniform values indenpendently of the length of the Roux-limb (t1/2 = 59.8 h resp. 59.3 h). Differences to the controls (t1/2 = 42.6 h) were highly significant (p<0.001). In the 99m-Tc-HIDA hepatic excretion into the connected small bowel was normal in all groups. But in rats with biliary anastomoses a marked stasis of the 99m-Tc-HIDA in the Roux-Y loop was apparent. Bowel transit time tested by 51-Cr-EDTA showed comparable results in all groups without significant differences. The results demonstrate an increased bile acid retention in Roux-Y biliary anastomoses. An alteration of the enterohepatic circulation due to stasis in the Roux-Y limb seems to be the underlying mechanism.
Zusammenfassung
In einer experimentellen Studie an 65 Ratten wurde der Einfluß verschiedener biliodigestiver Roux-Y-Anastomosen auf den enterohepatischen Kreislauf der Gallensäuren untersucht. Es kamen lange (10 cm) and kurze (3 cm) isoperistaltische sowie lange (10 cm) anisoperistaltische Roux-Schlingen zur Anwendung, die Ergebnisse wurden mit den Befunden scheinoperierter Kontrolltiere verglichen. Die synthetische Gallensäure 75-SeHCAT diente zur Beurteilung des enterohepatischen Kreislaufs. Der Gallefluß aus der Leber in den Dünndarm wurde mit dem 99m-Tc-HIDA untersucht. Die intestinale Passagezeit wurde nach oral verabreichtem 51-Cr-EDTA verglichen. Tiere mit einer biliodigestiven Roux-Y-Anastomose zeigten im Vergleich zu den Kontrollen eine erhöhte Retention der synthetischen Gallensäure 75-SeHCAT. Die höchsten Retentionswerte wiesen Tiere mit anisoperistaltischen Schlingen auf (t1/2 = 98,6 h). Bei isoperistaltischen Schlingen zeigten sich uniforme Werte unabhängig von der Schlingenlänge (t1/2 = 59,8 h bzw. 59,3 h). Die Unterschiede zu den Kontrollen (t1/2 = 42,6 h) waren hochsignifikant (p<0,001). Die hepatische 99m-Tc-HIDA Ausscheidung war in allen Gruppen normal, Tiere mit einer biliodigestiven Anastomose zeigten jedoch eine ausgeprägte Stase des 99m-Tc-HIDA in der Roux-Y-Schlinge. Die intestinale Passagezeit zeigte im 51-Cr-EDTA Test vergleichbare Ergebnisse in allen Gruppen ohne signifikante Unterschiede. Die Ergebnisse demonstrieren eine erhöhte Gallensäuren-Retention bei biliodigestiven Roux-Y-Anastomosen. Ursächlich scheint dieser Störung des enterohepatischen Kreislaufs eine Stase in der Roux-Y-Schlinge zugrunde zu liegen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Aabakken L (1989) 51Cr-Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid absorption test. Methodologic aspects. Scand J Gastroenterol 24:351–358
Badley BWD, Murphy GM, Bouchier IAD (1969) Intraluminal bile-salt deficiency in the pathogenesis of steatorrhoea. Lancet 11:400–402
Bjarnason I, O'Morain C, Levi AJ, Peters TJ (1983) Absorption of 51-chromium-labeled ethylenediaminetetraacetate in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 85:318–322
Boyd GS, Merrick MV, Monks R, Thomas IL (1981) Se-75-labeled bile acid analogues, new pharmaceuticals for investigating enterohepatic circulation. J Nucl Med 22:720–725
Clintock McC, Shiau YF (1983) Jejunum is more important than terminal ileum for taurocholate absorption in rats. Am J Physiol 244:G507-G514
Coelho JCU, Pupo CA, Mathias JEF, Marchesini JC (1990) Electromyographic evaluation of the gastrointestinal tract in patients with chronic Roux-en-Y limb. Surg Gynecol Obstet 170:399–402
Ehrlein HJ, Bühner S, Thoma G, Schemann M, Kleinke O, Tsiamitas C, Schumpelick V (1987) Gastric emptying after Roux-Y and Billroth-I gastrectomy depends on viscosity of meal and contractile pattern of small intestine in dogs. Dig Dis Sci 32:529–537
Ehrlein HJ, Thoma G, Kleinke O, Tsiamitas C, Schumpelick V (1987) Effects of nutrients on gastric emptying after gastrectomy with Roux-Y gastrojejunostomy. Dig Dis Sci 32:538–546
Galatola G, Jazrawi RP, Bridges C, Joseph AEA, Northfield TC (1988) Hepatic handling of a synthetic y-labeled bile acid [75SeHCAT]. Gastroenterology 94:771–778
Jazrawi RP, Ferraris R, Bridges C, Northfield TC (1988) Kinetics for the synthetic bile acid 75 selenohomocholic acid-taurine in humans: Comparison with [14C] taurocholate. Gastroenterology 95:164–169
Jensen SL, Nielsen OV, Lenz K, Nielen ML (1978) Fat malabsorption with Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy. Surg Gynecol Obstet 147:561–564
Juste C, Legrand-Defretin V, Carring T, Rerat A (1988) Intestinal absorption of bile acids in the pig. Role of distal bowel. Dig Dis Sci 33:67–73
Krag E, Phillips SF (1974) Active and passive bile acid absorption in man. Perfusionstudies of ileum and jejunum. J Clin Invest 53:1686–1694
Mahlstedt J (1987) 75-SeHCAT-Test — Indikation und Aussagekraft in der klinischen Diagnostik. Nuklearmedizin 10:183–196
Mathias JR, Fernandez A, Sninsky CA, Clench MH, Davis RH (1985) Nausea, vomiting, and upper intestinal pain after Rouxen-Y anastomosis: Motility of the jejunal limb. Gastroenterology 88:101–107
Maxton DG, Bjarnason I, Reynolds AP, Catt SD, Peters TJ, Menzies IS (1986) Lactulose, 51-Cr-labeled ethylenediaminetetraacetate, L-rhamnose and polyethyleneglycol 500 as probe markers for assessment in vivo of human intestinal permeability. Clin Sci 71:71–80
Penagini R, Misiewicz JJ, Frost PG (1988) Effect of jejunal infusion of bile acids on small bowel transit and fasting jejunal motility in man. Gut 29:789–794
Perino LE, Adcock KA, Goff JS (1988) Gastrointestinal Symptoms, motility, and transit after the Roux-en-Y Operation. Am J Gastroenterol 83:380–385
Schiff ER, Small CN, Dietschy JM (1972) Characterization of the passive and active transport mechanisms for bile acid absorption in the small intestine and colon of the rat. J Clin Invest 51:1351–1362
Wilson FA, Dietschy JM (1972) Characterization of bile acid absorption across the unstirred water layer and brush border of the rat jejunum. J Clin Invest 51:3015–3025
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arlt, G., Bolder, U., Bares, R. et al. Erhöhte Gallensäurenretention bei biliodigestiven Roux-Y-Anastomosen im Tierexperiment. Langenbecks Arch Chir 375, 283–288 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00184169
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00184169