Abstract
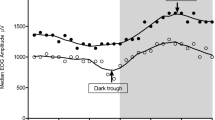
Visual evoked potentials (VEPs) were assessed under basal conditions and after photostress in normal control subjects, in insulin-dependent diabetic patients with retinopathy (IDDPWR) and in insulin-dependent diabetic patients without retinopathy (IDDP). The VEPs recorded under basal conditions showed a P100 latency significantly higher in IDDP and IDDPWR eyes than in control eyes and in IDDPWR than in IDDP eyes (P<0.01). N75-P100 amplitude was significantly lower in IDDP and IDDPWR eyes than in control eyes (P<0.01). No difference was recorded in the N75-P100 amplitudes between IDDP and IDDPWR eyes. In all eyes, the VEPs recorded after photostress showed an increase in latency and a decrease in amplitude. In both IDDPWR eyes and IDDP eyes VEPs recorded at 20, 40 and 60 s after photostress showed higher mean increments in P100 latency than in C control eyes, and IDDPWR eyes showed higher mean increments in P100 latency than IDDP eyes (IDDP vs control P<0.01, IDDPWR vs control P<0.01, IDDPWR vs IDDP P<0.017). The mean reductions in amplitude observed at 20, 40 and 60 s after photostress in IDDP and IDDPWR eyes were lower than in control eyes (IDDP vs control P=0.01, IDDPWR vs control P<0.01, IDDPWR vs IDDP P<0.01). VEPs were superimposable on the basal VEP (recovery time) at 73.9 s in control eyes, at 88.17 s in IDDP eyes and at 113.3 s in IDDPWR eyes. VEPs after photostress in IDDP patients with normal visual acuity and no fluorangiographic signs of retinopathy may show multiple modifications. This may indicate the presence of an early functional deficiency of the central retinal layers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Algan M, Ziegler O, Gehin P, Got I, Raspiller A, Weber M, Genton P, Saudax E, Drouin P (1989) Visual evoked potentials in diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 12:227–229
Arden GB, Hamilton AMP, Wilson-Holt J, Ryan S, Yudkin JS, Kurtz A (1986) Pattern electroretinograms become abnormal in the preproliferative stage: possible use as a screening test. Br J Ophthalmol 70:330–335
Armington JC (1974) The electroretinogram. Academic Press, New York
Baillart JP (1954) L'examen functionel de la macula. Rapport à la Societè d'Ophthalmologie de Paris. Bull Soc Ophtalmol Fr [Suppl] 4:I-LXVII
Bianchini E, Franchi A, Manni R, Villani LG, Cordella M, Botta GC (1987) Carotid occlusive disease: an electrophysiological macular investigation. J Cardiovasc Surg 28:524–527
Boschi MC, Frosini R, Menicucci R, Sodi A (1989) The influence of early diabetes on pattern electroretinogram. Doc Ophthalmol 71:369–374
Bresnik GH, Palta M (1987) Temporal aspects of the electroretinogram in diabetic retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 105:660–664
Bucci MG, Parisi V, Giannini R, Rossini PM (1991) Recordings of visual evoked potentials after photostress in artificially increased intraocular pressure. Clin Vis Sci 6:431–436
Cirillo D, Gonfiantini E, De Grandis D, Bongiovanni L, Robert JJ, Pinelli L (1984) Visual evoked potentials in diabetic children and adolescents. Diabetes Care 7:273–275
Collier A, Mitchell JD (1985) Visual evoked potentials and contrast sensitivity function in diabetic retinopathy. BMJ 291:248
Comi G, Martinelli V, Galardi G, Medaglini S, Poggi A, Beccaria L, Meschi F, Flores D'Arcais A (1986) Visual evoked potentials in diabetic teenagers: influence of metabolic control and relationship with peripheral neuropathy. Methods Pediatr Systems Ophthal 9:85–87
Comi G, Martinelli V, Galardi G, Medaglini S, Beccaria L, Meschi F, Rosti L, Bressani N, Chiumello G (1987) Evaluation of central nervous conduction by visual evoked potentials in insulin-dependent diabetic children. Metabolic and clinical correlation. Acta Diabetol Lat 24:157–162
Cracco J, Castells S, Mark E (1985) Spinal somatosensory evoked potentials in juvenile diabetes. Ann Neurol 15:55–58
Donald MW, Williams-Erdahl DL, Surridge DHC, Monga TN, Lawson JS, Bird CE, Latemendia FJJ (1984) Functional correlation of reduced central conduction velocity in diabetic subjects. Diabetes 33:627–633
Falsini B, Porciatti V, Scalia G, Caputo S, Minnella A, Di Leo MAS, Ghirlanda G (1989) Steady-state electroretinogram in insulin-dependent diabetics with no or minimal retinopathy. Doc Ophthalmol 73:193–200
Franchi A, Magni R, Lodigiani R, Cordella M (1987) Vep pattern after photostress: an index of macular function. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 225:291–194
Franzone M, Brunetti GM, Coggi G, Peronzini S (1985) Test del tempo di recupero maculare dopo abbagliamento: attendibilità dell'esame. Boll Oculistica 64 [Suppl 11/12]:141–151
Ghirlanda G, Di Leo MAS, Caputo S, Falsini B, Porciatti V, Marietti G, Greco AV (1991) Detection of inner retina dysfunction by steady-state focal electroretinogram pattern and flicker in early IDDM. Diabetes 9:1122–1127
Gjotteberg M (1974) The electroretinogram in diabetic retinopathy. A clinical study and critical survey. Acta Ophthalmol 52:521–533
Hollander H, Bisti S, Maffei L, Hebel R (1984) Electroretinographic responses and retrograde changes of retinal morphology after intracranial optic nerve section. Exp Brain Res 55:483–494
Klein BEK, Davis MD, Segal P (1984) Diabetic retinopathy: assessment of severity and progression. Ophthalmology 91:10–17
Lovasik JV (1983) An electrophysiological investigation of the macular photostress test. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 24:437–441
Maffei L, Fiorentini A (1981) Electroretinographic responses to alternating gratings before and after section of the optic nerve. Science 211:953–955
Maffei L, Fiorentini A (1982) Electroretinographic responses to alternating gratings in the cats. Exp Brain Res 48:327–334
Maffei L, Fiorentini A, Bisti S, Hollander H (1985) Pattern ERG in the monkey after section of the optic nerve. Exp Brain Res 59:423–425
Martinelli V, Merenda M, Natali-Sora MG, Meschi F, Beccaria L, Comi G (1987) Correlation between pattern electroretinopathy and visual evoked potentials in diabetes. Electroenceph Clin Neurophysiol 66:S64
Martinelli V, Filippi M, Meschi F, Pozza G, Canal N, Comi GC (1991) Electrophysiological study of optic pathways in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Clin Vis Sci 6:437–443
Mosci C, Polizzi A, Grillo N, Capris P, Zingirian M (1986) Ottimizzazione del test del recupero maculare nello studio dei soggetti diabetici. Boll Oculistica 65:347–356
Parisi V, Bucci MG (1992) Visual evoked potentials after photostress in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 33:436–442
Parisi V, Uccioli L, Monticone G, Carboni A, Falleni C, Ignagni T, Del Giudice R, Bucci MG (1994) Registrazioni di potenziali evocati visivi e dei potenziali oscillatori dell'elettroretinogramma fotopico in pazienti diabetici insulino-dipendenti con e senza retinopatia. Riv Med Militare (in press)
Porciatti V, von Berger GP (1983) Pattern electroretinogram and visual evoked potentials in optic nerve disease: early diagnosis and prognosis. Doc Ophthalmol Proc Ser 40:117–126
Pozzessere G, Rizzo PA, Valle E, Mollica MA, Sanarelli L, Morano S, Pietravalle P, Di Mario U, Morocutti C (1989) A longitudinal study of multimodal evoked potentials in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res 10:17–20
Puvanendran K, Davethasan G, Wong PK (1983) Visual evoked responses in diabetes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 46:543–547
Reske-Nielsen E, Lundbaek K, Rafaelsen OJ (1965) Pathological changes in the central and peripheral nervous system of young long-term diabetics. I. Diabetic encephalopathy. Diabetologica 1:223–241
Rizzo P, Carboni M, Passaro R, Parisi V, Del Giudice R, Rizzo A, Terrana P (1988) Potenziali evocati visivi da checkerboard pattern reversal: dati normativi. Riv Med Aeronautica Spaziale 2:99–105
Severin SL, Tour R, Kershaw H (1967) Macular function and the photostress test. Arch Ophthalmol 77:163–167
Simonsen SE (1975) Prognostic value of ERG (oscillatory potentials) in juvenile diabetics. Acta Ophthalmol [Suppl] 123:223–224
Trick GL, Burde RM, Gordon MO, Kilo C, Santiago JV (1988) Retinocortical conduction time in diabetics with abnormal pattern reversal electroretinogram and visual evoked potentials. Doc Ophthalmol 70:19–28
Van Der Torren K, Van Lith G (1989) Oscillatory potentials in early diabetic retinopathy. Doc Ophthalmol 71:375–379
Zingirian M, Castellazzo R, Trillo T (1968) Test del recupero maculare in soggetti normali. Standardizzazione del metodo. Boll Oculistica 47:883–848
Zingirian M, Polizzi A, Grillo N (1985) The macular recovery test after photostress in normal and diabetic subjects. Acta Diabetol Lat 22:169–172
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parisi, V., Uccioli, L., Monticone, G. et al. Visual evoked potentials after photostress in insulin-dependent diabetic patients with or without retinopathy. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 232, 193–198 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00184004
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00184004