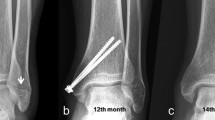
Summary
Cylindrical biodegradable rods of self-reinforced polyglycolide were constructed for internal fixation of fractures in cancellous bone. The self-reinforced texture was achieved by embedding polyglycolide fibres in a polyglycolide matrix. In a prospective clinical study, 62 patients with displaced bimalleolar fractures were managed by open reduction and internal fixation using these rods. The results were assessed between 1.1 and 3.4 years from implantation. One wound infection occurred (1.6%). Five patients (8.1%) developed a sterile accumulation of fluid at the site of operation which required drainage: the final outcome was not affected. Minor displacement of the fracture (1–2 mm) occurred in nine patients (14.5%) but did not need further operation. The functional result was excellent in 39 patients (63%). This was considered acceptable given the severity of the fractures. Consequently, at our hospital, when a displaced malleolar fracture needs internal fixation biodegradable rods are now the treatment of choice. The psychological and financial advantages of avoiding implant removal are considerable.
Résumé
Des clous cylindriques biodégradables de polyglycolide renforcé ont été mis au point pour la synthèse des fractures en os spongieux. Le renforcement de la texture a été obtenu par enrobement de fibres de polyglycolide (Dexon) dans une matrice de polyglycolide. Une étude clinique prospective de 62 patients atteints de fractures bimalléolaires déplacées, traitées par réduction à ciel ouvert et synthèse utilisant ce type de clous a été réalisée. Les résultats ont été appréciés entre 13 mois et 40 mois après implantation. Une infection a été observée (1.6%), cinq malades (8.1%) ont présenté un épanchement stérile nécessitant un drainage de la zone opératoire. Le résultat final n'en a pas été affecté. Un minime déplacement (1 à 2 mm) s'est produit dans neuf cas (14.5%) mais n'a pas nécessité de réintervention. Le résultat fonctionnel a été excellent dans 39 cas (63%) ce qui peut être considéré comme acceptable compte tenu de la gravité de ces fractures. En conséquence la fixation par clous biodégradables des fractures bimalléolaires déplacées représente pour nous le traitement de choix. L'inutilité d'une ablation de matériel présente des avantages psychologiques et financiers considérables.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Black J (1988) Editorial. Does corrosion matter? J Bone Jt Surg [Br] 70: 517–520
Bonfield W (1987) New trends in implant materials. In: Pizzoferrato A, Marchetti PG, Ravaglioli A, Lee AJ (eds) Biomaterials and clinical applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 13–21
Böstman O, Mäkelä EA, Törmälä P, Rokkanen P (1989) Transphyseal fracture fixation using biodegradable pins in children: brief report. J Bone Jt Surg [Br] 71: 706–707
Böstman O, Vainionpää S, Hirvensalo E, Mäkelä A, Vihtonen K, Törmälä P, Rokkanen P (1987) Biodegradable internal fixation for malleolar fractures. A prospective randomised trial. J Bone Jt Surg [Br] 69: 615–619
Bucknall TE (1983) Factors influencing wound complications: a clinical and experimental study. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 65: 71–77
Burwell HN, Charnley AD (1965) The treatment of displaced fractures at the ankle by rigid internal fixation and early joint movement. J Bone Jt Surg [Br] 47: 634–660
Claes L, Burri C, Kiefer H, Mutschler W (1986) Resorbierbare Implantate zur Refixierung von osteochondralen Fragmenten in Gelenkflächen. Akt Traumatol 16: 74–77
Eitenmüller J, Entenmann H, Muhr G (1988) Treatment of ankle fractures with complete biodegradable plates and screws of high molecular weight polylactide. Transactions of the Third World Biomaterials Congress. Kyoto, April 1988, p 195
Eitenmüller J, Gerlach KL, Schmickal T, Muhr G (1987) Semirigide Plattenosteosynthesen unter Verwendung absorbierbarer Polymere als temporäre Implantate. II. Tierexperimentelle Untersuchungen. Chirurg 58: 831–839
Gammelgaard N, Jensen J (1983) Wound complications after closure of abdominal incisions with Dexon or Vicryl. A randomized double-blind study. Acta Chir Scand 149: 505–508
Greve H, Holste J (1985) Refixation osteochondraler Fragmente durch resorbierbare Kunststoffstifte. Akt Traumatol 15: 145–149
Haas HG (1986) PDS-Splinte zur Frakturbehandlung. Handchirurgie 18: 295–297
Herrmann JB, Kelly RJ, Higgins GA (1970) Polyglycolic acid sutures. Laboratory and clinical evaluation of a new absorbable suture material. Arch Surg 100: 486–490
Hirvensalo E, Böstman O, Vainionpää S, Törmälä P, Rokkanen P (1988) Biodegradable fixation in intraarticular fractures of the elbow joint. Acta Orthop Scand 59 (Suppl 227): 78–79
Hollinger JO, Battistone GC (1986) Biodegradable bone repair materials. Synthetic polymers and ceramics. Clin Orthop 207: 290–305
Joy G, Patzakis MJ, Harvey JP (1974) Precise evaluation of the reduction of severe ankle fractures. Technique and correlation with end results. J Bone Jt Surg [Am] 56: 979–993
Lange DA, Zaret P, Merlotti GJ, Robin AP, Sheaff C, Barrett JA (1988) The use of absorbable mesh in splenic trauma. J Trauma 28: 269–273
Lauge-Hansen N (1952) Fractures of the ankle. IV. Clinical use of genetic roentgen diagnosis and genetic reduction. Arch Surg 64: 488–500
Leenslag JW, Pennings AJ, Bos RRM, Rozema FR, Boering G (1987) Resorbable materials of poly(L-lactide). VI. Plates and screws for internal fracture fixation. Biomaterials 8: 70–73
Lindsjö U (1985) Operative treatment of ankle fracture-dislocations. A follow-up study of 306/321 consecutive cases. Clin Orthop 199: 28–38
Mäkelä EA, Vainionpää S, Vihtonen K, Mero M, Laiho J, Törmälä P, Rokkanen P (1987) The effect of a penetrating biodegradable implant on the epiphyseal plate: an experimental study on growing rabbits with special regard to polyglactin 910. J Pediatr Orthop 7: 415–420
Mast JW, Teipner WA (1980) A reproducible approach to the internal fixation of adult ankle fractures: rationale, technique, and early results. Orthop Clin North Am 11: 661–679
Niederdellmann H, Bührmann K (1983) Resorbierbare Osteosyntheseschrauben aus Polydioxanon (PDS). Dtsch Z Mund-Kiefer-Gesichts-Chir 7: 399–400
Partio EK, Böstman O, Vainionpää S, Pätiälä H, Hirvensalo E, Vihtonen K, Törmälä P, Rokkanen P (1988) The treatment of cancellous bone fractures with biodegradable screws. Acta Orthop Scand 59 [Suppl 227]: 18
Pettrone FA, Gail M, Pee D, Fitzpatrick T, van Herpe LB (1983) Quantitative criteria for prediction of the results after displaced fracture of the ankle. J Bone Jt Surg [Am] 65: 667–677
Phillips WA, Schwartz HS, Keller CS, Woodward HR, Rudd WS, Spiegel PG, Laros GS (1985) A prospective, randomized study of the management of severe ankle fractures. J Bone Jt Surg [Am] 67: 67–78
Rokkanen P, Böstman O, Hirvensalo E, Vainionpää S, Törmälä P (1988) Three years' audit of biodegradable osteofixation in orthopedic surgery. Acta Orthop Scand 59 [Suppl 227]: 18–19
Rokkanen P, Böstman O, Vainionpää S, Vihtonen K, Törmälä P, Laiho J, Kilpikari J, Tamminmäki M (1985) Biodegradable implants in fracture fixation: early results of treatment of fractures of the ankle. Lancet 1: 1422–1424
Sedel L, Chabot F, Christel P, de Charentenay X, Leray J, Vert M (1978) Les implants biodégradables en chirurgie orthopédique. Rev Chir Orthop 64 [Suppl II]: 92–96
Skirving AP, Day R, Macdonald W, McLaren R (1987) Carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CRFP) plates versus stainless steel dynamic compression plates in the treatment of fractures of the tibiae in dogs. Clin Orthop 224: 117–124
Slätis P, Karaharju E, Holmström T, Ahonen J, Paavolainen P (1978) Structural changes in intact tubular bone after application of rigid plates with and without compression. J Bone Jt Surg [Am] 60: 516–522
Søndenaa K, Høigaard U, Smith D, Alho A (1986) Immobilization of operated ankle fractures. Acta Orthop Scand 57: 59–61
Starker M, Zichner L (1986) Untersuchungen an Korrosionsprodukten nach Osteosynthesen. Z Orthop 124: 523–526
Tayton K, Bradley J (1983) How stiff should semi-rigid fixation of the human tibia be? A clue to the answer. J Bone Jt Surg [Br] 65: 312–315
Törmälä P, Vainionpää S, Pellinen M, Heponen VP, Laiho J, Tamminmäki M, Mikkola J, Rokkanen P (1988) Totally biodegradable polymeric self-reinforced (SR) rods and screws for fixation of bone fractures. Transactions of the Third World Biomaterials Congress. Kyoto, April 1988, p 501
Tunc DC, Rohovsky MW, Zadwadsky JP, Spieker JE, Strauss ED (1986) Evaluation of body absorbable screw in avulsion type fractures. Transactions of the 12th Annual Meeting of the Society for Biomaterials. Minneapolis St Paul, May 1986, p 168
Uhthoff HK, Dubuc FL (1971) Bone structure changes in the dog under rigid internal fixation. Clin Orthop 81: 165–170
Vainionpää S, Vihtonen K, Mero M, Pätiälä H, Rokkanen P, Kilpikari J, Törmälä P (1986) Fixation of experimental osteotomies of the distal femur of rabbits with biodegradable material. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 106: 1–4
Vihtonen K, Vainionpää S, Mero M, Pätiälä H, Rokkanen P, Kilpikari J, Törmälä P (1987) Fixation of experimental osteotomy of the distal femur with biodegradable thread in rabbits. Clin Orthop 221: 297–303
Vert M, Christel P, Chabot F, Leray J (1984) Bioresorbable plastic materials for bone surgery. In: Hastings GW, Ducheyne P (eds) Macromolecular biomaterials. CRC Press, Boca Raton Florida, pp 120–142
Weber BG (1972) Die Verletzungen des oberen Sprung-gelenkes. 2. Auflage. Hans Huber Verlag, Bern Stuttgart Wien
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Böstman, O., Hirvensalo, E., Vainionpää, S. et al. Degradable polyglycolide rods for the internal fixation of displaced bimalleolar fractures. International Orthopaedics 14, 1–8 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00183354
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00183354