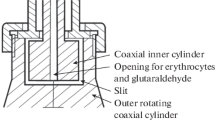
Abstract
Reversible aggregation of erythrocytes was investigated after alteration of the phospholipid content in the membrane outer leaflet either by disturbance of endogenous transmembrane lipid asymmetry through changes in cellular free calcium, or by incorporation of exogenous lyso-derivatives. It was found that both calcium loading and lyso-phosphatidylcholine (LPC) addition induce a strong increase in red cell-red cell adhesive energy, whereas lyso-phosphatidylserine (LPS), added in the same amount as LPC, does not. Red cell morphological studies show differences in the shape change efficiency of LPS, LPC and calcium loading. However, it was further demonstrated that shape change is not directly responsible for the observed adhesive energy increase, since neuraminidase or trypsin treatment abolish this increase, even though the shape changes induced by alteration of phospholipid organization are not affected. The latter experiment strongly suggests that the red cell adhesive energy increase results from an alteration of the glycocalyx structure, which could be in turn a consequence of the shape change.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Hepes:
-
4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethane-sulfonic acid
- EGTA:
-
(Ethylenebis(oxyethylenenitrilo)tetraacetic acid)
- DMSO:
-
dimethyl-sulfoxide
References
Bergmann WL, Dressler V, Haest CWM, Deuticke B (1984) Reorientation rates and asymmetry of distribution of lyso-phospholipids between the inner and outer leaflet of the erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta 772: 328–336
Bierbaum TJ, Bouma SR, Huestis WH (1979) A mechanism of erythrocyte lysis by lysophosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta 555: 102–110
Bitbol M, Fellmann P, Zachowski A, Devaux PF (1987) Ion regulation of phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine outside-inside translocation in human erythrocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta 904: 268–282
Brooks DE (1973) The effect of neutral polymers on the electrokinetic potential of cells and other charged particles. IV. Electrokinetic effect in dextran-mediated cellular interaction. J Colloid Interface Sci 43: 714–726
Cevc G, Marsh D (1987) Phospholipid bilayers. Physical principles and models. Wiley, New York
Chandra R, Joshi PC, Bajpai VK, Gupta CM (1987) Membrane phospholipid organization in calcium-loaded human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 902: 253–262
Chien S, Jan KM (1973) Ultrastructure basis of the mechanisms of rouleaux formation. Microvasc Res 5: 155–161
Chien S, Sung LA, Kim S, Burke AM, Usami S (1984) Quantitation of red cell aggregation under shear flow. Ann NY Acad Sci 416: 190–206
Daleke DL, Huestis WH (1985) Incorporation and translocation of amino-phospholipids in human erythrocytes. Biochemistry 24: 5406–5416
Fahraeus R (1929) The suspension stability of blood. Physiol Rev 9: 241–258
Friederichs E, Germs J, Lakomek M, Winkler H, Tillmann W (1984) Increased erythrocyte aggregation in infectious diseases: Influence of “acute phase proteins”. Clin Hemorheol 4: 237–244
Gast AP, Leibler L (1986) Interactions of sterically stabilized particules suspended in a polymer solution. Macromolecules 19: 686–691
Hubbell WL, McConnell HM (1971) Molecular motion in spin label phospholipids and membranes. J Am Chem Soc 93: 314–326
Malher E, Martin D, Duvivier C, Volochine B, Stoltz JF (1983) Les méthodes d'électrophorèse des cellules. In: Stoltz JF (ed) Techniques avancées en hémorhéologie, 603–623, DPIC-INPL, Nancy, France
Marikovski Y, Khodadad JK, Weinstein RS (1978) Influence of red cell shape on surface charge topography. Exp Cell Res 116: 191–197
Marikovski Y, Weinstein RS, Skutelsky E, Danon D (1985) Changes of cell shape and surface charge topography in ATP-depleted human red blood cells. Mech Ageing Dev 29: 309–316
McEvoy L, Williamson P, Schlegel RA (1986) Membrane phospholipid asymmetry as a determinant of erythrocyte recognition by macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci 83: 3311–3315
Meiselman HJ (1978) Rheologie of shape transformed human red cells. Biorheology 15: 225–237
Mills P, Snabre P (1983) Agrégamétrie optique de la suspension sanguine. In: Stoltz JF (ed) Techniques avancées en hémo-rhéologie, 580–598, DPIC-INPL, Nancy, France
Mills P, Quemada D, Dufaux J (1980) Etude de la cinétique d'agrégation érythrocytaire dans un écoulement de Couette. Rev Phys Appl 15: 1357–1366
Mohandas N, Evans EA (1984) Adherance of sickle erythrocytes to cells. Requirement for both cell membrane changes and plasma factors. Blood 64: 282–287
Othmane A, Bitbol M, Snabre P, Thiam B, Mills P (1986) Etude comparative de l'agrégation érythrocytaire chez deux sujets ayant un groupe sanguin différent. Innov Tech Biol Med 7: 76–81
Othmane A, Bitbol M, Snabre P, Grimaldi A, Bosquet F (1989) Red-cell aggregation in insulin-dependent diabetics. Clin Hemorheol 9: 281–295
Schlegel RA, Williamson P (1987) Membrane phospholipid organization as a determinant of blood cell-reticuloendothelial cell interactions. J Cell Physiol 132: 381–384
Schlegel RA, Prendergast TW, Williamson P (1985) Membrane phospholipid asymmetry as a factor in erythrocyte-endothelial cell interactions. J Cell Physiol 123: 215–218
Schwartz RS, Tanaka Y, Fidler IJ, Tsun-Yee Chu D, Lubin B, Schroit AJ (1985) Increased adherance of sickled and phosphatidylserine enriched human erythrocyte to cultured human peripheral blood monocytes. J Clin Invest 75: 1965–1972
Seigneuret M, Devaux PF (1984) ATP-dependent asymmetric distribution of spin-labeled phospholipids in the erythrocyte membrane: Relation to shape changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 3751–3755
Sheetz MP, Singer SJ (1974) Biological membranes as bilayer couples. A molecular mechanism of drug-erythrocyte interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71: 4457–4461
Snabre P, Mills P (1985) Effect of dextran polydispersity on red cell aggregation. Colloid Polym Sci 263: 478–483
Snabre P, Mills P (1986a) Effect of dextran polymer on glycocalyx structure and cell electrophoretic mobility. Colloid Polym Sci 263: 494–500
Snabre P, Mills P (1986b) Role des interactions électrostatiques dans les phénomènes d'agrégation érythrocytaire. In: Stoltz JF (ed) Hémorhéologie et agrégation érythrocytaire. Editions médicales internationales. Paris, pp 98–110
Snabre P, Bitbol M, Mills P (1987) Cell disaggregation behavior in shear flow. Biophys J 51: 795–807
Snabre P, Mills P, Othmane A, Thiam BA (1989) Mechanisms of non specific aggregation and rheology of concentrated red blood suspension. Biorheology (in press)
Tilley D, Coakley WT, Gould RK, Hewison LA (1987) Real time observations of polylysine, dextran and polyethylene glycol induced mutual adhesion of erythrocytes held in suspension in an ultrasonic standing wave field. Eur Biophys J 14: 499–507
Verkleij AJ, Zwaal RFA, Roelofsen B, Comfurius P, Kastelijn D, Van Deenen LLM (1973) The asymmetry distribution of phospholipids in the human red-cell membrane. A combined study using phospholipases and freeze-etching electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 323: 178–193
Warren L (1959) The thiobarbiturie acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem 234: 1972–1975
Weed RI, Chailley B (1973) Calcium-pH interactions in the production of shape change in erythrocytes. In: Bessis M, Weed RI, Leblond PF (eds) Red cell shape, physiology, pathology, ultrastructure. Springer, New York Berlin Heidelberg, pp 55–67
Williamson P, Algarin L, Bateman J, Choe HR, Schlegel RA (1985) Phospholipid asymmetry in human erythrocyte ghosts. J Cell Physiol 123: 209–214
Zachowski A, Favre E, Cribier S, Hervé P, Devaux PF (1986) Outside-Inside translocation of aminophospholipids in the human erythrocyte membrane is mediated by a specific enzyme. Biochemistry 25: 2585–2590
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: A. Othmane
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Othmane, A., Bitbol, M., Snabre, P. et al. Influence of altered phospholipid composition of the membrane outer layer on red blood cell aggregation: relation to shape changes and glycocalyx structure. Eur Biophys J 18, 93–99 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00183268
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00183268