Summary
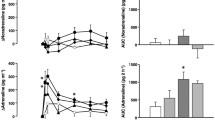
Plasma noradrenaline and adrenaline concentrations, plasma renin concentration (PRC), and serum and brain yohimbine concentrations were measured in conscious Sprague-Dawley rats after the s. c. and i. v. injection of yohimbine. The s.c. and i.v. administration of 1 and 3 mg/kg of yohimbine (30 min post-injection) elicited equivalent and dose-related increases in plasma noradrenaline concentration. At 30 min post-injection, the 1 mg/kg dose given s. c. or i. v. did not increase plasma adrenaline concentration or PRC, whereas the 3 mg/kg dose caused comparable increases in plasma adrenaline concentration and PRC when given s. c. or i. v. Brain yohimbine concentration increased in a dose-related manner whereas serum yohimbine concentration was not significantly different 30 min after treatment with the 1 and 3 mg/kg doses regardless of the route of injection. Despite the fact that serum yohimbine concentration was 5-fold greater after i. v. injection as compared to s. c. administration (1 and 3mg/kg doses), brain yohimbine concentrations were comparable after s. c. and i. v. injection and thus not dependent on either the route of administration or serum yohimbine concentration. The fact that the s. c. and i. v. injection of yohimbine lead to comparable dose-related increases in both brain yohimbine concentrations and neuroendocrine responses suggests that increased sympathetic outflow resulted primarily from an action of yohimbine at central, rather than peripheral, a2-adrenoceptors. However, the data also are consistent with a purely peripheral prejunctional action of the 1 mg/kg dose and a combined central and peripheral action of the 3 mg/kg dose.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andén NE, Grabowska M, Strömbom U (1976) Different alpha-adrenoceptors in the central nervous system mediate biochemical and functional effects of clonidine and receptor blocking agents. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 292:43–52
Drew GM, Gower JA, Marriott AS (1979) α2-Adrenoceptors mediate clonidine-induced sedation in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 67:133–141
Goldberg MR, Robertson D (1983) Yohimbine: A pharmacological probe for study of the α2-adrenoceptor. Pharmacol Rev 35:143 -180
Graham RM, Stephenson WH, Pettinger WA (1980) Pharmacological evidence for a functional role of the presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor in noradrenergic neurotransmission in the conscious rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 311:129–138
Haeusler G (1974) Clonidine-induced inhibition of sympathetic nerve activity: No indication for a central presynaptic or an indirect sympathomimetic mode of action. NaunynSchmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 286:97–111
Hubbard JW, Pfister SL, Biediger AM, Herzig TC, Keeton TK (1988) The pharmacokinetic properties of yohimbine in the conscious rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337:583–587
Keeton TK, Biediger AM (1989) The differential effects of prazosin and hydralazine on sympathoadrenal activity in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol 164:479–486
Kobinger W, Pichler L (1980) Investigation into different types of post- and presynaptic α-adrenoceptors at cardiovascular sites in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 65:393–402
Lambert GA, Lang WJ, Friedman E, Meller E, Gershon S (1978) Pharmacological and biochemical properties of isomeric yohimbine alkaloids. Eur J Pharmacol 49:39–48
Majewski H, L. Hedler L, Starke K (1983) Modulation of noradrenaline release in the conscious rabbit through-α-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol 93:255–264
Pfister SL, Keeton TK (1988) The mechanism of yohimbine-induced renin release in the conscious rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337:35–46
Ramage AG, Tomlinson A (1985) The effect of yohimbine, WY 26392 and idazoxan on sympathetic nerve activity. Eur J Pharmacol 109:153–160
Rockhold RW, Gross F (1981) Yohimbine diastereoisomers: Cardiovascular effects after central and peripheral application in the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 315:227–231
Sharma TR, Wakade TD, Malhorta RK, Wakade AR (1986) Secretion of catecholamines from the perfused adrenal gland of the rat is not regulated by α-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol 122:167–172
Starke K, Borowski E, Endo T (1975) Preferential blockade of presynaptic α-adrenoceptors by yohimbine. Eur J Pharmacol 34:385–388
Szabo B, Hedler L, Starke K (1989) Peripheral presynaptic and central effects of clonidine, yohimbine and rauwolscine on the sympathetic nervous system in rabbits. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 340:648–657
Weitzell R, Tanaka T, Starke K (1979) Pre- and postsynaptic effects of yohimbine stereoisomers on noradrenergic transmission in the pulmonary artery of the rabbit. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 308:127–136
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to T. Kent Keeton at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuo, YJ.J., Keeton, T.K. Is the sympathoexcitatory effect of yohimbine determined by brain yohimbine concentration?. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 344, 308–313 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00183005
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00183005