Abstract
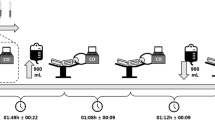
Experimental studies have suggested that dipyridamole may inhibit red blood cell labelling with technetium-99m. To evaluate whether this effect is clinically relevant to the performance of radionuclide ventriculography after dipyridamole-thallium stress testing, in vitro red blood cell labelling was compared immediately before and after thallium-201 stress scintigraphy combined with either dipyridamole infusion (30 patients) or exercise stress (20 patients). Modified in vivo red blood cell labelling efficiency was assessed in a further 36 patients following dipyridamole infusion and was compared with that in 15 patients following exercise stress. The importance of a reversal of the dipyridamole effects by aminophylline was evaluated for in vitro and modified in vivo techniques. The red blood cell labelling efficiency was not significantly different in patients following dipyridamole compared with that obtained following exercise stress for both in vitro (93% ± 4% versus 91% ± 4%) and modified in vivo (87% ± 19% versus 90% ± 6%) techniques. Also, in vitro red blood cell labelling efficiency after dipyridamole was not different to that before stress testing (93% ± 4% versus 92% ± 4%). Reversal with aminophylline had no significant effect on the in vitro labelling efficiency with either the in vitro technique (94% ± 3% with reversal versus 92% ± 5% without) or the modified in vivo technique (91% ± 4% with reversal versus 82% ± 26% without). These results suggest that the red blood cell labelling efficiency is not compromised by the preceding dipyridamole-thallium stress testing but can be optimised by using in vitro labelling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boucher CA, Brewster DC, Darling RC, Okada RD, Strauss HW, Pohost GM (1985) Determination of cardiac risk by dipyridamole-thallium imaging before peripheral vascular surgery. N Engl J Med 312:389–394
Callahan RJ, Rabito CA (1991) Radiolabeling of erythrocytes with technetium-99m: role of band-3 protein in the transport of pertechnetate across the cell membrane. J Nucl Med 31:2004–2010
Callahan RJ, Froelich JW, McKusick KA, Leppo J, Strauss HW (1982) A modified method for the in vito labelling of red blood cells with Tc-99m: concise communication. J Nucl Med 23:315–318
Deuticke B (1968) Transformation and restoration of biconcave shape of human erythrocytes induced by amphophilic agents and changes of ionic environment. Biochim Biophys Acta 163:494–500
Eagle KA, Coley CM, Newell JB, Brewstrauss HW, Boucher CA (1989) Combining clinical and thallium data optimized preoperative assessment of cardiac risk before major vascular surgery. Ann Intern Med 110:859–866
Goldman L, Caldera DL, Nussbaum SR, et al. (1977) Multifactorial index of cardiac risk in noncardiac surgical procedures. N Engl J Med 297:845–850
Leppo J, Plaja C, Gionet M, Tumolo J, Paraskos JA, Cutler BS (1987) Noninvasive evaluation of cardiac risk before elective vascular surgery. J Am Coll Cardiol 9:269–276
Mahony C, Wolfram KM, Cocchetto DM, Bjornsson TD (1982) Dipyridamole kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 31:330–338
Porter WC, Dees SM, Freitas JE, Dworkin HJ (1983) Acid-citrate-dextrose compared with heparin in the preparation of in vivo/in vitro technetium-99m red blood cells. J Nucl Med 24:383–387
Rehani MM, Sharma SK (1980) Site of Tc-99m binding to the red blood cell: concise communication. J Nucl Med 21:676–678
Schnell KF (1972) On the mechanism of inhibition of the sulfate transfer across the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta 282:265–276
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: R.J. Hicks
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hicks, R.J., Eu, P. & Barry Arkles, L. Efficiency of labelling of red blood cells with technetium-99m after dipyridamole infusion for thallium-201 stress testing. Eur J Nucl Med 19, 1050–1053 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180867
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180867