Abstract
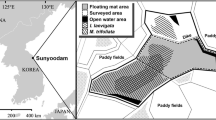
Floating marshes occur over 70% of the western Terrebonne Basin, Louisiana, USA, freshwater coastal wetlands. They are of several types: A free-floating thick-mat (45–60 cm) marsh dominated by Panicum hemitomon and Sagittaria lancifolia; a thick mat marsh dominated by Panicum hemitomon and Sagittaria lancifolia that floats part of the year, but whose vertical floating range is damped compared to adjacent water; and an irregularly-floating thin mat (< 30 cm) dominated by Eleocharis spp. in the spring and Ludwigia leptocarpa and Bidens laevis in the summer and fall. Floating mats must be almost entirely organic in order to be buoyant enough to float. The western Terrebonne wetlands receive large winter/spring supplies of suspended sediments from the Atchafalaya River. Even though sediment concentrations in the adjacent bayou are as high as 100 mg l−1, the Panicum hemitomon/Sagittaria lancifolia free-floating marsh probably receives no over-surface sediments since it floats continuously. The bulk density data of the damped-floating marsh, however, suggest some mineral sediment input, probably during winter when this marsh is submerged. These two types of floating marsh could not have developed in the present sediment regime of the Atchafalaya River, but as long as they remain floating can continue to exist. Thin floating mats are found in areas receiving the least sediment (<20 mg 1−1 suspended sediment concentration in adjacent bayous). This low sediment environment probably made possible their formation within the past 20 years. They may represent a transitional stage in mat succession from (1) existing thick-mat floating marsh to a degrading floating marsh, or (2) a floating marsh developing in shallow open water.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumann, R.H., and Adams, R.D. 1981. Remote sensing as a tool to determine probable impacts of flood control and navigation structures on wetland restoration in the lower Atchafalaya system. Estuaries 4 (3): 267 (Abstract).
Baumann, R.H., Day, J.W., and Miller, C.A. 1984. Mississippi deltaic wetland survival: sedimentation versus coastal submergence. Science 224: 1093–1095.
Beadle, L.C. 1974. Hydrobiological investigations on tropical swamps. Verh. Internat. Ver. Limnol. 13: 855–857.
Britsch, L.D., and Kemp, E.B. 1990. Land loss rates: Mississippi River Deltaic Plain. Technical Report GL-90–2. US Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station, Vicksburg, MS.
Butler, T.J.B. 1975. Aquatic metabolism and nutrient flux in a south Louisiana swamp and lake system. M.S. thesis. Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge. 58 p.
Chabreck, R.H., Pilcher, B.K., and Ensminger, A.B. 1983. Growth, production, and wildlife use of delta duck potatoes in Louisiana. Thirty-seventh annual conference of the Southeastern Association of Fish and Wildlife Agencies.
Correll, D.S. and Correll, H.B. 1975. Aquatic and wetland plants of southwestern United States, Vols. I and II. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California, USA.
Cypert, E. 1972. The origin of houses in the Okefenokee prairies. American Midland Naturalist 87: 448–458.
Delaune, R.D., Smith, C.J., Patrick Jr., W.H., and Roberts, H.H. 1987. Rejuvenated marsh and bay-bottom accretion on the rapidly subsiding coastal plain of the U.S. Gulf coast: a second-order effect of the emerging Atchafalaya delta. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 25: 381–389.
Delaune, R.D., Baumann, R.H., and Gosselink, J.G. 1983. Relationships among vertical accretion, coastal submergence, and erosion in a Louisiana Gulf coast marsh. J. Sed. Petrology 553: 147–157.
Donnell, B.P., and Letter Jr., J.V. 1992. Two-dimensional modeling of alternative plans and impacts on the Atchafalaya Bay and Terrebonne marshes. U.S. Dept Army Engineers, Waterways Experiment Station, Vicksburg, MS. Tech. Report HL-82–15. 46 p. and 68 plates.
Dunbar, J.B., Britch, L.D. and Kemp, E.B. 1992. Land loss rates: Louisiana Coastal Plain. Report 3, Technical Report GL-90–2, US Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station, Vicksburg, MS.
Ellery, K., Ellery, W.N., Rogers, K.H., and Walker, B.H. 1990. Formation, colonization and fate of floating sudds in the Maunachira river system of the Okavango Delta, Botswana. Aquatic Botany 38: 315–329.
Evers, D.E., Gosselink, J.G., Sasser, C.E., and Hill, J.M. 1992. Wetland loss dynamics in southwestern Barataria basin, Louisiana (USA), 1945–1985. Wetlands Ecology and Management 2: 103–118.
Evers, D.E., Sasser, C.E., Gosselink, J.G., Fuller, D.A., and Visser, J.M. (In review) The impact of vertebrate herbivores on wetland vegetation in Atchafalaya Bay, Louisiana.
Feijtel, T.C. 1986. Biochemical cycling of metals in Barataria Basin. Ph.D. Dissertation, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge. 279 p.
Fuller, D.A., Sasser, C.E., Johnson, W.B., and Gosselink, J.G. 1985. The effects of herbivory on vegetation on islands in Atchafalaya Bay, Louisiana. Wetlands 4: 105–114.
Gagliano, S.M. and van Beek, J.L. 1970. Geologic and geomorphic aspects of deltaic processes. Mississippi delta system. Hydrologic and Geologic Studies of Coastal Louisiana Report No. 1. Coastal Studies Institute, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, USA.
Gagliano, S.M., Meyer-Arendt, K.J. and Wicker, K.M. 1981. Land loss in the Mississippi River Deltaic Plain. Trans. Gulf Coast Assoc. Geological Societies 31: 295–300.
Gaudet, J. 1976. Nutrient relationships in the detritus of a tropical swamp. Arch. Hydrobiol. 78: 213–239.
Gaudet, J.J. 1977. Uptake, accumulation, and loss of nutrients by papyrus in tropical swamps. Ecology 58: 415–422.
Gaudet, J.J. 1982 Nutrient dynamics of papyrus swamps. In: Wetlands Ecology and Management, National Institute of Ecology and International Scientific Publications, Jaipur, India. Edited by B. Gopal, R.E. Turner, R.G. Wetzel, and D.F. Whigham. pp. 305–319.
Gosselink, L. 1984. Hydrology and the effects of canals in western Terrebonne Parish marsh, Louisiana. M. S. thesis, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, USA.
Hogg, E.H. and Wein, R.W. 1988a. Seasonal change in gas content and buoyancy of floating Typha mats. Journal of Ecology 76: 1055–1068.
Hogg, E.H., and Wein, R.W. 1988b. The contribution of Typha components to floating mat bouyancy. Ecology 69: 1025–1031.
Hopkinson, C.S., and Day, J.W. 1979. Aquatic productivity and water quality at the upland-estuary interface in Barataria Basin, Louisiana. In: R. Livingston (ed), Ecological Processes in Coastal and Marine Systems. Plenum Press, New York, N.Y., pp. 291–314.
Huffman, R., and Lonard, R. 1983. Successional patterns on floating vegetation mats in a southwestern Arkansas cypress swamp. Castanea 48: 73–78.
Junk, W. 1970. Investigations on the ecology and production biology of the floating meadows (Paspalo-Echinochloetum) on the Middle Amazon. i. The floating vegetation and its ecology. Amazoniana 2: 449–495.
Junk, W.J., and Howard-Williams, C. 1984. Ecology of aquatic macrophytes in Amazonia. In: H. Sioli (ed), The Amazon limnology and landscape ecology of a mighty tropical river and its basin. Dr. W. Junk Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands. pp. 267–291.
Kinler, N.W., Linscombe, G.L., and Chabreck, R.H. 1980. Smooth beggartick: its distribution, control, and impact on nutria in coastal Louisiana. In: Proc. Worldwide Furbearer Conf., Frostburg State College, Frostburg, MD.
Migahid, A.M. 1947. An ecological survey of the “Sudd” swamps of the Upper Nile. Proceedings of the Egyptian Academy of Sciences 3: 57–86.
Nyman, J.A., Delaune, R.D., and Patrick, W.H., Jr. 1990. Wetland soil formation in the rapidly subsiding Mississippi River Deltaic Plain: mineral and organic matter relationships. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 31: 57–69.
O'Neil, T. 1949. The muskrat in the Louisiana coastal marshes. Louisiana Wildlife and Fisheries Commission, New Orleans, LA, USA.
Pallis, M. 1915. The structure and history of Plav: the floating fen of the delta of the Danube. Linnaean Journal of Botany 43: 233–290.
Rejmanek, M., Sasser, C.E., and Peterson, G.W. 1988. Hurricane-induced sediment deposition in a Gulf coast Marsh. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 27: 217–222.
Rodewald-Rudescu, L. 1974. Das Schilfrohr. Die Binnengewasser 27. Schwiezerbartsche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Stuttgart
Russell, R.J. 1942. Flotant. Geographical Review 32: 74–98.
Rzoska, J. 1974. The Upper Nile swamps, a tropical wetland study. Freshwater Biology. 4: 1–30.
SAS Institute, Inc. 1985. SAS User's Guide: Statistics, Version 5. SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, North Carolina.
Sasser, C.E. and Gosselink, J.G. 1984. Vegetation and primary production in a floating freshwater marsh in Louisiana. Aquatic Botany 20: 245–255.
Sasser, C.E., Dozier, M.D., Gosselink, J.G. and Hill, J.M. 1986. Spatial and temporal changes in Louisiana's Barataria basin marshes. 1945–1980. Environmental Management 10: 671–680.
Sasser, C.E., Gosselink, J.G., Evers, D.E., and Visser, J.M. In press. The colonization and development of vegetation in the Atchafalaya delta, Louisiana. In:: J.W. Day Jr. (ed), Dynamics of a shallow deltaic system: the Atchafalaya Delta region. American Geophysics Union.
Sasser, C.E., Gosselink, J.G., Swenson, E.M., Swarzenski, C.M. and Leibowitz, N.C. (manuscript). Vegetation, substrate, and hydrology in floating marshes in the Mississippi River Delta Plain wetlands, USA: a basis for classification.
Seaton, A.M. 1979. Nutrient chemistry in the Barataria basin — a multivariate approach. M.S. thesis, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge. 124 p.
Stern, M.K., Day, J.W., Jr., and Teague, K.G. 1986. Seasonality of materials transport through a coastal freshwater marsh: riverine vs. tidal forcing. Estuaries 9: 301–308.
Stern, M.K., Day Jr., J.W., and Teague, K.G. 1991. Nutrient transport in a riverine-influenced, tidal freshwater bayou in Louisiana. Estuaries 14: 382–394.
Swarzenski, C.M., Swenson, E.M., Sasser, C.E. and Gosselink, J.G. 1991. Marsh mat flotation in the Louisiana delta plain. Journal of Ecology 79: 999–1011.
Swenson, E.M., Baumann, R.H., and Adams, R.D. 1981. Water and sediment flux in the northern Terrebonne marshes. Louisiana State Univ., Center for Wetland Resources, Baton Rouge. Unpubl. Report.
Taylor, N.C. 1985. Ecological characterization of Jean Lafitte National Historical Park, Louisiana: Basis for a management plan. M.S. thesis, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, USA.
Thompson, K. 1976. Swamp development in the head waters of the White Nile. In: J. Rzoska (ed), The Nile, Biology of an Ancient River. W. Junk Publishers, The Hague, pp. 177–196.
Thompson, K. 1985. Emergent plants of permanent and seasonally flooded wetlands. In: P. Denny (ed), The Ecology and Management of African Wetlands. Dr. W. Junk, The Hague. pp. 43–107.
Tyler, P.A. 1976. Lagoon of Islands, Tasmania — Death knell for a unique ecosystem? Biological Conservation. 9: 2–11.
U.S. Geological Survey. 1982. Water quality of the Barataria unit, Jean Lafitte National Historical Park, Louisiana (April 1981–March 1982). U.S. Department of Interior, Geological Survey. Open-File Report 82-691.
Verhoeven, J.T.A. 1992. Fens and bogs in the Netherlands: Vegetation, History, Nutrient Dynamics, and Conservation. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Wang, F.C. 1987. Effects of levee extension on marsh flooding. Journal of Water Resource Planning Management 113: 161–176.
Wang, F.C., Wei, J.S., and Amft, J.A. 1985. Computer simulation of western Terrebonne Parish marsh hydrology and hydrodynamics. Technical Report, Sea Grant publication, Center for Wetland Resources, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, USA.
Wang, F.C., Liu, T., and Sikora, W.B. 1993. Intertidal marsh suspended sediment transport processes, Terrebonne Bay, Louisiana, U.S.A. Journal of Coastal Research 9: 209–220.
Wheeler, B.D. 1980. Plant communites of rich-fen systems in England and Wales. I. Introduction. Tall sedge and reed communities. Journal of Ecology 68: 365–395.
Zimmerli, V. 1988. Vegetation and site conditions of floating mats in Switzerland. Veroffentlichungen des Geobotanischen Institutes der ETH, Stiftung Rubel, Zurich, 102, Heft. p. 99.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Corresponding editor: D. Whigham
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasser, C.E., Gosselink, J.G., Swenson, E.M. et al. Hydrologic, vegetation, and substrate characteristics of floating marshes in sediment-rich wetlands of the Mississippi river delta plain, Louisiana, USA. Wetlands Ecol Manage 3, 171–187 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180023
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180023