Abstract
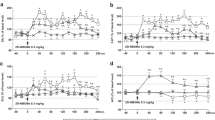
Conditioning of behavioural effects produced by two drugs acting differently upon dopaminergic neurotransmission was studied. Nomifensine and the putative dopamine autoreceptor agonist B-HT 920 produce contrasting effects on motility, namely increases in locomotor activity and stereotypies as compared to hypokinesia and ptosis. The administration of each of these drugs (US) was repeatedly associated with well-defined environmental stimuli (CS): a wire cage associated with an auditory and on olfactory stimulus. The rats were conditioned for 7 days with 20 mg/kg nomifensine IP each day. After conditioning, the rats were treated with the solvent alone in presence of the CS. Not only did sniffing and licking occur, but also gnawing, even though the latter response was not evident after acute administration of the drug or during the conditioning period. Nomifensine (20 mg/kg IP) also acutely decreased the ratio of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid/dopamine concentrations (DOPAC/DOPAMINE); this ratio was not altered in the conditioned rats, 60 min after solvent administration in presence of the CS. Rats were conditioned with 0.02 mg/kg IP B-HT 920 daily for 8 days. During the conditioning phase, akinesia and ptosis showed a slight enhancement and a faster onset. After conditioning, when the rats were treated with the solvent alone, the majority of them showed akinesia and/or ptosis during the observation period, in contrast to pseudoconditioned controls. When these rats were conditioned or pseudoconditioned, respectively, with B-HT 920 for further 5 days using 0.02 mg/kg again, treatment with the same dose in presence of the CS produced a significant enhancement and acceleration of these signs in conditioned as compared with pseudoconditioned control rats. The results show that stereotypies producd by nomifensine and akinesia and ptosis produced by B-HT 920 can be conditioned and that, in addition, a sign of stereotypies which was not manifest during the conditioning period appeared as conditioned response.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abercombie ED, Jacobs BL (1985) Dopaminergic modulation of sensory responses of striatal neurons: single unit studies. Brain Res 358:27–33
Andén NE, Rubenson A, Fuxe K, Hökfelt T (1967) Evidence for dopamine receptor stimulation by apomorphine. J Pharm Pharmacol 19:627–629
Andén NE, Golembiowska-Nikitin K, Thornström U (1982) Selective stimulation of dopamine and noradrenaline autoreceptors by B-HT 920 and B-HT 933, respectively. Nauny-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 321:100–104
Barr GA, Sharpless NS, Cooper S, Schiff SR, Paredes W, Bridger WH (1983) Classical conditioning, decay and extinction of cocaine-induced hyperactivity and stereotypy. Life Sci 33:1341–1351
Carlsson A (1975) Receptor-mediated control of dopamine metabolism. In: Usdin E, Bunney WE (eds) Pre- and postsynaptic receptors. Dekker, New York, pp 49–53
Cools AR, Broekkamp CLE, van Rossum JM (1977) Subcutaneous injections of apomorphine, stimulus generalization and conditioning: serious pitfalls for the examiner using apomorphine as a tool. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 6:705–708
Cools AR (1986) Mesolimbic dopamine and its control of locomotor activity in rats: difference in pharmacology and light/dark periodicity between the olfactory tubercle and the nucleus accumbens. Psychopharmacology 88:451–459
Costall B, Naylor RJ (1973) The role of telecephalic dopaminergic system in the mediation of apomorphine-stereotyped behaviour. Eur J Pharmacol 24:8–24
Ellinwood EH, Jr (1971) Accidental conditioning with chronic methamphetamine intoxication: implications for a theory of drug habituation. Psychopharmacology 21:131–138
Ernst AM (1967) Mode of action of apomorphine and dexamphetamine in gnawing compulsion in rats. Psychopharmacology 10:316–323
Fray PJ, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW, Koob GF, Iversen SD (1980) An observational method for quentifying the behavioral effects of dopamine agonists: Contrasting effects of d-amphetamine and apomorphine. Psychopharmacology 69:253–259
Havemann U, Magnus B, Möller HG, Kuschinsky K (1986) Individual and morphological differences in the behavioural response to apomorphine in rats. Psychopharmacology 90:40–48
Hebb (1949) The organization of behavior: a neuropsychological theory. Wiley, New York, cited after: Gonzalez-Lima F, Scheich H (1984) Classical conditioning enhances auditory 2-deoxyglucose patterns in the interferior colliculus. Neurosci Lett 51:79–83
Hunt P, Kannengiesser MH, Raynaud JP (1974) Nomifensine: a new potent inhibitor of dopamine uptake into synaptosomes from rat brain corpus striatum. J Pharm Pharmacol 26:370–371
Joyce EM, Iversen SD (1984) Dissociable effects of 6-OHDA-induced lesions of neostriatum on anorexia, locomotor activity and stereotypy: the role of behavioural competition. Psychopharmacology 83:363–366
Kamat KA, Dutta SN, Pradhan SN (1974) Conditioning of morphine-induced enhancement of motor activity. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 7:367–373
Kelly PH, Seviour PW, Iversen SD (1975) Amphetamine and apomorphine responses in the rat following 6-OHDA lesions of the nucleus accumbens septi and corpus striatum. Brain Res 94:507–522
Möller HG, Kuschinsky K (1986) Interaction of morphine with apomorphine: behavioural and biochemical studies. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 334:452–457
Möller HG, Nowak K, Kuschinsky K (1987a) Conditioning of pre- and post-synaptic behavioural responses to the dopamine receptor agonist apomorphine in rats. Psychopharmacology 91:50–55
Möller HG, Nowak K, Kuschinsky K (1987b) Studies on interactions between conditioned and unconditioned behavioural responses to apomorphine in rats. Nauny-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 335:673–679
Nickolson VJ, van Riezen H, van Delft ML (1984) Response changes after repeated low apomorphine: dopamine autoreceptor desensitization or learning? Psychopharmacology 83:188–193
Schiff SR (1982) Conditioned dopaminergic activity. Biol Psychiatry 17:135–154
Ungerstedt U (1979) Central dopamine mechanism and unconditioned behaviour. In: Horn AS, Korf J, Westerink BHC (eds) The neurobiology of dopamine. Academic, London New York San Francisco, pp 577–596
Vezina P, Stewart J (1984) Conditioning and place-specific sensitization of increase in activity induced by morphine in the VTA. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 20:925–934
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nowak, K., Möller, HG. & Kuschinsky, K. Conditioning of behavioural signs produced by nomifensine and by B-HT 920 in rats. Psychopharmacology 93, 182–187 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00179931
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00179931