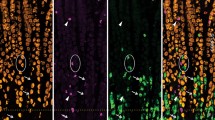
Abstract
The distributions of nerve fibres immunoreactive for the peptides calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), enkephalin (ENK), neuropeptide Y (NPY), somatostatin (SOM), substance P (SP), and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and the catecholamine-synthesizing enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) were studied in healthy colon and samples of ganglionic and aganglionic colon from cases of proven Hirschsprung's disease. Studies of coexistence of reactivities in nerve fibres were performed to predict the possible origins of fibres that are found in the aganglionic bowel, e. g., from sensory or sympathetic ganglia. The muscularis externa of the ganglionic colon contained many nerve fibres immunoreactive for ENK, SP, and VIP, fewer for NPY, and only rare fibres reactive for CGRP, SOM, or TH. In ganglionic colon reactivities for SP and ENK coexisted in nerve fibres in the muscularis externa but in aganglionic colon no ENK immunoreactivity was found and most SP fibres were double-labelled with CGRP reactivity, indicating their probable sensory nature. Abnormally increased numbers of somatostatin-reactive fibres and noradrenergic fibres (marked by TH) were noted in the external muscle, but no coexistence was seen between these reactivities and only a small proportion of the noradrenergic fibres in the muscle showed NPY reactivity although almost all around blood vessels did. Many fibres in the diseased segment had coexistence of NPY and VIP reactivities; these may arise from more orally located intrinsic cell bodies or from pelvic parasympathetic ganglia. In the mucosa of aganglionic colon there was a striking lack of SP-reactive fibres while other fibre types were often normal in number. It is concluded that nerve fibres from sensory ganglia, sympathetic ganglia, nerve cells located more oral in the ganglionated part, and possibly from pelvic parasympathetic ganglia invade the aganglionic bowel in Hirschsprung's disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auerbach L (1862) Über einen Plexus myentericus, einen bisher unbekannten ganglionervösen Apparat im Darmkanal der Wirbeltiere. E Morgenstern, Breslau, pp 1–13
Bennett A, Garrett JR, Howard ER (1968) Adrenergic myenteric nerves in Hirschsprung's disease. Br Med J 1: 487–489
Bishop AE, Polak JM, Lake BD, Bryant MG, Bloom SR D (1981) Abnormalities of the colonic regulatory peptides in Hirschsprung's disease. Histopath 5: 679–688
Buchan AMJ, Sikova LKJ, Levey JG, McIntosh CHS, Dyck I, Brown JC (1985) An immunocytochemical investigation with monoclonal antibodies to somatostatin. Histochem 83: 175–180
Careskey JM, Weber TR, Grosfeld JL (1982) Total colonic aganglionosis. Am J Surg 143: 160–168
Costa M, Furness JB, Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Davies B, Oliver J (1980) An immunohistochemical study of the projections of somatostatin containing neurons in the guinea-pig intestine. Neuroscience 5: 841–852
Costa M, Furness JB, Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Cuello AC (1981) Projections of substance P-containing neurons within the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience 6: 411–424
Costa M, Furness JB (1983) The origins, pathways and terminations of neurons with VIP-like immunoreactivity in the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience 18: 665–676
Costa M, Furness JB (1983) Immunohistochemistry in whole mount preparations. In: Cuello AC (ed) Methods in neuroscience, vol. 13. Immunohistochemistry 373–398
Costa M, Furness JB (1984) Somatostatin is present in a subpopulation of noradrenergic nerve fibres supplying the intestine. Neuroscience 13: 911–919
Costa M, Furness JB, Gibbins IL (1986) Chemical coding of enteric neurons. In: Hökfelt T, Fuxe K, Pernow B (eds) Progress in brain research, vol. 68. Elsevier Science Publishers B. V. pp 217–239
Cowen T, Haven AJ, Burnstock G (1984) Pontamine sky blue: a counterstain for background autofluorescence and immunofluorescence histochemistry. Histochemistry 82: 205–208
Daniel EE, Furness JB, Costa M, Belbeck L (1987) The projections of chemically identified nerve fibres in canine ileum. Cell Tiss Res 247: 377–384
Dupont C, Navarro J, Chenut B, Rosselin G (1980) Modifications of VIP intestinal content associated with abnormal nervous myenteric plexus: a biologic feature of chronic intestinal obstruction. J Pediatrics 96: 1037–1039
Ehrenpreis T, Pernow B (1952) On the occurrence of substance P in the rectosigmoid region in Hirschsprung's disease. Acta Phys Scand 27: 380–388
Ekblad E, Winther C, Ekman R, Haokanson R, Sundler F (1987) Projections of peptide-containing neurons in rat small intestine. Neuroscience 20: 167–188
Furness JB, Costa M (1974) The adrenergic innervation of the gastrointestinal tract. Rev Physiol 69: 1–51
Furness JB, Costa M, Walsh JH (1981) Evidence for and significance of projections of VIP neurons from the myenteric plexus to the taenia coli of the guinea-pig. Gastroenterology 80: 1557–1561
Furness JB, Costa M, Miller RJ (1983) Distribution and projections of nerves with enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience 8: 653–664
Furness JB, Costa M, Emson PC et al. (1983) Distribution, pathways and reactions to drug treatments of nerves with neuropeptide Y- and pancreatic polypeptide-immunoreactivity in the guinea-pig digestive tract. Cell Tiss Res 234: 71–92
Furness JB, Costa M, Keast JR (1984) Choline acetyltransferase- and peptide-immunoreactivity of submucous neurons in the small intestine of the guinea-pig. Cell Tiss Res 237: 328–336
Furness JB, Costa M, Gibbins IL, Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Oliver JR (1985) Neurochemically similar myenteric and submucous neurons directly traced to the mucosa of the small intestine. Cell Tiss Res 421: 155–163
Furness JB, Costa M (1987) The enteric nervous system. Edinburgh, Churchill-Livingstone
Freund HR, Humphrey CS, Fischer JE (1981) Reduced tissue content of vasoactive intestinal peptide in aganglionic colon of Hirschsprung's disease. Am J Surg 141: 243–244
Gannon BJ, Noblett HR, Burnstock G (1969) Adrenergic innervation of bowel in Hirschsprung's disease. Br Med J 3: 338–340
Garrett JR, Howard ER, Nixon HH (1969) Autonomic nerves in rectum and colon in Hirschsprung's disease. Arch Dis Childh 44: 406–417
Gershon MD, Thompson EB (1973) The maturation of neuromuscular function in a multiply innervated structure: development of the longitudinal smooth muscle of the foetal mammalian gut and its cholinergic, adrenergic inhibitory and nonadrenergic inhibitory innervation. J Physiol 234: 257–277
Gibbins IL, Furness JB, Costa M (1987) Pathway-specific patterns of co-existence of substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide, cholecystokinin and dynorphin in neurons of the dorsal root ganglion of guinea-pig. Cell Tiss Res 248: 417–437
Gibbins IL, Wattchow DA, Coventry B (1987) Two immunohistochemically identified populations of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-immunoreactive axons in human skin. Brain Res 414: 143–148
Hamada Y, Bishop AE, Frederici G, Rivosecchi M, Talbot I, Polak JM (1987) Increased neuropeptide Y-immunoreactive innervation of aganglionic bowel in Hirschsprung's disease. Virchows Arch A 411: 369–377
Hirschsprung H (1888) Stuhlträgheit Neugeborener in Folge von Dilatation und Hypertrophie des Colons. Reproduced in Dis Col Rect 1981; 24: 408–410
Hökfelt T, Elfvin LG, Elde R, Schulzberg M, Goldstein M, Luft R (1977) Occurrence of somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in some peripheral sympathetic noradrenergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 3587–3591
Ju G, Hökfelt T, Brodin E et al. (1987) Primary sensory neurons of the rat showing substance P-, somatostatin-, galanin-, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and cholecystokinin-immunoreactive ganglion cells. Cell Tiss Res 247: 417–431
Keast JR, Furness JB, Costa M (1984) Origins of peptide and norepinephrine nerves in the mucosa of the guinea-pig small intestine. Gastroenterology 86: 637–644
Keast JR, Furness JB, Costa M (1985) Distribution of certain peptide-containing nerve fibres and endocrine cells in the gastrointestinal mucosa in five mammalian species. J Comp Neurol 236: 403–422
Larsson LT (1986) Neuropeptides in Hirschsprung's disease. Thesis, University of Lund, Sweden
Lindh B, Hökfelt T, Elfvin L-G et al. (1986) Topography of NPY-, somatostatin-, and VIP-immunoreactive, neuronal subpopulations in the guinea-pig celiac-superior mesenteric ganglia and their projections to the pylorus. J Neuroscience 6: 2371–2383
Maccarone C, Jarrott B (1985) Differences in regional brain concentrations of neuropeptide Y in spontaneously hypertensive (SH) and Wistar-Kyoto rats. Brain Res 345: 165–169
MacRae IM, Furness JB, Costa M (1986) Distribution of subgroups of noradrenaline neurons in the coeliac ganglion of the guinea-pig. Cell Tiss Res 244: 173–180
Meissner G (1857) Über die Nerven der Darmwand. A Ration Med N F 8: 364–366
Miller RJ, Chang KJ, Cooper B, Cuatrecacas P (1978) Radioimmunoassay and characterization of enkephalins in rat tissues. J Biol Chem 253: 531–538
Morris HR, Panico M, Etienne T, Tippins J, Girgis SJ, MacIntyre I (1984) Isolation and characterization of human calcitonin gene-related peptide. Nature 305: 746–748
Morris JL, Gibbins IL, Furness JB, Costa M, Murphy R (1985) Co-localization of neuropeptide Y, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and dynorphin in non-adrenergic axons of the guinea-pig uterine artery. Neuroscience Letters 62: 31–39
Morris JL, Gibbins IL, Campbell G, Murphy R, Furness JB, Costa M (1986) Innervation of the large arteries and heart of the toad (Bufo marinus) by adrenergic and peptide-containing neurons. Cell Tiss Res 243: 171–184
Okamoto E, Satani M, Kuwata K (1982) Histologic and embryologic studies on the innervation of the pelvic viscera in patients with Hirschprung's disease. Surg Gyn Obstet 155: 823–828
Smith B (1967) Myenteric plexus in Hirschsprung's disease. Gut 8: 308–312
Stefanini MC, De Martino L, Zamboni L (1967) Fixation of ejaculated spermatozoa for electron microscopy. Nature 216: 173–174
Swenson O, Rheinlander H, Diamond I (1949) Hirschsprung's disease: a new concept of the etiology. New Eng J Med 241: 551–556
Wattchow DA, Furness JB, Costa M (1988) The distribution and coexistence of peptides in nerve fibers in the external muscle of the human gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology 95: 32–41
Wessendorf MW, Elde RP (1985) Characterization of an immunofluorescence technique for the demonstration of coexisting neurotransmitters within nerve fibers and terminals. J Histochem Cytochem 33: 984–994
Whitehouse FR, Kernohan JW (1948) Myenteric plexus in congenital megacolon. Arch Int Med 82: 75–111
Tafuri WL, Maria TA, Pittella JE, Bogliolo L (1974) An electron microscope study of the Auerbach's plexus and determination of substance P of the colon in Hirschprung's disease. Virchows Arch A 362: 41–50
Taguchi T, Tanaka K, Ikeda K, Matsubayashi S, Yanaihara N (1983) Peptidergic innervation irregularaties in Hirschsprung's disease. Virchows Arch (Path Anat) 401: 223–275
Talwalker VC (1976) Aganglionosis of the entire intestine. J Ped Surg 11: 213–216
Tsuto T, Okamura H, Fukui H et al. (1982) An immunohistochemical investigation of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the colon of patients with Hirschsprung's disease. Neurosci Letts 34: 57–62
Zeulser WW, Wilson JL (1948) Functional intestinal obstruction on a congenital neurogenic basis in infancy. Am J Dis Child 75: 40–64
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wattchow, D.A., Furness, J.B., Costa, M. et al. The distributions and coexistence of peptides in nerve fibres of large bowel affected by Hirschsprung's disease. Pediatr Surg Int 6, 322–332 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00178648
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00178648