Abstract
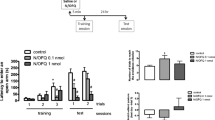
These experiments examined the involvement of opioid peptides in the memory-modulating effects of post-training epinephrine (Epi). Mice were trained on inhibitory avoidance (IA) and Y-maze discrimination (YMD) tasks and given post-training injections followed by retention tests 24 h later. In the IA task retention was enhanced by low doses of Epi and impaired by high doses. In both tasks, naloxone facilitated retention and blocked the memory-impairing effects of Epi. These findings are consistent with other evidence suggesting that the memory-impairing effects of β-endorphin are mediated by the release of opioid peptides. Previous studies have shown that a novel exploratory experience given 1 h prior to training blocks the release of brain β-endorphin and blocks the memory-enhancing effects of post-training naloxone. In the present study we found that a novel experience given 1 h prior to training blocked the memory-impairing effect of post-training Epi otherwise obtained in both tasks. The effects of a low, memory-enhancing dose of Epi appear not to involve the release of opioid peptides: a low dose of Epi blocked the memory-impairing effect of β-endorphin. Further, low doses of Epi and naloxone, which were ineffective when administered alone, significantly enhanced retention when administered together. We interpret these findings as indicating that the memory-enhancing and memory-impairing effects of Epi are mediated by different mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbilla H, Langer SZ (1978) Morphine and beta-endorphin inhibit release of noradrenaline from cerebral cortex but not of dopamine from rat striatum. Nature 271:559–561
Baratti CM, Introini IB, Huygens P (1984) Possible interaction between central cholinergic muscarinic and opioid peptidergic systems during memory consolidation in mice. Behav Neural Biol 40:155–169
Borrell J, de Kloet ER, Versteeg DHG, Bohus B (1983) The role of adrenomedullary catecholamines in the modulation of memory by vasopressin. In: Endroczi E, de Wied D, Angelucci L, Scapagnini V (eds) Integrative neurohumoral mechanisms: developments in neuroscience. Elsevier/North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 85–90
Carrasco MA, Dias RD, Perry MLS, Wofchuk ST, Souza DO, Izquierdo I (1982) Effect of morphine, ACTH, epinephrine, Met-, Leu- and des-Tyr-Met-enkephalin on beta-endorphin-like immunoreactivity of rat brain. Psychoneuroendocrinology 7:229–234
Castellano C (1975) Effects of morphine and heroin on discrimination learning and consolidation in mice. Psychopharmacologia 42:235–242
Fanelli RJ, Rosenberg RA, Gallagher M (1986) Role of noradrenergic function in the opiate antagonist facilitation of spatial memory. Behav Neurosci (in press)
Gallagher M, Kapp BS (1978) Manipulation of opiate activity in the amygdala alters memory processes. Life Sci 23:1973–1978
Gallagher M, King RA, Young NB (1983) Opiate antagonists improve spatial memory. Science 221:975–976
Gallagher M, Rapp PR, Fanelli RJ (1985) Opiate antagonist facilitation of time-dependent memory processes: Dependence upon intact norepinephrine function. Brain Res 347:284–290
Gold PE, van Buskirk R (1975) Facilitation of time-dependent memory processes with postrial epinephrine injections. Behav Biol 13:145–153
Gold PE, Zornetzer SF (1983) The mnemon and its juices: Neuromodulation of memory processes. Behav Neural Biol 38:151–189
Gold PE, McCarty R, Sternberg DB (1982) Peripheral catecholamines and memory modulation. In: Marsan CA, Matthies H (eds) Neuronal plasticity and memory formation. Raven, New York, pp 327–338
Introini-Collison IB, Baratti CM (1986) Opioid peptidergic systems may modulate the activity of β-adrenergic mechanisms during memory consolidation processes. Behav Neural Biol 46:227–241
Introini-Collison I, McGaugh JL (1986) Epinephrine modulates long-term retention of an aversively-motivated discrimination task. Behav Neural Biol 45:358–365
Introini IB, McGaugh JL, Baratti CM (1985) Pharmacological evidence of a central effect of naltrexone, morphine and beta-endorphin and a peripheral effect of Met-and Leu-enkephalin on retention of an inhibitory response in mice. Behav Neural Biol 44:434–446
Izquierdo I (1979) Effect of naloxone and morphine on various forms of memory in the rat: Possible role of endogenous opiate mechanisms in memory consolidation. Psychopharmacology 66:199–203
Izquierdo I (1982) Beta-endorphin and forgetting. TIPS 3:455–457
Izquierdo I, Graudenz M (1980) Memory facilitation by naloxone is due to release of dopaminergic and beta-adrenergic systems from tonic inhibition. Psychopharmacology 67:265–268
Izquierdo I, Dias RD (1983a) Memory as a state dependent phenomenon: Role of ACTH and epinephrine. Behav Neural Biol 38:144–151
Izquierdo I, Dias RD (1983b) Effect of ACTH, epinephrine, β-endorphin, naloxone, and of the combination of naloxone or β-endorphin with ACTH or epinephrine on memory consolidation. Psychoneuroendocrinology 8:81–87
Izquierdo I, McGaugh JL (1985) Effect of a novel experience prior to training or testing on retention of an inhibitory avoidance response in mice: Involvement of an opioid system. Behav Neural Biol 44:228–238
Izquierdo I, Souza DO, Dias RD, Carrasco MA, Perry ML, Eisinger S, Elisabetsky E, Vendite DA (1980) Beta-endorphin causes retrograde amnesia and is released from the rat brain by various forms of training and stimulation. Psychopharmacology 70:173–177
Izquierdo I, Perry MLS, Dias RD, Orsinger OA, Carrasco MA (1981) Effect of training and testing rats in two different behavioral paradigms on brain beta-endorphin immunoreactivity. Arqu Biol Tecnol (Parana) 24:327–331
Izquierdo I, Souza DO, Dias RD, Carrasco MA, Vokmer N, Perry MLS, Netto CA (1984) Effect of various behavioral training and testing procedures on brain beta-endorphin-like immunoreactivity, and the possible role of beta-endorphin in behavioral regulation. Psychoneuroendocrinology 9:381–389
Izquierdo I, Netto CA, Carrasco MA, Dias RD, Volkmer N (1985) Time course of the decrease of hypothalamic β-endorphin induced by training, and the development of the effect of β-endorphin on retrieval of inhibitory avoidance in rats. Brazil J Med Biol Res 18:391–395
Jaim-Etcheverry G, Zieher LM (1980) DSP-4 a novel compound with neurotoxic effects on noradrenergic neurons of adults and developing rats. Brain Res 188:513–523
Jonsson G, Hallman H, Ponzio F, Ross SB (1981) DSP 4 (N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-ethyl-2-bromobenzylamine). A useful denervation tool for central and peripheral noradrenaline neurons. Eu J Pharmacol 72:173–188
Lader MH, Tyrer PJ (1972) Central and peripheral effects of propranolol and sotalol in normal subjects. Br J Pharmacol 45:557–560
Liang KC, McGaugh JL (1983) Lesions of the stria terminalis attenuate the enhancing effect of posttraining epinephrine on retention of an inhibitory avoidance response. Behav Brain Res 9:49–58
Liang KC, Juler R, McGaugh JL (1986) Modulating effects of posttraining epinephrine on memory: Involvement of the amygdala noradrenergic system. Brain Res 368:125–133
Lucion AB, Rosito G, Sapper D, Palmini A, Izquierdo I (1982) Intracerebroventricular administration of nanogram amounts of beta-endorphin and Met-enkephalin causes retrograde amnesia in rats. Behav Brain Res 4:111–115
McGaugh JL (1983) Hormonal influences on memory. Annu Rev Psychol 34:297–323
McGaugh JL, Gold PE (1986) Hormonal modulation of memory. In: Brush RB, Levine S (eds) Psychoendocrinology. Academic, New York
McGaugh JL, Landfield PW (1970) Delayed development of amnesia following electroconvulsive shock. Physiol Behav 5:1109–1111
McGaugh JL, Introini-Collison IB, Juler RG, Izquierdo I (1986) Stria terminalis lesions attenuate the effects of posttraining naloxone and β-endorphin on retention. Behav Neurosci 100:839–844
Messing RB, Jensen RA, Martinez Jr JL, Spiehler VR, Vasquez BJ, Soumireu-Mourat B, Liang KC, McGaugh JL (1979) Naloxone enhancement of memory. Behav Neural Biol 27:266–275
Sternberg DB, Korol D, Novack GD, McGaugh JL (1986) Epinephrine-induced memory facilitation: Attenuation by adrenergic receptor antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol 129:189–193
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Introini-Collison, I.B., McGaugh, J.L. Naloxone and β-endorphin alter the effects of post-training epinephrine on memory. Psychopharmacology 92, 229–235 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00177921
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00177921