Summary
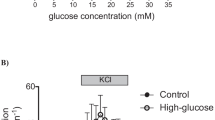
Propylthiouracil and methylthiouracil have been shown to potentiate glucose-induced insulin secretion from rat pancreatic islets: the effect of methylthiouracil being less pronounced than that of propylthiouracil. In this study the effects of these substances on cAMP levels, 86Rb+ efflux, 45Ca2+ net uptake, and 45Ca2+ efflux were tested in isolated rat islets in order to obtain information on their possible mechanism of action. Propylthiouracil and to a lesser extent methylthiouracil increased islet cyclic AMP in a concentration-related manner. Maximum increases at the highest concentrations tested were 261% and 190% respectively. In the presence of 3 mM glucose propylthiouracil and methylthiouracil led to a decrease in the 86Rb efflux rate. With 5.6 mM glucose, both thiourea derivatives produced an increase in the 86Rb+ efflux rate which was independent of the presence or absence of calcium in the medium. Propylthiouracil and methylthiouracil augmented the 45Ca2+ efflux rate in the presence as well as in the absence of external calcium at various glucose concentrations. Propylthiouracil did not change, and methylthiouracil only slightly augmented, 45Ca2+ net uptake into the isolated islets. It is suggested that the synergistic effect of propylthiouracil and methylthiouracil on glucose-induced insulin release is at least in part due to an increase in islet cAMP levels. Whether the two substances have additional direct effects on ionic fluxes which contribute to their insulinotropic action or whether the observed changes in ion movements are secondary to the elevation of cAMP levels remains to be unclear and needs further investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahamsson H, Rorsman P (1984) Cyclic AMP potentiation of insulin release from pancreatic β-cells is not mediated by an increased cytosolic Ca activity. Diabetologia 27:250A
Ammon HPT, Melien MCM, Pfäffle T (1984) Potentiation of glucose-induced insulin release by thiourea and thiourea derivatives. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 327:234–237
Ammon HPT, Willer AB (1984) Effect of forskolin on islet cyclic AMP, insulin secretion, blood glucose and intravenous glucose tolerance in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 326:364–367
Ammon HPT, Fahmy A, Mark M, Strölin W, Wahl MA (1985) Failure of glucose to affect 86 Rubidium efflux and 45Calcium uptake of fetal rat pancreatic islets. J Physiol 358:365–372
Ammon HPT, Mark M (1985) Thiols and pancreatic β-cell function: a review. Cell Biochem Funct 3:157–171
Ammon HPT, Hehl K-H, Enz G, Setiadi-Ranti A, Verspohl J (1987) Cysteine derivatives potentiate glucose-induced insulin release in vitro. Diabetes (in press)
Brisson GR, Malaisse-Lagae F, Malaisse WJ (1972) The stimulussecretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. VII. A proposed site of action for adenosine-3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate. J Clin Invest 51:232–241
Henquin JC (1980) Metabolic control of the potassium permeability in pancreatic islet cells. Biochem J 186:541–550
Henquin JC, Meissner HP (1984a) Significance of ionic fluxes and changes in membrane potential for stimulus-secretion coupling in pancreatic B-cells. Experientia 40:1043–1052
Henquin JC Meissner HP (1984b) The ionic, electrical, and secretory effects of endogenous cyclic adenosine monophosphate in mouse pancreatic B cells: studies with forskolin. Endocrinology 115:1125–1134
Henquin JC (1985) The interplay between cyclic AMP and ions in the stimulus-secretion coupling in pancreatic B-cells. Arch Int Physiol Biochem 93:37–48
Herchuelz A, Malaisse WJ (1978) Regulation of calcium fluxes in pancreatic islets: Dissociation between calcium and insulin release. J Physiol 283:409–424
Kawazu S, Sener A, Couturier E, Malaisse WJ (1980) Metabolic, cationic and secretory effects of hypoglycemic sulfonylureas in pancreatic islets. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 312:277–283
Lacy PE, Kostaniovsky M (1967) Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes 16:35–39
Lebrun P, Malaisse WJ, Herchuelz A (1982) Paradoxical activation by glucose of quinine-sensitive potassium channels in the pancreatic β-cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 107:350–356
Wollheim CB, Siegel EG, Kikuchi M, Renold AE, Sharp GWG (1980) The role of extracellular Ca2+ and islet calcium stores in the regulation of biphasic insulin release. Horm Metab Res [Suppl] 10:108–115
Wollheim CBP, Sharp GWG (1981) Regulation of insulin release by calcium. Physiol Rev 61:914–973
Wollheim CB, Ullrich S, Pozzan T (1984) Glyceraldehyde, but not cyclic AMP-stimulated insulin release is preceded by a rise in cytosolic free Ca2+ FEBS Lett 177:17–22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to H. P. T. Ammon at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mark, M., Fitzel, E., Youssif, N. et al. Effects of propylthiouracil and methylthiouracil on cyclic AMP and ion movements in rat pancreatic islets. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 335, 194–199 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00177723
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00177723