Abstract
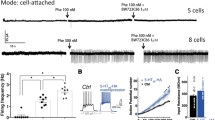
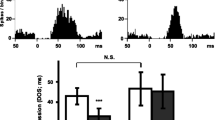
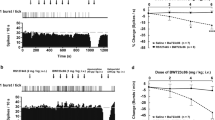
Electrophysiological and autoradiographic approaches were used to assess possible changes in 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) 5-HT1A receptors in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus after a subchronic treatment with fluoxetine or paroxetine, two specific serotonin reuptake inhibitors with antidepressant properties. Fluoxetine or paroxetine were injected daily (5 mg/kg, i.p.) for various time periods up to 21 days. Electrophysiological recordings performed 24 h after the last injection showed that the potency of the 5HT1A receptor agonist, 8-OH-DPAT, to depress the firing of serotoninergic neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus within brain stem slices was significantly reduced as early as after a 3-day treatment with either drug. The proportion of recorded neurons showing desensitization of somatodendritic 5-HT1A autoreceptors increased along the treatment from ∼40% on the 3rd day to 60–80% on the 21st day. At no time during the treatment, was the specific binding of [3H]8-OHDPAT (agonist radioligand) or [3H] WAY-100 635 (antagonist radioligand) to 5-HT1A receptors modified in the dorsal raphe nucleus or in other brain areas, suggesting that neither the density nor the coupling of these receptors to G-proteins were probably altered in rats injected with fluoxetine or paroxetine for up to 21 days.
These results show that adaptive desensitization of somatodendritic 5-HT1A autoreceptors within the dorsal raphe nucleus can already be detected after a 3-day treatment with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Rather than the desensitization per se, it may be the progressive increase in the number of serotoninergic neurons with desensitized 5-HT1A autoreceptors which plays a critical role in the (slowly developing) antidepressant action of these drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Artigas F, Perez V, Alvarez E (1994) Pindolol induces a rapid improvement of patients treated with serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51:248–251
Blier P, de Montigny C (1987) Modification of 5-HT neuron properties by sustained administration of the 5-HT1A agonist gepirone: electrophysiological studies in the rat brain. Synapse 1:470–480
Briley M, Moret C (1993) Neurobiological mechanisms involved in antidepressant therapies. Clin Neuropharmacol 16:387–400
Caldecott-Hazard S, Morgan DG, De Leon-Jones F, Overstreet DH, Janowsky D (1991) Clinical and biochemical aspects of depressive disorders: II. Transmitter/receptor theories. Synapse 9:251–301
Chang AS, Chang SM, Starnes DM (1993) Structure-activity relationships of serotonin transport: relevance to nontricyclic antidepressant interactions. Fur J Pharmacol 247:239–248
Chaput Y, Blier P, De Montigny C (1988) Acute and long-term effects of antidepressant serotonin (5-HT) reuptake blockers on the efficacy of 5-HT neurotransmission: electrophysiological studies in the rat central nervous system. Adv Biol Psychiatry 17:1–17
De Montigny C, Blier P, Chaput Y (1990) Electrophysiological investigation of the effects of antidepressant treatments on serotonin receptors. In: Vanhoutte PM, Paoletti R, Brunello N, Maggi FM (eds) Serotonin: from cell biology to pharmacology and therapeutics. Kluwer Acad Publ, Dordrecht, pp 499–504
Delgado PL, Charney DS, Price LH, Aghajanian GK, Landis H, Heninger GR (1990) Serotonin function and the mechanism of antidepressant action: reversal of antidepressant induced remission by rapid depletion of plasma tryptophan. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:411–418
Emerit MB, El Mestikawy S, Gozlan H, Rouot B, Hamon M (1990) Physical evidence of the coupling of solubilized 5-HT1A binding sites with G regulatory proteins. Biochem Pharmacol 39:7–18
Fletcher A, Bill DJ, Cliffe IA, Forster EA, Jones D, Reilly Y (1994) A pharmacological profile of WAY-100635, a potent and selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol 112:91P
Fuller RW (1994) Minireview: Uptake inhibitors increase extracellular serotonin concentration measured by brain microdialysis. Life Sci 55:163–167
Fuller RW, Wong DT, Robertson DW (1991) Fluoxetine, a selective inhibitor of Serotonin uptake. Med Res Rev 11:17–34
Gobbi M, Frittoli E, Mennini T, Garattini S (1992) Releasing activities of d-fenfluramine and fluoxetine on rat hippocampal synaptosomes preloaded with [3H]Serotonin. NaunynSchmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 345:1–6
Gozlan H, Thibault S, Laporte A, Lima L, Hamon M (1995) The selective 5-HT1A antagonist radioligand [3H]WAY 100635 labels both G-protein-coupled and free 5-HT1A receptors in rat brain membranes. Fur J Pharmacol-Mol Pharmacol 288:173–186
Haj-Dahmane S, Hamon M, Lanfumey L (1991) K+ channel and 5-hydroxytryptamine1A autoreceptor interactions in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus: an in vitro electrophysiological study. Neuroscience 41:495–505
Hall MD, El Mestikawy S, Emerit MB, Pichat L, Hamon M, Gozlan H (1985) [3H]8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin binding to pre- and post- synaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine sites in various regions of the rat brain. J Neurochem 44:1685–1696
Hensler JG, Kovachich GB, Frazer A (1991) A quantitative autoradiographic study of serotonin1A receptor regulation. Effect of 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine and antidepressant treatments. Neuropsychopharmacology 4:131–144
Hoyer D, Clarke D, Fozard J, Hartig P, Martin G, Mylecharane E, Saxena P, Humphrey P (1994) VII. International Union of Pharmacology classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Pharmacol Rev 46:157–203
Hyttel J (1994) Pharmacological characterization of selective scrotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Int Clin Psychopharmacol 9 [suppl 1]:19–26
Jolas T, Haj-Dahmane S, Kidd EJ, Langlois X, Lanfumey L, Fattaccini CM, Vantalon V, Laporte AM, Adrien J, Gozlan H, Hamon M (1994) Central pre- and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors in rats treated chronically with a novel antidepressant, cericlamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 268:1432–1443
Jolas T, Haj-Dahmane S, Lanfumey L, Fattaccini CM, Kidd EJ, Adrien J, Gozlan H, Guardiola-Lemaitre B, Hamon M (1993) (−)Tertatolol is a potent antagonist at pre- and postsynaptic serotonin 5-HT1A receptors in the rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 347:453–463
Kidd EJ, Haj-Dahmane S, Jolas T, Lanfumey L, Fattaccini CM, Guardiola-Lemaitre B, Gozlan H, Hamon M (1993) New methoxy-chroman derivatives, 4[N-(5-methoxy-chroman-3-yl) N-propylamino]butyl-8-azaspiro-(4,5)-decane-7,9-dione [(±)-S 20244] and its enantiomers, (+)-S 20499 and (−)-S 20500, with potent agonist properties at central 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:863–872
Lesch K (1993) 5-HT1 receptors in depression and related disorders. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 3:302–303
Lesch KP, Hough CJ, Aulakh CS, Wolozin BL, Tolliver TJ, Hill JL, Akiyoshi J, Chuang DM, Murphy DL (1992) Fluoxetine modulates G protein αs, αq, and α12 subunit mRNA expression in rat brain. Fur J Pharmacol-Mol Pharmacol 227:233–237
Li Q, Brownfield MS, Levy AD, Battaglia G, Cabrera TM, Van de Kar LD (1994) Attenuation of hormone responses to the 5-HT1A agonist ipsapirone by long-term treatment with fluoxetine, but not desipramine, in male rats. Biol Psychiatry 36:300–308
Maj J, Meryl E (1993) Effects of fluoxetine given chronically on the responsiveness of 5-HT receptor subpopulations to their agonists. Fur Neuropsychopharmacol 3:85–94
Nemeroff CB (1993) Paroxetine: an overview of the efficacy and safety of a new selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor in the treatment of depression. J Clin Psychopharmacol 13:10S-17S
Newman ME, Lerer B, Shapira B (1993) 5-HTIA receptor-mediated effects of antidepressants. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 17:1–19
Newman ME, Shapira B, Lerer B (1992) Regulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor function in rat hippocampus by shortand long- term administration of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A agonists and antidepressants. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 260:16–20
Rigdon GC, Wang CM (1991) Serotonin uptake blockers inhibit the firing of presumed serotonergic dorsal raphe neurons in vitro. Drug Dev Res 22:135–140
Schechter LE, Bolafios FJ, Gozlan H, Lanfumey L, Haj-Dahmane S, Laporte AM, Fattaccini C, Hamon M (1990) Alterations of central serotoninergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission in rats chronically treated with ipsapirone: biochemical and electrophysiological studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 255:1335–1347
Scheffel U, Kim S, Cline EJ, Kuhar MJ (1994) Occupancy of the serotonin transporter by fluoxetine, paroxetine, and sertraline: in vivo studies with [125I]RTI-55. Synapse 16:263–268
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1967) Statistical methods. Iowa State College Press, Ames
Spurlock G, Buckland P, O'Donovan M, McGuffin P (1994) Lack of effect of antidepressant drugs on the levels of mRNAs encoding serotonergic receptors, synthetic enzymes and 5-HT transporter. Neuropharmacology 33:433–440
Stahl SM, Gastpar M, Keppel Hesselink JM, Traber J (eds) (1992) Serotonin1A receptors in depression and anxiety. Raven Press, New York, 216 p
Thomas DR, Nelson DR, Johnson AM (1987) Biochemical effects of the antidepressent paroxetine, a specific 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake inhibitor. Psychopharmacology 93:193–200
Tignol J (1993) A double-blind, randomized, fluoxetine-controlled, multicenter study of paroxetine in the treatment of depression. J Clin Psychopharmacol 13:18S-22S
Vandermaelen CP, Agbajanian GK (1983) Electrophysiological and pharmacological characterization of serotoninergic dorsal raphe neurons recorded extracellularly and intracellularly in rat brain slices. Brain Res 289:109–119
Welner SA, De Montigny C, Desroches J, Desjardins P, Suranyi-Cadotte BE (1989) Autoradiographic quantification of serotonin1A receptors in rat brain following antidepressant drug treatment. Synapse 4:347–352
Wieland S, Fischette CT, Lucki I (1993) Effect of chronic treatments with tandospirone and imipramine on Serotonin-mediated behavioral responses and monoamine receptors. Neuropbarmacology 32:561–573
Wong DT, Threlkeld PG, Robertson DW (1991) Affinities of fluoxetine, its enantiomers, and other inhibitors of scrotonin uptake for subtypes of serotonin receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 5:43–47
Yates M, Ferrier IN (1990) 5-HTIA receptors in major depression. J Psychopharmacol 4:69–74
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le Poul, E., Laaris, N., Doucet, E. et al. Early desensitization of somato-dendritic 5-HT1A autoreceptors in rats treated with fluoxetine or paroxetine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 352, 141–148 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00176767
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00176767