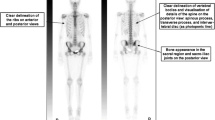
Abstract
Gamma-scintigraphy is applied extensively in the development and evaluation of pharmaceutical drug delivery systems. It is used particularly for monitoring formulations in the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts. The radiolabelling is generally achieved by the incorporation of an appropriate technetium-99m or indium-111 labelled radiopharmaceutical into the formulation. In the case of complex dosage forms, such as enteric-coated tablets, labelling is best undertaken by the addition of a non-radioactive tracer such as samarium-152 oxide or erbium-170 oxide followed by neutron activation of the final product. Systems investigated include tablets and multiparticulates for oral administration, enemas and suppositories, metered dose inhalers and nebulisers, and nasal sprays and drops. Gamma-scintigraphy provides information on the deposition, dispersion and movement of the formulation. The combination of such studies with the assay of drug levels in blood or urine specimens, pharmacoscintigraphy, provides information concerning the sites of drug release and absorption. Data acquired from the scintigraphic evaluation of pharmaceutical dosage forms are now being used increasingly at all stages of product development, from the assessment of prototype delivery systems to supporting the product licence application.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashworth HL, Wilson CG, Sims EE, Wotton PK, Hardy JG (1991) Delivery of propellant soluble drug from a metered dose inhaler. Thorax 46:245–247
Bechgaard H, Christensen FN, Davis SS, Hardy JG, Taylor MJ, Whalley DR, Wilson CG (1985) Gastrointestinal transit of pellet systems in ileostomy subjects and the effect of density. J Pharm Pharmacol 37:718–721
Bond SW, Hardy JG, Wilson CG (1984) Deposition and clearance of nasal sprays. In: Aiache JM, Hirtz J (eds) Proceedings of 2nd European congress of biopharmaceutics and pharmacokinetics. Lavoisier, Paris, pp 93–98
Borgström L, Nilsson M (1990) A method for determination of the absolute pulmonary bioavailability of inhaled drugs: terbutaline. Pharm Res 7:1069–1070
Borgström L, Newman SP, Morén F (1991) Pulmonary deposition of inhaled terbutaline. A comparison of two methods: scanning gamma-camera and urinary excretion. J Aerosol Med 4:8
Caruso I, Porro GB (1980) Gastroscopic evaluation of anti-inflammatory agents. Br J Med 280:75–78
Chaffman M, Brogden RN (1985) Diltiazem. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs 39:387–454
Christrup LL, Davis SS, Frier M, Melia CD, Rasmussen SN, Washington N, Wilding IR, Andersen C (1990) Deposition of a model substance, 99mTc E-Hida, in the oral cavity after administration of lozenges, chewing gum and sublingual tablets. Int J Pharm 66:169–174
Coupe AJ, Davis SS, Evans DF, Wilding IR (1991a) Correlation of the gastric emptying of non-disintegrating tablets with gastrointestinal motility. Pharm Res 8:1281–1285
Coupe AJ, Davis SS, Wilding IR (1991b) Variation in gastrointestinal transit of pharmaceutical dosage forms in healthy subjects. Pharm Res 8:360–364
Coupe AJ, Davis SS, Evans DF, Wilding IR (1992a) The effect of sleep on the gastrointestinal transit of pharmaceutical dosage forms. Int J Pharm 78:69–76
Coupe AJ, Davis SS, Evans DF, Wilding IR (1992b) Nocturnal scintigraphic imaging to investigate the gastrointestinal transit of dosage forms. J Contr Rel 20:155–162
Daly PB, Davis SS, Frier M, Hardy JG, Kennerley JW, Wilson CG (1982) Scintigraphic assessment of the in-vivo dissolution rate of a sustained release tablet. Int J Pharm 10:17–24
Dashe CK, Ponto RA, Ganapes CM, Drage CW, Kronenberg RS (1974) The distribution of nebulised isoproterenol and its effects on regional ventilation and perfusion. Am Rev Respir Dis 110:293–300
Davies DS (1975) Pharmacokinetics of inhaled substances. Postgrad Med J 51 [Suppl 7]:69–75
Davis SS, Feely LC (1989) Correlation of phenylpropanolamine bioavailability with gastrointestinal transit by scintigraphic monitoring of 111In-labelled hydroxypropylmethylcellulose matrices. Pharm Res 6:274–278
Davis SS, Daly PB, Frier M, Hardy JG, Kennerley JW, Wilson CG (1981) The design and evaluation of sustained release formulations for oral and buccal administration. Adv Pharmacother 1:17–25
Davis SS, Kennerley JW, Taylor MJ, Hardy JG, Wilson CG (1983) Scintigraphic studies on the in-vivo dissolution of a buccal tablet. In: Goldberg AAJ, Parsons DG (eds) Modern concepts in nitrate delivery systems. R Soc Med Int Cong Symp series no 54:29–33
Davis SS, Hardy JG, Taylor MJ, Stockwell A, Whalley DR, Wilson CG (1984a) The in-vivo evaluation of an osmotic device (Osmet) using gamma scintigraphy. J Pharm Pharmacol 36:740–742
Davis SS, Hardy JG, Taylor MJ, Whalley DR, Wilson CG (1984b) A comparative study of the gastrointestinal transit of a pellet and a tablet formulation. Int J Pharm 21:167–177
Davis SS, Hardy JG, Taylor MJ, Whalley DR, Wilson CG (1984c) The effect of food on the gastrointestinal transit of pellets and an osmotic device. Int J Pharm 21:331–340
Davis SS, Hardy JG, Fara J (1986a) The intestinal transit of pharmaceutical dosage forms. Gut 27:886–892
Davis SS, Stockwell AF, Taylor MJ, Hardy JG, Whalley DR, Wilson CG, Bechgaard H, Christensen FN (1986b) The effect of density on the gastric emptying of single and multiple unit dosage forms. Pharm Res 3:208–213
Davis SS, Hardy JG, Wilson CG, Feely LC, Palin KJ (1986c) Gastrointestinal transit of a controlled release naproxen tablet formulation. Int J Pharm 32:85–90
Davis SS, Khosla R, Wilson CG, Washington N (1987) The gastrointestinal transit of a controlled release pellet formulation of tiaprofenic acid. Int J Pharm 35:253–258
Davis SS, Christensen FN, Khosla R, Feely LC (1988a) Gastric emptying of large single unit dosage forms. J Pharm Pharmacol 40:205–207
Davis SS, Washington N, Parr GD, Short AH, John VA, Lloyd P, Walker SM (1988b) Relationship between the rate of appearance of oxprenolol in the systemic circulation and the location of an oxprenolol Oros 16/260 drug delivery system within the gastrointestinal tract as determined by scintigraphy. Br J Clin Pharmacol 26:435–443
Davis SS, Parr GD, Feely LC, Malkowska S, Lockwood GF (1989) The gastrointestinal transit investigation of a controlled release aminophylline formulation. Int J Pharm 49:183–188
Davis SS, Khosla R, Wilson CG, Washington N, Leslie ST, Malkowska S (1990) The gastrointestinal transit of a controlled release formulation of indomethacin. Int J Pharm 60:191–196
Davis SS, Robertson C, Wilding IR (1991) Gastrointestinal transit of a multiparticulate tablet formulation in patients with active ulcerative colitis. Int J Pharm 68:199–204
Devereux JE, Newton JM, Short MB (1990) The influence of density on the gastrointestinal transit of pellets. J Pharm Pharmacol 42:500–501
Digenis GA, Sandefer EP, Parr A, Beihn RM, McClain C, Scheinthal BM, Ghebre-Sellassie I, Iyer U, Nesbitt RU, Randinitis E (1990) Gastrointestinal behavior of orally administered radio-labeled erythromycin pellets in man as determined by gamma scintigraphy. J Clin Pharmacol 30:621–631
Dolovich M, Ruffin RE, Roberts R, Newhouse MT (1981) Optimal delivery of aerosols from metered dose inhalers. Chest 80 [Suppl]:911–915
Edgington SM (1991) The anatomy of access: peptide drug delivery. Biotechnology 9:1326–1331
Fischer W, Boertz A, Davis SS, Khosla R, Cawello W, Sandrock K, Cordes G (1987) Investigation of the gastrointestinal transit and in-vivo drug release of isosorbide-5-nitrate pellets. Pharm Res 4:480–485
Geoghegan EJ, Mulligan S, Panoz DE (1988) Controlled absorption diltiazem formulations. European Patent 0320097
Hardy JG, Wilson CG, Wood E (1985a) Drug delivery to the proximal colon. J Pharm Pharmacol 37:874–877
Hardy JG, Lee SW, Wilson CG (1985b) Intranasal drug delivery by spray and drops. J Pharm Pharmacol 37:294–297
Hardy JG, Lee SW, Clark AG, Reynolds JR (1986) Enema volume and spreading. Int J Pharm 31:151–155
Hardy JG, Evans DF, Zaki I, Clark AG, Tonnesen HH, Gamst ON (1987a) Evaluation of an enteric coated naproxen tablet using gamma scintigraphy and pH monitoring. Int J Pharm 37:245–250
Hardy JG, Healey JNC, Lee SW, Reynolds JR (1987b) Gastrointestinal transit of an enteric-coated delayed-release 5-aminosalicylic acid tablet. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1:209–216
Hardy JG, Healey JNC, Reynolds JR (1987c) Evaluation of an enteric-coated delayed-release 5-aminosalicylic acid tablet in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1:273–280
Hardy JG, Feely LC, Wood E, Davis SS (1987d) The application of gamma scintigraphy for the evaluation of the relative spreading of suppository bases in rectal hard gelatin capsules. Int J Pharm 38:103–108
Hardy JG, Davis SS, Khosla R, Robertson CS (1988) Gastrointestinal transit of small tablets in patients with ulcerative colitis. Int J Pharm 48:79–82
Hardy JG, Lamont GL, Evans DF, Haga AK, Gamst ON (1991a) Evaluation of an enteric-coated naproxen pellet formulation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 5:69–75
Hardy JG, Everard ML, Coffiner M, Fossion J (1991 b) Lung deposition of a nacystelyn metered dose inhaler formulation. J Aerosol Med 4 [Suppl 1]
Harris AS, Nilsson IM, Wagner ZG, Alkner U (1986) Intranasal administration of peptides: nasal deposition, biological response and absorption of desmopressin. J Pharm Sci 75:108–113
Haslock I (1989) Review of NSAID-induced upper gastrointestinal morbidity and mortality. In: Cheli R (ed) R S M Int Cong Symp Ser 147:3–10
Hermann PH, Rodger SD, Remones G, Thenot JP, London DR, Morselli PL (1983) Pharmacokinetics of diltiazem after intravenous and oral administration. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 24:349–352
Hunter E, Fell JT, Calvert RT, Sharma H (1980) In-vivo disintegration of hard gelatin capsules in fasting and non-fasting subjects. Int J Pharm 4:175–183
Hunter E, Fell JT, Sharma H (1982) The gastric emptying of pellets contained in hard gelatin capsules. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 8:751–757
Jay M, Beihn RM, Digenis GA, DeLand FH, Caldwell L, Mlodozeniec AR (1985) Disposition of radiolabelled suppositories in humans. J Pharm Pharmacol 37:266–268
Johnson MA, Newman SP, Bloom R, Talaee N, Clarke SW (1989) Delivery of albuterol and ipratropium bromide from two nebuliser systems in chronic stable asthma. Efficacy and pulmonary deposition. Chest 96:1–10
Khosla R, Davis SS (1987) The effect of polycarbophil on the gastric emptying of pellets. J Pharm Pharmacol 39:47–49
Khosla R, Davis SS (1989) Gastrointestinal transit of non-disintegrating tablets in fed subjects. Int J Pharm 53:107–117
Khosla RC, Davis SS (1990) The effect of tablet size on the gastric emptying of non-disintegrating tablets. Int J Pharm 62:R9-R11
Khosla R, Feely LC, Davis SS (1989) Gastrointestinal transit of non-disintegrating tablets in fed subjects. Int J Pharm 53:107–117
Köhler D, Fleischer W, Matthys H (1988) A new method for easy labelling of beta-2 agonists in the metered dose inhaler with Tc99m. Respiration 53:65–73
Lee SW, Hardy JG, Wilson CG, Smelt GJC (1984) Nasal sprays and polyps. Nucl Med Commun 5:697–703
Millar AB, Agnew JE, Newman SP, Lopez-Vidriero MT, Pavia D, Clarke SW (1986) A comparison of nasal and tracheobronchial clearance using similar techniques in normal subjects. Thorax 40:724
Morén F (1985) Aerosol dosage forms and formulations. In: Morén F, Newhouse MT, Dolovich MB (eds) Aerosols in medicine: principles, diagnosis and therapy. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 261–287
Mundy MJ, Wilson CG, Hardy JG (1989) The effect of eating on transit through the small intestine. Nucl Med Commun 10:45–50
Mygind N (1985) The upper airway: nose, pharynx and larynx. In: Morén F, Newhouse MT, Dolovich MB (eds) Aerosols in medicine: principles, diagnosis and therapy. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–20
Newman SP, Pavia D, Morén F, Sheahan NF, Clarke SW (1981a) Deposition of pressurised aerosols in the human respiratory tract. Thorax 36:52–55
Newman SP, Morén F, Pavia D, Little F, Clarke SW (1981b) Deposition of pressurised aerosols inhaled through extension devices. Am Rev Respir Dis 124:317–320
Newman SP, Pavia D, Clarke SW (1982a) Effects of various inhalation modes on the deposition of radioactive pressurised aerosols. Eur J Respir Dis 63 [Suppl 119]:57–65
Newman SP, Morén F, Pavia D, Corrado O, Clarke SW (1982b) The effects of changes in metered volume and propellant vapour pressure on the deposition of pressurised inhalation aerosols. Int J Pharm 11:337–344
Newman SP, Millar AB, Lennard-Jones TR, Morén F, Clarke SW (1984a) Improvement of pressurised aerosol deposition with Nebuhaler spacer device. Thorax 39:935–941
Newman SP, Killip M, Pavia D, Morén F, Clarke SW (1984b) The effect of changes in particle size on the deposition of pressurised inhalation aerosols. Int J Pharm 19:333–337
Newman SP, Woodman G, Clarke SW, Sackner MA (1986) The effect on InspirEase on the deposition of metered dose aerosols in the human respiratory tract. Chest 89:551–556
Newman SP, Morén F, Clarke SW (1987a) The nasal distribution of metered dose inhalers. J Laryngol Otol 101:127–132
Newman SP, Morén F, Clarke SW (1987b) Deposition pattern from a nasal pump spray. Rhinology 25:77–82
Newman SP, Woodman G, Clarke SW (1988a) Deposition of carbenicillin aerosols in cystic fibrosis: effects of nebuliser system and breathing pattern. Thorax 43:318–322
Newman SP, Morén F, Clarke SW (1988b) Deposition pattern of nasal sprays in man. Rhinology 26:111–120
Newman SP, Clark AR, Talaee N, Clarke SW (1989a) Pressurised aerosol deposition in the human lung with and without an “open” spacer. Thorax 44:706–710
Newman SP, Morén F, Trofast E, Talaee N, Clarke SW (1989b) Deposition and clinical efficacy of terbutaline sulphate from Turbuhaler, a new multi-dose powder inhaler. Eur Respir J 2:247–252
Newman SP, Weisz A, Clarke SW (1990) Bronchodilator delivery from Gentle-haler, a new low-velocity pressurised aerosol inhaler. Am Rev Respir Dis 141:A18
Newman SP, Clark AR, Talaee N, Clarke SW (1991a) Lung deposition of 5 mg Intal from a pressurised metered dose inhaler assessed by radiotracer technique. Int J Pharm 74:203–208
Newman SP, Weisz AWB, Talaec N, Clarke SW (1991b) Improvement of drug delivery with a breath actuated pressurised aerosol for patients with poor inhaler technique. Thorax 46:712–716
Newman SP, Talaec N, Clarke SW (1991c) Salbutamol aerosol delivery with the Rondo spacer. Acta Therapeutica 17:49–58
Newman SP, Moren F, Trofast E, Talaee N, Clarke SW (1991d) Terbutaline sulphate Turbuhaler: effect of inhaled flow rate on drug deposition and efficacy. Int J Pharm 74:209–213
O'Callaghan C, Hardy JG, Stammers J, Stephenson TJ, Hull D (1992) Evaluation of techniques for delivery of steroids to lungs of neonates using a rabbit model. Arch Dis Child 67:20–24
Ollerenshaw KJ, Norman S, Wilson CG, Hardy JG (1987) Exercise and small intestinal transit. Nucl Med Commun 8:105–110
O'Reilly S, Wilson CG, Hardy JG (1987) The influence of food on multiparticulate dosage forms. Int J Pharm 34:213–216
Park HM, Chernish JM, Rosenbek BD, Brunelle RL, Hargrove B, Wellman HN (1984) Gastric emptying of enteric coated tablets. Dig Dis Sci 29:207–212
Parker G, Wilson CG, Hardy JG (1988) The effect of capsule density on transit through the proximal colon. J Pharm Pharmacol 40:376–377
Parr AF, Beihn RM, Franz RM, Szpunar GJ, Jay M (1987) Correlation of ibuprofen bioavailability with gastrointestinal transit by scintigraphic monitoring of 171Er labeled sustained-release tablets. Pharm Res 4:486–489
Pemberton RE, Strand LJ (1979) A review of upper gastrointestinal effects of the newer NSAIDs. Dig Dis Sci 24:53–64
Pennington AK, Ratcliffe JH, Wilson CG, Hardy JG (1988) The influence of solution viscosity on nasal spray deposition and clearance. Int J Pharm 43:221–224
Phillips SF (1988) Small bowel. In: Kumar D, Gustavsson S (eds) An illustrated guide to gastrointestinal motility. John Wiley, Chichester, pp 187–206
Phipps PR, Gonda I, Bailey DL, Borham P, Bautovich G, Andersen SD (1989) Comparisons of planar and tomographic gamma scintigraphy to measure the penetration index of inhaled aerosols. Am Rev Respir Dis 139:1516–1523
Pool PE, Herron JM, Rosenblatt S, Reeves RL, Nappi JM, Staker LV, Dipette DJ, Evans RR (1989) Sustained release diltiazem: duration of antihypertensive effect. J Clin Pharmacol 29:533–537
Price JMC, Davis SS, Wilding IR (1991) The effect of fibre on gastrointestinal transit times in vegetarians and omnivores. Int J Pharm 76:123–131
Proctor DF (1977) The upper airway I. Nasal physiology and defence of the lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis 115:97–129
Robertson CS, Hardy JG (1988) Oesophageal transit of small tablets. J Pharm Pharmacol 40:595–596
Ruffin RE, Dolovich MB, Wolff RK, Newhouse MT (1978) The effects of preferential deposition of histamine in the human airway. Am Rev Respir Dis 117:485–492
Simonds AK, Newman SP, Johnson MA, Talaee N, Lee C, Clarke SW (1989) Alveolar targeting of aerosol pentamidine: towards a rational delivery system. Am Rev Respir Dis 141:827–829
Smelt GJC, Lee SW, Hardy JG, Wilson CG (1987) The effect of Mucodyne on nasal clearance in healthy adults. Clin Otolaryngol 12:7–10
Thorsson L, Newman SP, Weisz A, Trofast E, Morén F (1992) Nasal distribution of budesonide inhaled via a powder inhaler. Rhinology (in press)
Tothill P, McLoughlin GP, Heading RC (1978) Techniques and errors in scintigraphic measurements of gastric emptying. J Nucl Med 19:256–261
Trondstad RI, Aadland E, Holler T, Olaussen B (1985) Gastroscopic findings after treatment with enteric-coated and plain naproxen tablets in healthy subjects. Scand J Gastroenterol 20:239–242
Vidgren M, Karkkainen A, Karjalainen P, Paronen P (1987) A novel labelling method for measuring the deposition of drug particles in the respiratory tract. Int J Pharm 37:239–244
Wilding IR, Hardy JG, Davis SS, Melia CD, Evans DF, Short AH, Sparrow RA, Yeh KC (1991a) Characterisation of the in-vivo behaviour of a controlled release formulation of levodopa (Sinemet CR). Clin Neuropharmacol 14:305–321
Wilding IR, Davis SS, Hardy JG, Robertson CS, John VA, Powell MA, Leal M, Lloyd P, Walker SM (1991b) Relationship between the systemic drug absorption and gastrointestinal transit after the simultaneous oral administration of carbamazepine as a controlled release system and a suspension of 15N-labelled drug to healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 32:573–579
Wilding IR, Hardy JG, Maccari M, Ravelli V, Davis SS (1991c) Scintigraphic and pharmacokinetic assessment of a multiparticulate sustained release formulation of diltiazem. Int J Pharm 76:133–143
Wilding IR, Davis SS, Bakhshaee M, Stevens HNE, Sparrow RA, Brennan J (1992a) Gastrointestinal transit and systemic absorption of captopril from a pulsed release formulation. Pharm Res 9:654–657
Wilding IR, Davis SS, Sparrow RA, Horton RJ (1992b) The role of gastric emptying in the absorption and metabolism of nifedipine from a sustained release pellet formulation. Int J Pharm (in press)
Wilding IR, Davis SS, Sparrow RA, Bloor JR, Hayes G, Ward GT (1992c) The effect of food on the in-vivo behaviour of a novel sustained release formulation of tiaprofenic acid. Int J Pharm (in press)
Williams CN, Haber G, Aquino JA (1987) Double-blind, placebo-controlled evaluation of 5-ASA suppositories in active distal proctitis and measurement of extent of spread using 99mTc-labeled 5-ASA suppositories. Dig Dis Sci 32 [Suppl]:71S–75S
Wood E, Wilson CG, Hardy JG (1985) The spreading of foam and solution enemas. Int J Pharm 25:191–197
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: S.P. Newman
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davis, S.S., Hardy, J.G., Newman, S.P. et al. Gamma scintigraphy in the evaluation of pharmaceutical dosage forms. Eur J Nucl Med 19, 971–986 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175865
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175865