Abstract
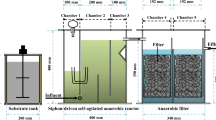
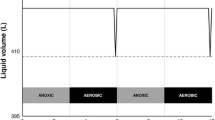
In this study an attempt has been made to find a solution to the problem of disposal of distillery effluents through anaerobic followed by aerobic treatment. Accordingly, experimental studies were planned and carried out in two phases. The first phase experimentation was conducted to study the performance of Semicontinuous Fixed Film Anaerobic Reactors (SCFFAR) which simulate Downflow Stationary Fixed Film anaerobic reactors (DSFF) for partial treatment of distillery waste. Second phase experimentation included studies on degradation of anaerobically treated effluent employing semicontinuous aerobic reactors with sludge recycle. The results indicated that the distillery waste should be diluted to bring down the COD to about 50 000 mg L−1 before the same is treated by stationery fixed film anaerobic reactors and this dilution can be achieved by circulating the treated effluent. Further the reduction of COD beyond 9000 to 10 000 mg L−1 by anaerobic treatment appears to be uneconomical. Results of second phase of the study show that the aerobic degradation of anaerobically treated effluent can achieve significant COD reduction (approx. 67%). However, reduction of COD of final effluent below 500 mg L−1 appears to be very difficult. The settling characteristics of the sludge produced in aerobic study depended on the BSRT value and improved with increase in BSRT.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA, AWWA, WPCF: 1981, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 15th, Ed., Washington, D.C., U.S.A.
Benefield, L. D. and Randall, C. W.: 1980, Biological Process Design for Wastewater Treatment, Prentice Hall Inc., Englewood Cliffs, N.J., U.S.A.
Dellalo, R. and Albertson, O. F.: 1961, J. Water Poll. Control Fed. 33, 356.
Dick, R. I. and Young, K. W.: 1972, Analysis of Thickening Performance of Final Settling Tanks, Presented at the 27 th Purdue Industrial Conference, May 1972, Lafayette, Indiana.
Henze, M. and Harremoes, P.: 1983, Water. Sci. Tech. 15, 1.
Iyengar, L., Tare, V., and Venkobachar, C.: 1986, ‘Comparative Evaluation of Different Support Media, in Attached Growth Anaerobic Treatment of Distillery Waste’, Proc. Annual Conf. Indian Assoc. Water Poll. Control, 22–27.
Jewel, W. J.: 1982, ‘Anaerobic Attached Film Expanded Bed Fundamentals, Proc. First Intl. Conf. on Fixed Film Biological Processes 1, 17–42.
Kuester, J. L. and Mize, J. H.: 1973, Optimisation Techniques in Fortran, McGraw-Hill Inc., N.Y., U.S.A.
Lutskaya, B. P. and Cherkashina, N. V.: 1986, Fermentn. Spirit. Prom.-st. 5, 8.
Seth, R.: 1986, Modelling and Simulation of Fixed Film Once-Through Anaerobic Reactors, M. Tech. Thesis, Dept. of Civil Engineering, IIT, Kanpur, India.
Shrihari, S.: 1987, 'Anaerobic-Aerobic Treatment of Distillery Effluents, M. Tech. Thesis, Dept. of Civil Engineering, IIT, Kanpur, India.
Tambe, M.: 1986, CEW, Chemical Engg World 21, 59.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Author for all correspondence.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shrihari, S., Tare, V. Anaerobic-aerobic treatment of distillery wastes. Water Air Soil Pollut 43, 95–108 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175586
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175586