Summary
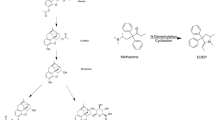
Assays for the potent, highly lipophilic analgesic buprenorphine described in the literature include the radioimmunoassay (RIA), radioreceptor assay (RRA) and selected ion-monitoring. Problems arise with the use of hazardous and unstable ligand in the RIA and RRA and the need for an extraction step for RRA and selected ion-monitoring. An enzyme immunoassay (EIA) was developed to allow rapid and simple analysis of plasma concentrations of drug without these disadvantages. The N-dealkylated derivative of buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine, was labelled with β-d-galactosidase using the linking agent N-(γ-maleimidobutyryloxy) succinimide. This enzyme-labelled hapten was used to develop an EIA for buprenorphine. The assay is sensitive enough to measure 10 pg of buprenorphine. Endogenous opioid peptides do not cross-react in the assay; norbuprenorphine itself was completely cross-reactive. Since the presence of plasma (100 μl) has no effect on the standard curve, plasma levels in humans were determined by this EIA without extraction after intravenous or sublingual administration of the drug. The EIA therefore represents a good alternative to existing assays for buprenorphine-like material with the advantages of simplicity, safety, sensitivity and ease of handling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartlett AJ, Lloyd-Jones JG, Rance MJ, Flockhart IR, Dockray GJ, Bennett MRD, Moore RA (1980) The radioimmunoassay of buprenorphine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 18:339–345
Blom Y, Bondesson U (1985) Analysis of buprenorphine and its N-dealkylated metabolite in plasma and urine by selected-ion monitoring. J Chromatogr 338:89–98
Bullingham RES, McQuay HJ, Porter EJB, Allen MC, Moore RA (1982) Sublingual buprenorphine used postoperatively: ten hour plasma drug concentration analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol 13:665–673
Kato K, Hamaguchi Y, Fukui H, Ishikawa E (1975) I. Novel method for synthesis of the insulin- β-d-galactosidase conjugate and its applicability for insulin assay. J Biochem 78:235–237
Kitagawa T, Aikawa T (1976) Enzyme coupled immunoassay of insulin using a novel coupling reagent. J Biochem 79:233–236
Kitagawa T, Kawasaki T, Munechika H (1982) Enzyme immunoassay of Blasticidin S with high sensitivity: a new and convenient method for preparation of immunogenic (hapten-protein) conjugates. J Biochem 92:585–590
Tanimori H, Kitagawa T, Tsunoda T, Tsuchiya R (1981) Enzyme immunoassay of neocarzinostatin using β-galactosidase as label. J Pharm Dyn 4:812–819
Ueno A, Oh-Ishi S, Kitagawa T, Katori M (1981) Enzyme immunoassay of bradykinin using β-d-galactosidase as a labelling enzyme. Biochem Pharmacol 30:1659–1664
Villiger JW, Boas RA, Taylor KM (1981) A radioreceptor assay for opiate drugs in human cerebrospinal fluid and plasma. Life Sci 29:229–233
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by a Scholarship from Reckitt and Colman to G. K. L. Tiong
Send offprint requests to G. K. L. Tiong at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiong, G.K.L., Olley, J.E. Enzyme immunoassay of buprenorphine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 338, 202–206 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00174871
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00174871