Summary
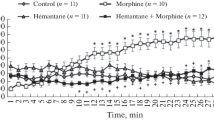
The influences of the indirect serotonin agonist fenfluramine (5; 10 mg/kg s.c.), the serotonin antagonist metergoline (5; 10 mg/kg s.c.) and the 5-HT1A agonist 8-OHDPAT (0.1; 0.2; 0.46 mg/kg s. c.) on haloperidol-induced catalepsy in rats or mice and on morphine-induced catalepsy in rats were studied. Morphine-induced catalepsy was enhanced by fenfluramine and attenuated by metergoline, whereas neither fenfluramine nor metergoline had any effect on haloperidol-induced catalepsy. 8-OHDPAT strongly antagonised catalepsy induced by morphine or haloperidol. We conclude that serotonergic transmission plays a major role in effectuating morphine catalepsy but not in effectuating haloperidol catalepsy. The antagonistic effect of 8-OHDPAT suggests a secondary, modulating role for 5-HT1A receptor mediated events in both types of catalepsy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnt J, Hyttel J, Bach-Lauritsen T (1986) Further studies on the mechanism behind scopolamine-induced reversal of antistereotypic and cataleptogenic effect of neuroleptics in rats. Acta Pharmacol et Toxicol 59:319–324
Balsara JJ, Jadhav JH, Chandorkar AG (1979a) Effects of drugs influencing central serotonergic mechanisms on haloperidolinduced catalepsy. Psychopharmacology 62:67–69
Balsara JJ, Jadhav JH, Muley MP, Chandorkar AG (1979b) Effect of drugs influencing central 5-hydroxytryptaminergic mechanisms on morphine-induced catalepsy in the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol 31:255–257
Barnett A, Goldstein J, Fiedler E, Taber R (1975) Etonitazineinduced rigidity and its antagonism by centrally acting muscle relascants. Eur J Pharmacol 30:23–28
Berendsen HHG, Broekkamp CLE (1987) Drug induced penile erections in rats: indications for serotoninIB-receptor mediation. Eur J Pharmacol 135:279–287
Broekkamp CL, LePichon M, Lloyd KG (1984) Akinesia after locally applied morphine near the nucleus raphe pontis of the rat. Neurosci Lett 50:313–318
Bruinvels J (1970) Effects of noradrenaline, dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine on body temperature in the rat after intracisternal administration. Neuropharmacology 9:277–282
Carter CJ, Pycock CJ (1977) Possible importance of 5-hydroxytryptamine in neuroteptic-induced catalepsy in rats. Br J Pharmacol 60:267P
Carter CJ, Pycock CJ (1978) A study of the sites of interaction between dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine for the production of fluphenazine-induced catalepsy. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 304:135–139
Ceulemans DLS, Gelders YG, Hoppenbrouwers MLJA, Reyntjens AJM, Janssen PAJ (1985) Effect of serotonin antagonism in schizophrenia: A pilot study with setoperone. Psychopharmacology 85:329–332
Costall B, Naylor RJ (1974) On catalepsy and catatonia and the predictability of the catalepsy test for neuroleptic activity. Psychopharmacology 34:233–241
De Ryck M, Schallert T, Teitelbaum P (1980) Morphine versus haloperidol catalepsy in the rat: a behavioral analysis of postural support mechanisms. Brain Res 201:143–172
Engel G, Göthert M, Hoyer D, Schlicker E, Hillenbrand K (1986) Identity of inhibitory presynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) autoreceptors in the rat brain cortex with 5-HT1B binding sites. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 332:1–7
Fuenmayor LD, Vogt M (1979) The influence of cerebral 5-hydroxytryptamine on catalepsy induced by brain-amine depleting neuroleptics or by cholinomimetics. Br J Pharmacol 67:309–318
Grahame-Smith DG (1971) Studies in vivo in the relationship between brain tryptophan, brain 5-HT synthesis and hyperactivity in rats treated with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor and l-tryptophan. J Neurochem 18:1053–1066
Goodwin GM, Green AR (1985) A behavioural and biochemical study in mice and rats of putative selective antagonists for 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 84:743–753
Heuring RE, Peroutka SJ (1987) Characterization of a novel 3H-5-hydroxytryptamine binding site subtype in bovine brain membranes. J Neurosci 7:894–903
Janssen PAJ, Niemegeers CJE, Awouters F, Schellekens KHL, Megens AAHP, Meert TF (1988) Pharmacology of risperidon (R 64 766), a new antipsychotic with serotonin-S2 and dopamine-D2 antagonistic properties. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 244:685–693
Juul Povlsen U, Noring U, Lund Larssen A, Korsgaard S, Gerlach J (1986) Effect of serotonergic and anticholinergic drugs in haloperidol-induced dystonia in cebus monkeys. Clin Neuropharmacol 9:84–90
Koella WP, Czicman J (1966) Mechanism of the EEG-synchronizing action of serotonin. Am J Physiol 211(4):926–934
Korsgaard S, Friis T (1986) Effects of mianserin in neurolepticinduced parkinsonism. Psychopharmacology 88:109–111
Kostowski W, Gumulka W, Czlonkowski A (1972) Reduced cataleptogenic effects of some neuroleptics in rats with lesioned midbrain raphe and treated with p-chlorophenylalanine. Brain Res 48:443–446
Maj J, Mogilnicka E, Przewlocka B (1975) Antagonistic effect of cyproheptadine on neuroleptic-induced catalepsy. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 3:25–27
McMillen BA, Mattiace LA (1983) Comparative neuropharmacology of buspirone and MJ-13805, a potential anti-anxiety drug. J Neural Trans 57:255–265
Sarnek J, Baran L (1975) The effect of 5-hydroxytryptamine synthesis inhibitors on neuroleptic-induced catalepsy in rats. Arch Immunol et Ther Exp 23:511–516
Scott SM, DaVanzo EA, McMillen BA (1987) Reversal of neuroleptic induced catalepsy by novel aryl-piperazine anxiolytic drugs. Soc Neurosci Abstr 13:453
Scheel-Krüger J, Golembiowska K, Mogilnicka E (1977) Evidence for increased apomorphine-sensitive dopaminergic effects after acute treatment with morphine. Psychopharmacology 53:55–63
Svendsen O, Arnt J, Boeck V, Bøgesø KP, Christensen AV, Hyttel J, Larsen JJ (1986) The neuropharmacological profile of tefludazine, a potential antipsychotic drug with dopamine and serotonin receptor antagonistic effects. Drug Develop Res 7:35–47
Tricklebank MD, Forler C, Fozard JR (1984) The involvement of subtypes of the 5-HT1 receptor and of catecholaminergic systems in the behavioural response to 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 106:271–282
Vidali M, Fregnan GB (1979) Effect of different CNS-active drugs on the catalepsy induced by neuroleptics. Curr Therap Res 25(4):544–556
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to C. L. E. Broekkamp at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Broekkamp, C.L.E., Oosterloo, S.K., Berendsen, H.H.G. et al. Effect of metergoline, fenfluramine, and 8-OHDPAT on catalepsy induced by haloperidol or morphine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 338, 191–195 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00174869
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00174869