Abstract
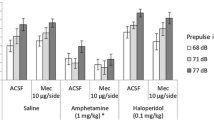
Rats were presented with noise bursts alone or noise bursts 60 ms after presentation of either a 60 dB or an 80 dB prepulse after injection of the dopamine agonists apomorphine (3 mg/kg) or d-amphetamine (4 mg/kg), the glycine antagonist strychnine (1.5 mg/kg) or the α2 antagonist yohimbine (5 mg/kg). Presentation of prepulses inhibited startle, with greater inhibition following an 80 dB versus 60 dB prepulse. Apomorphine, d-amphetamine and strychnine increased overall startle levels but did not attenuate prepulse inhibition, since the absolute change in startle following prepulse presentation was significantly greater after administration of these drugs. A lower dose of apomorphine also increased startle but had no effect on prepulse inhibition using test intervals of 10, 60, 100, 200 or 1000 ms. While these drugs did decrease per cent prepulse inhibition, this seemed wholly attributable to their increasing overall startle levels, rather than a real attenuation of prepulse inhibition. Yohimbine did not alter either startle baseline or prepulse inhibition. The results do not support the conclusion that overactivity of dopamine systems attenuates prepulse inhibition and, in addition, suggest that prepulse inhibition does not result from activation of either glycine or norepinephrine projecting to α2 adrenergic receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown MC, Nuttall AL, Masta RI (1983) Intracellular recordings from cochlear inner hair cells: effects of stimulation of the crossed olivocochlear efferents. Science 222:69–71
Cassella JV, Davis M (1986) The design and calibration of a startle measurement system. Physiol Behav 36:377–383
Davis M (1980) Neurochemical modulation of sensory-motor reactivity: acoustic and tactile startle reflexes. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 4:241–263
Davis M (1982) A primary acoustic startle circuit: lesion and stimulation studies. J Neurosci 2:791–805
Davis M, Aghajanian GK (1976) Effects of apomorphine and haloperidol on the acoustil startle response in rats. Psychopharmacology 47:217–223
Davis M, Astrachan DI (1981) Spinal modulation of acoustic startle: opposite effects of clonidine and d-amphetamine. Psychopharmacology 75:219–225
Davis M, Cedarbaum JM, Aghajanian GK, Gendelman DS (1977) Effects of clonidine on habituation and sensitization of acoustic startle in normal, decerebrate and locus coeruleus lesioned rats. Psychopharmacology 51:243–253
Daigneault EA (1981) Pharmacology of the cochlear effects. In: Brown DR, Daigneault EA (eds) Pharmacology of hearing experimental and clinical bases. Wiley, New York, pp 137–151
Fechter LD (1974a) Central serotonin involvement in the elaboration of the startle reaction in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2:161–171
Fechter LD (1974b) The effects of l-DOPA, clonidine, and apomorphine on the acoustic startle reaction in rats. Psychopharmacologia 39:331–344
Fechter LD, Young JS (1983) Discrimination of auditory from nonauditory toxicity by reflex modulation audiometry: effects of triethyltin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 70:216–227
Galambos R (1956) Suppression of auditory nerve activity by stimulation of efferent fibers to cochlea. J Neurophysiol 19:424–437
Geyer MA, Mansbach R, Braff DL (1987) Dopamine agonists and antagonists in an animal model of sensory gating and schizophrenia. Proc Soc Biol Psychiatry, pp 156
Guinan JJ Jr, Warr WB, Norris BE (1983) Differential olivocochlear projections from lateral versus medial zones of the superior olivary complex. J Comp Neurol 221:358–370
Guinan JJ Jr, Warr WB, Norris BE (1984) Topographic organization of the olivocochlear projections from the lateral and medial zones of the superior olivary complex. J Comp Neurol 226:21–27
Hoffman H, Cohen ME, English LM (1985) Reflex modification by acoustic signals in newborn infants and in adults. J Exp Child Psychol 39:562–579
Hoffman HS, Ison JR (1980) Reflex modification in the domain of startle: I. some empirical findings and their implications for how the nervous system processes sensory input. Psychol Rev 2:175–189
Hoffman HS, Searle JL (1965) Acoustic variables in the modification of startle reaction in the rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol 60:53–58
Kehne JH, Sorenson CA (1978) The effects of pimozide and phenoxybenzamine pretreatments on amphetamine and apomorphine potentiation of the acoustic startle response in rats. Psychopharmacology 58:137–144
Kehne JH, Gallager DW, Davis M (1981) Strychnine: brainstem and spinal mediation of excitatory effects on acoustic startle. Eur J Pharmacol 76:177–186
Leitner DS, Cohen ME (1985) Role of the inferior colliculus in the inhibition of acoustic startle in the rat. Physiol Behav 34:65–70
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA, Braff DL (1988) Dopaminergic stimulation disrupts sensorimotor gating in the rat. Psychopharmacology (in press)
Ornitz EM, Guthrie D, Kaplan AR, Lane SJ, Norman RJ (1986) Maturation of startle modulation. Psychophysiology 23:624–634
Parisi T, Ison JR (1979) Development of the acoustic startle response in the rat: ontogenetic changes in the magnitude of inhibition by prepulse stimulation. Dev Psychobiol 12:219–230
Saitoh K, Shaw S, Tilson HA (1986) Noradrenergic influence on the prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle. Toxicol Lett 34:209–216
Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Geyer MA, Koob GF (1986) Central dopamine hyperactivity in rats mimics abnormal acoustic startle response in schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry 21:23–33
Swerdlow NR, Koob GF, Geyer MA, Mansbach R, Braff DL (1988) A cross-species model of psychosis: mesolimbic dopamine hyperactivity in rats mimics abnormal acoustic startle response in schizophrenics. In: Soubrie P (ed) Animal models of psychiatric disorders. Karger, Zurich (in press)
Wecker JR, Ison JR (1986) Effects of motor activity on the elicitation and modification of the startle reflex in rats. Anim Learn Behav 14:287–292
White JS, Warr WB (1983) The dual origins of the olivocochlear bundle in the albino rat. J Comp Neurol 219:203–214
Young JS, Fechter LD (1983) Reflex inhibition procedures for animal audiometry: a technique for assessing ototoxicity. J Acoust Soc Am 73:1686–1693
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davis, M. Apomorphine, d-amphetamine, strychnine and yohimbine do not alter prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex. Psychopharmacology 95, 151–156 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00174500
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00174500