Summary
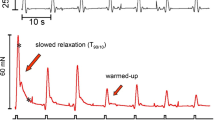
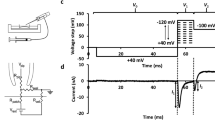
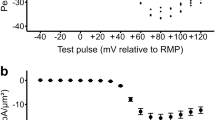
The purpose of the present study was to analyze the effects of cromakalim (BRL 34915), a potent drug from a new class of drugs characterized as “K+ channel openers”, on the electrical activity of human skeletal muscle. Therefore, intracellular recordings were used to measure the effects of cromakalim on the membrane potential and input conductance of fibres from human skeletal muscle biopsies. Cromakalim in a concentration above 1 μmol/l induced an increase in membrane K+ conductance. This effect resulted in a membrane hyperpolarization. The magnitude of this polarization depended on the difference between resting and K+ equilibrium potential. The effect had a rapid onset and was quickly reversible after washing. Fibres from two patients with hyperkalaemic periodic paralysis showed an excessive membrane depolarization during and also after exposure to an slightly elevated extracellular K+ concentration. In the latter situation, cromakalim repolarized the fibres to the normal resting potential. Tolbutamide (1 mmol/l) and Ba2+ (3 mmol/l) strongly antagonized the effect of cromakalim. The data show that cromakalim hyperpolarizes depolarized human skeletal muscle fibres maintained in vitro. The underlying mechanism is probably an activation of otherwise “silent”, ATP-regulated K+ channels. Such an effect may be of therapeutic benefit in a situation in which a membrane depolarization causes muscle paralysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian RH, Marshall MW (1977) Sodium currents in mammalian muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 268: 223–250
Alzheimer C, ten Bruggencate G (1988) Actions of BRL 34915 (cromakalim) upon convulsive discharges in guinea pig hippocampal slices. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337: 429–434
Ashcroft FM (1988) Adenosine 5′-triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels. Annu Rev Neurosci 11: 97–118
Belles B, Hescheler J, Trube G (1987) Changes of membrane currents in cardiac cells induced by long whole-cell recordings and tolbutamide. Pflügers Arch 409: 582–588
Bendheim PE, Reale EO, Berg BO (1985) β-Adrenergic treatment of hyperkalaemic periodic paralysis. Neurology 35: 746–749
Bretag AG (1969) Synthetic interstitial fluid for isolated mammalian tissue. Life Sci 8: 319–329
Castle NA, Haylett DG (1987) Effect of channel blockers on potassium efflux from metabolically exhausted frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 383: 31–43
Escande D, Thuringer D, Leguern S, Cavero I (1988) The potassium channel opener cromakalim (BRL 34915) activates ATP-dependent K+ channels in isolated cardiac myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 154: 620–625
Gallant EM (1983) Barium-treated mammalian skeletal muscle: similarities to hypokalaemic periodic paralysis. J Physiol (Lond) 335: 577–590
Hamilton TC, Weir SW, Weston AH (1986) Comparison of the effects of BRL 34915 and verapamil on electrical and mechanical activity in rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol 88: 103–111
Hollingsworth M, Amédée T, Edwards D, Mironneau J, Savineau JP, Small RC, Weston AH (1987) The relaxant action of BRL 34915 in rat uterus. Br J Pharmacol 91: 803–813
Horowicz P, Spalding BC (1986) Electrical and ionic properties of the muscle cell membrane. In: Engel AG, Banker BO (eds) Myology. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 445–470
Iaizzo PA, Lehmann-Horn F (1988) Long cut muscle fibers repolarize and possess electrical and mechanical properties of intact human skeletal muscle. Pflügers Arch 411: R191
Kreye VAW, Gerstheimer F, Weston AH (1987) Effects of the anti-hypertensive, BRL 34915, on membrane potential and 86Rb efflux in rabbit tonic vascular smooth muscle. Pflügers Arch 408: R79
Lehmann-Horn F, Rüdel R, Ricker K, Lorkovic H, Dengler R, Hopf HC (1983) Two cases of adynamia episodica hereditaria: in vitro investigation of muscle cell membrane and contraction parameters. Muscle Nerve 6: 113–121
Lehmann-Horn F, Küther G, Ricker K, Grafe P, Ballanyi K, Rüdel R (1987a) Adynamia episodia hereditaria with myotonia: a non-inactivating sodium current and the effect of extracellular pH. Muscle Nerve 10: 363–374
Lehmann-Horn F, Rüdel R, Ricker K (1987b) Membrane defects in paramyotonia congenita (Eulenburg). Muscle Nerve 10: 633–641
Osterrieder W (1988) Modification of K+ conductance of heart cell membrane by BRL 34915. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337: 93–97
Quast U (1987) Effect of the K+ efflux stimulating vasodilator BRL 34915 on 86Rb+ efflux and spontaneous activity in guinea-pig portal vein. Br J Pharmacol 91: 569–578
Rüdel R (1986) The pathophysiological basis of the myotonias and the periodic paralyses. In: Engel AG, Banker BQ (eds) Myology. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1297–1311
Spruce AE, Standen NB, Stanfield PR (1987) Studies of the unitary properties of adenosine 5′-triphosphate-regulated potassium channels of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 382: 213–236
Stanfield PR (1987) Nucleotides such as ATP may control the activity of ion channels. TINS 10: 335–339
Sturgess NC, Ashford MLJ, Cook DL, Hales CN (1985) The sulphonylurea receptor may be an ATP-sensitive potassium channel. The Lancet 11: 474–475
Wang P, Clausen T (1976) Treatment of attacks in hyperkalaemic familial periodic paralysis by inhalation of salbutamol. The Lancet I: 221–223
Weir SW, Weston AH (1986) The effects of BRL 34915 and nicorandil on electrical and mechanical activity and on 86Rb efflux in rat blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol 88: 121–128
Weston AH, Abbott A (1987) New class of antihypertensive acts by opening K+ channels. TIPS 8: 283–284
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to A. Spuler at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spuler, A., Lehmann-Horn, F. & Grafe, P. Cromakalim (BRL 34915) restores in vitro the membrane potential of depolarized human skeletal muscle fibres. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 339, 327–331 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173587
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173587