Summary
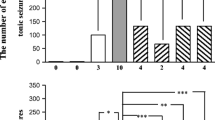
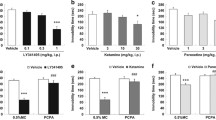
The effects of the non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist GYKI 52466 (2.4 and 4.8 mg/kg, i.p.) on spontaneous locomotor activity and haloperidol-induced catalepsy (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.) were assessed in naive rats and in rats pretreated with the NMDA antagonist dizocilpine (0.08 mg/kg, i.p.). GYKI 52466 given alone did not alter locomotor activity and haloperidol-induced catalepsy, but significantly antagonized the dizocilpine-induced locomotor stimulation and counteracted the anti-cataleptic effects of dizocilpine on haloperidol-induced catalepsy. Thus blockade of non-NMDA glutamate receptors antagonized the behavioural stimulant effects of a NMDA receptor blockade.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albin RL, Young AB, Penney JB (1989) The functional anatomy of basal ganglia disorders. Trends Neurosci 12:366–375
Albin RL, Makowiec RL, Hollingsworth ZR, Dure IV LS, Penney JB, Young AB (1992) Excitatory amino acid binding sites in the basal ganglia of the rat: A quantitative autoradiographic study. Neuroscience 46:35–48
Arvin B, Moncada C, Le Peillet E, Chapman A, Meldrum BS (1992) GYKI 52466 blocks the increase in extracellular glutamate induced by ischaemia. Neuro Rep 3:235–238
Brotchie JM, Mitchell IJ, Sambrook MA, Crossman AR (1991) Alleviation of Parkinsonism by antagonism of excitatory amino acid transmission in the medial segment of the globus pallidus in rat and primate. Movement Dis 6:133–138
Brotchie JM, Mitchell IJ, Crossman AR (1992) The NMDA receptor-associated glycine site: A target for symptomatic treatment of Parkinson's disease? Eur J Neurosci [Suppl] 5:237
Bubser M, Keseberg U, Notz PK, Schmidt WJ (1992) Differential behavioural and neurochemical effects of competitive and non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonists in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 229:75–82
Carlsson M, Carlsson A (1989) The NMDA antagonist MK-801 causes marked locomotor stimulation in monoamine depleted mice. J Neural Transm 75:221–226
Chen H-SV, Pellegrini JW, Aggarwal SK, Lei SZ, Warach S, Jensen FE, Lipton SA (1992) Open-channel block of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) responses by memantine: Therapeutic advantage against NMDA receptor-mediated neurotoxicity. J Neurosci 12:4427–4436
Graham WC, Robertson RG, Sambrook MA, Crossman AR (1990) Injection of excitatory amino acid antagonists into the medial pallidal segment of a 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) treated primate reverses motor symptoms of parkinsonism. Life Sci 47:91–97
Greenamyre JT (1992) Actions of glutamate antagonists in the MPTP primate model of Parkinson's disease. Eur J Neurosci [Suppl] 5: p 238
Hauber W, Schmidt WJ (1990) The NMDA antagonist dizocilpine (MK-801) reverses haloperidol-induced movement initiation deficits. Behav Brain Res 41:161–166
Headley PM, Grillner S (1991) Excitatory amino acids and synaptic transmission: the evidence for a physiological function. In: Lodge D, Collingridge G (eds) The pharmacology of excitatory amino acids. Trends Pharmacol Sci (Special Report), pp 30–36
Hoffman DC (1992) Typical and atypical neuroleptics antagonize MK-801-induced locomotion and stereotypy in rats. J Neural Transm 89:1–10
Honoré T (1991) Inhibitors of kainate and AMPA ionophore receptors. In: Meldrum BS (ed) Excitatory Amino Acid Antagonists, Blackwell Scientific, Oxford pp 180–194
Honoré T, Davies SN, Drejer J, Fletcher EJ, Jakobsen P, Lodge D, Nielsen FE (1988) Quinoxalinediones: Potent competitive non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonists. Science 241:701
Imperato A, Honoré T, Jensen LH (1990) Dopamine release in the nucleus caudatus and in the nucleus accumbens is under glutamatergic control through non-NMDA receptors: A study in freely-moving rats. Brain Res 530:223–228
Klockgether T, Turski L, Honoré T, Zhang Z, Gash DM, Kurlan R, Greenamyre JT (1991) The AMPA receptor antagonist NBQX has antiparkinsonian effects in monoamine-depleted rats and MPTP-treated monkeys. Ann Neurol 30:717–723
Löschmann P-A, Lange KW, Kunow M, Rettig K-J, Jähnig P, Honoré T, Turski L, Wachtel H, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1991) Synergism of the AMPA-antagonist NBQX and the NMDA-antagonist CPP with L-Dopa in models of Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm 3:203–213
Monaghan DT, Bridges RJ, Cotman CW (1989) The excitatory amino acid receptors: Their classes, pharmacology, and distinct properties in the function of the central nervous system. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 29:365–402
Quardouz M, Durand J (1991) GYKI 52466 antagonizes glutamate responses but not NMDA and kainate responses in rat abducens motoneurones, Neurosci Lett 125:5–8
Papa SM, Engber TM, Boldry RC, Chase TN (1993) Opposite effects of NMDA and AMPA receptor blockade on catalepsy induced by dopamine receptor antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol 232:247–253
Sanberg PR, Bunsey MD, Giordano M, Norman AB (1988) The catalepsy test: its ups and downs. Behav Neurosci 102:748–759
Scheel-Krüger J (1983) The GABA receptor and animal behavior. In: Enna SJ (ed) The GABA receptors. Clifton NJ, The Humana Press, pp 215–256
Schmidt WJ, Bubser M (1989) Anticataleptic effects of the N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist MK-801 in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 32:621–623
Schmidt WJ, Bubser M, Hauber W (1992) Behavioural pharmacology of glutamate in the basal ganglia. J Neural Transm 38:65–89
Smith SE, Dürmüller N, Meldrum BS (1991) The Non-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists, GYKI 52466 and NBQX are anticonvulsant in two animal models of reflex epilepsy. Eur J Pharmacol 201:179–183
Svensson A, Carlsson A, Carlsson ML (1992) Differential locomtor interactions between dopamine D1/D2 receptor agonists and the NMDA antagonist dizocilpine in monoamine-depleted mice. J Neural Transm 90:199–217
Tarnawa I, Farkas S, Berzsenyi P, Pataki A, Andrasi F (1989) Electrophysiological studies with a 2,3-benzodiazepine muscle relaxant: GYKI 52466. Eur J Pharmacol 167:193
Tarnawa I, Engberg I, Flatman JA (1990) GYKI 52466, an inhibitor of spinal reflexes is a potent quisqualate antagonist. In: Lubec G, Rosenthal GA (eds) Amino acids. Chemistry, Biology, and Medicine, Escom, Leiden, pp 538–546
Tiedke PI, Bischoff C, Schmidt WJ (1990) MK-801-induced stereotypy and its antagonism by neuroleptic drugs. J Neural Transm 81:173–182
Yoshida Y, Ono T, Kizu A, Fukushima R, Miyagishi T (1991) Striatal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in haloperidol-induced catalepsy. Eur J Pharmacol 203:173–180
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: W. Hauber at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hauber, W., Andersen, R. The non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist GYKI 52466 counteracts locomotor stimulation and anticataleptic activity induced by the NMDA antagonist dizocilpine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 348, 486–490 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173207
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173207