Abstract
The aim of this study was to compare the stimulus-response characteristics of the cholinergic and tachykininergic excitatory transmission to the circular muscle of the guinea-pig proximal colon and their susceptibility to inhibition by the N-type calcium channel blocker ω-conotoxin (CTX). All experiments were performed in the presence of guanethidine (3 μM), indomethacin (10 μM), L-nitroarginine (L-NOARG, 30 μM) and apamin (0.1 μM). In the presence of the tachykinin receptor antagonists, FK 888 (10 μM) and GR 94800 (3 μM), to block NK1 and NK2 receptors, respectively, electrical field stimulation (EFS) produced frequency-dependent atropine- (1 μM) sensitive contractions. In the presence of atropine (1 μM), EFS produced tachykininergic contractions which were abolished by the combined administration of FK 888 (10 μM) and GR 94 800 (3 μM). The maximal responses produced by cholinergic and tachykininergic neurotransmission ranged between 80 and 100% of the maximal contractile response to 80 mM KCI. The frequency of stimulation, pulse width and voltage required to produce 50% of the maximal cholinergic and tachykininergic contraction were not different from each other, although cholinergic transmission appeared more efficient in producing twitch contractions in response to single pulse EFS. Furthermore, cholinergic transmission was more efficient than tachykininergic transmission in producing contraction in response to short periods of EFS.
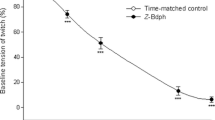
CTX (0.1 μM for 30 min) produced a large and comparable rightward shift of the cholinergic and tachykininergic frequency-response curve (19 and 17 fold increase in the frequency of stimulation producing 50% of the maximal response, respectively) and markedly depressed (51 and 43% inhibition, respectively) the maximal concentrations response. CTX failed to affect the contraction of the colon produced by submaximally effective concentrations of the muscarinic receptor agonist, methacholine (0.1–0.3 μM) and those produced by the tachykinin NK1 and NK2 receptor selective agonists [Sar9] substance P sulfone and [\Ala8] neurokinin A (4–10) (1–3 nM).
The present findings demonstrate that the cholinergic and tachykininergic components of the excitatory transmission to the circular muscle of the guinea-pig colon are activated at comparable intensities of nerve stimulation and are both inhibited, in a qualitatively and quantitatively comparable manner, by CTX at the prejunctional level. These findings are consistent with the idea that acetylcholine and tachykinins are co-released from the same population of enteric motoneurones which innervate the circular muscle of the colon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartho L, Holzer P (1985) Search for a physiological role of substance P in gastrointestinal motility. Neuroscience 16:1–32
Brookes SJH, Steele PA, Costa M (1991) Identification and immunohistochemistry of cholinergic and noncholinergic circular muscle motor neurons in the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience 42:863–878
Bucsics A, Holzer P, Lippe ITH, Pabst MA, Lembeck F (1986) Density distribution of guinea-pig myenteric plexus nerve endings containing immunoreactive substance P. Peptides 7:761–765
Costa M, Furness JB (1976) The peristaltic reflex: an analysis of the nerve pathways and their pharmacology. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 294:47–70
De Luca GG, Li CG, Rand MJ, Reid JJ, Thaina P, Wong-Dusting HK (1990) Effects of ω-conotoxin GVIA on autonomic neuroeffector transmission in various species. Br J Pharmacol 101:437–447
Furness JB, Costa M (1987) The enteric nervous system. Churchill Livingstone Edinburgh
Grider JR, Makhlouf GM (1986) Colonic peristaltic reflex: identification of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide as mediator of descending relaxation. Am J Physiol 251:G40-G45
Hökfelt T, Millhorn D, Seroogy K, Tsuruo Y, Ceccatelli S, Lindh B, Meister B, Melander T, Schalling M, Bartfai T, Terenius L (1987) Coexistence of peptides with classical transmitter. Experientia 43:768–780
Holzer P, Maggi CA (1994) Synergistic role of muscarinic acetylcholine and tachykinin NK2 receptors in intestinal peristalsis. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 349:194–201
Holzer P, Schluet W, Maggi CA (1993) Ascending enteric reflex contraction: roles of acetycholine and tachykinins in relation to distension and propagation of excitation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264: 391–396
Kupfermann I (1991) Functional studies of cotransmission. Physiol Rev 71:683–732
Maggi CA, Giuliani S (1993) Multiple inhibitory mechanisms mediate nonadrenergic noncholinergic relaxation in the circular muscle of the guinea-pig colon. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 347:630–634
Maggi CA, Patacchini R, Santicioli P, Lippe ITh, Giuliani S, Geppetti P, Del Bianco E, Selleri S, Meli A (1988) The effect of ω-conotoxin GVIA, a peptide modulator of the N-type voltage-sensitive calcium channels, on motor responses produced by activation of efferent and sensory nerves in mammalian smooth muscle. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 338:107–113
Maggi CA, Patacchini R, Meini S, Giuliani S (1994a) Effect of longitudinal muscle-myenteric plexus removal and indomethacin on the response to tachykinin NK2 and NK3 receptor agonists in the circular muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. J Autonom Pharmacol 14:49–60
Maggi CA, Patacchini R, Meini S, Quartara L, Sisto A, Potier E, Giuliani A, Giachetti A (1994b) Comparison of tachykinin NK1 and NK2 receptors of the guinea-pig ileum and proximal colon. Br J Pharmacol 112:150–160
Marino F, Marcoli M, De Ponti F, Lecchini S, Castelletti CM, Frigo GM (1993) Inhibition of endogenous acetylcholine release by blockade of voltage-dependent calcium channels in enteric neurons of the guinea-pig colon. J Pharm Pharmacol 45:449–452
Miller RJ (1987) Multiple calcium channels and neuronal function. Science 235:46–52
Yau WM, Mandel KG, Dorsett JA, Youther ML (1992) NK3 receptor regulation of acetylcholine release from myenteric plexus. Am J Physiol 263:G659-G664
Zagorodnyuk V, Santicioli P, Maggi CA (1993) Tachykinin NK1 but not NK2 receptors mediate non-cholinergic excitatory junction potentials in the circular muscle of guinea-pig colon. Br J Pharmacol 110:795–803
Zagorodnyuk V, Maggi CA (1994) Different role for tachykinin NK1 and NK2 receptors in mediating nonadrenergic noncholinergic (NANC) transmission in the guinea-pig colon. Neuropeptides 26 [Suppl 1]:58
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: C. A. Maggi at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maggi, C.A., Holzer, P. & Giuliani, S. Effect of ω-conotoxin on cholinergic and tachykininergic excitatory neurotransmission to the circular muscle of the guinea-pig colon. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 350, 529–536 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173023
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173023