Abstract
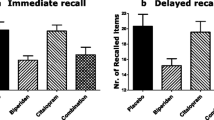
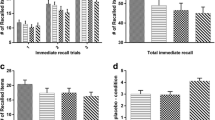
The effects on memory and psychomotor functions of four antidepressants which differ in sedative and anticholinergic properties were assessed. Amitriptyline (37.5, 70 mg), trazodone (100, 200 mg) viloxazine (100, 200 mg), protriptyline (10, 20 mg) or placebo were administered in a double blind, independent groups design in which 90 subjects participated. Subjects completed a battery of tests before and 2 and 4 h after drug administration. The different antidepressants produced different patterns of effects across tasks. The relatively non-sedating compounds viloxazine and protriptyline produced very similar profiles and did not impair psychomotor or memory functions. In contrast, the two more sedative antidepressants produced global impairments on test of attention, manual motor speed, recoding skills and primary memory. Although both amitriptyline and trazodone impaired performance on episodic memory tasks, the effect of amitriptyline was significantly greater and this may reflect specific anticholinergic action over and above global sedative effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baddeley AD, Sutherland A, Harris J (1982) How well do laboratory-based psychological tests predict patient's performance outside the laboratory? Aging 19:141–148
Bartus RT, Dean RL, Beer B, Lippa AS (1982) The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science 217:408–417
Bättig WF, Montague WE (1969) Category norms for verbal items in 56 categories: A replication and extension of the Connecticut Category Norms. J Exp Psychol 80:1–46
Bayliss PFC, Duncan SM (1974) The clinical pharmacology of viloxazine hydrochloride — a new antidepressant of novel chemical structure. Br J Clin Pharmac 1:431–437
Bond AJ, Lader MH (1974) The use of analogue scales in rating subjective feelings. Br J Med Psychol 47:211–218
Branconnier RJ, Devitt DR, Cole JO, Spera KF (1982) Amitriptyline selectively disrupts verbal recall from secondary memory of the normal aged. Neurobiol Aging 3:55–59
Brown J, Lewis V, Brown MW, Horn G, Bowes JB (1982) A comparison between transient amnesias induced by two drugs (diazepam and lorazepam) and amnesia of organic origin. Neuropsychologia 20:55–70
Bye C, Clubley M, Peck AW (1978) Drowsiness, impaired performance and tricyclic antidepressants drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol 6:155–162
Caine ED, Weingartner H, Ludlow CL, Cudahy EA, Wehry S (1981) Quantitative analysis of scopolamine-induced amnesia. Psychopharmacology 74:74–80
Collerton D (1986) Cholinergic function and intellectual decline in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience 19:1–28
Curran HV (1981) Tranquillizing memories: a review of the effects of benzodiazepines on human memory. Biol Psychol 23:179–213
Curran HV, Lader M (1986) The psychopharmacological effects of repeated doses of fluvoxamine, mianserin and placebo in healthy human subjects. Eur J Pharmacol 29:601–607
Curran HV, Shine P, Lader M (1986) Effects of repeated doses of fluvoxamine, mianserin and placebo on memory and measures of sedation. Psychopharmacology 89:360–363
Curran HV, Schiwy W, Lader M (1987) Differential amnesic properties of benzodiazepines: a dose-response comparison of two drugs with similar elimination half-lives. Psychopharmacology 92:358–364
Deutsch J (1971) The cholinergic synapse and the site of memory. Science 174:788–794
Drachman DA (1978) Central cholinergic system and memory. In: Lipton MA (ed) Psychopharmacology: a generation of progress. Raven Press, New York
Drachman DA, Leavitt J (1974) Human memory and the cholinergic system: a relationship to ageing? Arch Neurol 30:113–121
Frey PW, Colliver JA (1973) Sensitivity and responsivity measures for discrimination learning. Learn Motiv 4:327–342
Gershon S (1984) Comparative side effect profiles of trazodone and imipramine: special reference to the geriatric population. Psychopathology 17:39–50
Gershon S, Newton R (1980) Lack of anticholinergic side effects with a new antidepressant — trazodone. J Clin Psychiatry 41:100–104
Greenwood DT (1982) Viloxazine and neurotransmitter function. In: Costa E, Racagni G (eds) Typical and atypical antidepressants: molecular mechanisms. Raven Press, New York
Kirby M, Turner P (1974) Some preliminary observations on ICI 58,834, a new psychotropic agent in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1:169
Lamping DL, Spring B, Gelenberg AJ (1984) Effects of two antidepressants on memory performance in depressed outpatients: a double-blind study. Psychopharmacology 84:254–261
Mattilla MJ, Liljequist R, Seppala T (1978) Effects of amitriptyline and mianserin on psychomotor skills and memory in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 5S:53–55
Milner B (1971) Interhemispheric differences in the localisation of psychological processes in man. Br Med Bull 27:272–277
Peck RE (1959) The SHP-test — an aid in the detection and measurement of depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1:35–40
Richelson E (1984) The newer antidepressants: structures, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and proposed mechanisms of action. Psychopharmacol Bull 20:213–223
Thompson PJ, Trimble MR (1982) Non-MAOI antidepressant drugs and cognitive functions: a review. Psychol Med 12:539–548
Turner P, Bayliss PF, Ghose K (1975) Clinical pharmacology of viloxazine (Vivalan). J Int Med Res 3:41–49
Weingartner H, Silberman E (1982) Models of cognitive impairment: cognitive changes in depression. Psychopharmacol Bull 18:27–42
Wolkowitz OM, Weingartner H, Thompson K, Picker D, Paul SM, Hommer DW (1987) Diazepam-induced amnesia: a neuropharmacological model of an “organic amnestic syndrome”. Am J Psychiatry 144:25–29
Zornetzer SF (1978) Neurotransmitter modulation and memory: a new neuropharmacological phrenology. In: Lipton LA et al. (eds) Psychopharmacology, a generation of progress. Raven Press, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Curran, H.V., Sakulsriprong, M. & Lader, M. Antidepressants and human memory: an investigation of four drugs with different sedative and anticholinergic profiles. Psychopharmacology 95, 520–527 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00172967
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00172967