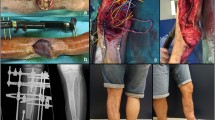
Abstract
Old age, diabetes and atherosclerotic disease all have been considered to be relative contraindications for microsurgery. As such, gangrenous lesions of the lower limb traditionally resulted in staged amputations. A more aggressive approach, combining revascularization and free tissue transfer, allowed us to limit the level of amputation and to start early ambulation and rehabilitation, without the need for major orthotic help. Performing the vascular procedure, debridement, and free tissue transfer in one single intervention greatly reduces the number of operative procedures without substantial increase in operative time. Twenty consecutive patients underwent a combined free flap and revascularization procedure, two patients died perioperatively. One free flap was lost and needed replacement. All surviving patients were ambulating postoperatively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atiyeh B, Sfeir R, Hussein M (1995) Preliminary arteriovenous fistual for free-flap reconstruction in the diabetic foot. Plast Reconstr Surg 95:1062–1069
Black M, Chait L, O'Brien B (1978) How soon may the axial vessels of a surviving free flap be safely ligated: a study in pigs. Br J Plast Sung 31:205–209
Bodily K, Burgess E (1983) Contralateral limb and patient survival after leg amputation. Am J Surg 146:280–282
Bonawitz S, Schnarrs R, Rosenthal A (1991) Free-tissue transfer in elderly patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 87:1075–1079
Briggs S, Banis J, Kaebnick H (1985) Distal revascularization and microvascular free tissue transfer; an alternative to amputation in ischemic lesions of the lower extremity. J Vase Surg 2:806–811
Buchbinder D, Pasch A, Verta M (1985) Ankle bypass: should we go the distance? Am J Surg 150:216–219
Chowdary R, Celani V Goodreau J (1991) Free-tissue transfers for limb salvage utilizing in situ saphenous vein bypass conduit as the inflow. Plast Reconstr Surg 87:529–535
Ciresi K, Anthony J, Hoffman W (1993) Limb salvage and wound coverage in patients with large ischemic ulcers: a multidisciplinary approach with revascularization and free tissue transfer. J Vase Surg 18:648–655
Colen L (1987) Limb salvage in the patient with severe peripheral vascular disease: the role of microsurgical free tissue transfer. Plast Reconstr Surg 79:389–395
Cooper G, Austin C, Brannigan P (1990) Outflow resistance and early occlusion of infrainguinal bypass grafts. Eur J Vasc Surg 4:279–283
Cronewett J, McDaniel M, Zwolak R (1989) Limb salvage despite extensive tissue-loss. Arch Surg 124:609–615
Dabb R, Davis R (1984) Latissimus dorsi free flaps in the elderly: an alternative to below-knee amputation. Plast Reconstr Surg 73:633–640
Furnas H, Canales F, Lineaweaver (1991) Microsurgical tissue transfer in patients more than 70 years of age. Ann Plast Surg 26:133–139
Herrera H, Geary J, Whitehead P (1991) Revascularization of the lower extremity with omentum. Clin Plast Surg 18:491–495
Houghton AD, Taylor PR, Thurlow S (1992) Success rates for rehabilitation of vascular amputees: implications for preoperative assessment and amputation level. Br J Surg 79:753–755
Karp N, Kasabian A, Siebert J (1994) Microvascular free-flap salvage of the diabetic foot: a 5 year experience. Plast Reconstr Surg 94:834–840
Khoo C, Bailey (1982) The behaviour of free muscle and musculocutaneous flaps after early loss of axial blood supply. Br J Plast Surg 35:43–46
Kucan J, Robson M (1986) Diabetic foot infections: fate of the contralateral foot. Plast Reconstr Surg 77:439–441
Lai C, Lin S, Yang C (1991) Limb salvage of infected diabetic foot ulcers with microsurgical free-muscle transfer. Ann Plast Surg 26:212–219
Lindholt IS, Bovling S, Fasting H (1994) Vascular surgery reduces the frequency of lower limb major amputations. Eur J Vasv Surg 8:31–35
LoGerfo F, Coffman J (1992) Vascular and microvascular disease of the foot in diabetes, implications for foot care. N Engl J Med 311:1615–1619
LoGerfo F, Gibbons G, Pomposelli F (1992) Trends in the care of the diabetic foot, expanded role of arterial reconstruction. Arch Surg 127:617–621
Lovett J, Shestak K, Makaroun M (1994) Analysis of lower extremity blood flow in the patient with peripheral vascular insufficiency: a guide for plastic surgeons. Ann Plast Surg 32:101–106
Menzolan J, La Morte W, Cantelmo N (1985) The preoperative angiogram as a predictor of peripheral vascular runoff. Am J Surg 150:346–352
Mimoun M, Hilligot P, Baux S (1989) The nutrient flap: a new concept of the role of the flap and application to the salvage of arteriosclerotic lower limbs. Plast Reconstr Surg 84:458–467
Murphy R, Rojy Th (1995) Prosthetic vascular graft and autogenous vein graft with free-tissue transfer in attempted lower-limb salvage. J Reconstr Microsurg: 11:31–35
Oishi S, Levin S, Pederson W (1993) Microsurgical management of extremity wounds in diabetics with peripheral vascular disease. Plast Reconstr Surg 92:485–492
Paaske WP, Laustsen J (1995) Femorodistal bypass grafting: quality of life and socioeconomic aspects. Eur J Vase Endovase Surg 10:226–230
Parvin S, Evans D, Bell P (1985) Peripheral resistance measurement in the assessment of severe peripheral vascular disease. Br J Surg 72:751–753
Pell JP, Donnan PT, Fowkes FGR (1993) Quality of life following lower limb amputation for peripheral arterial disease. Eur J Vase Surg 7:448–451
Pevec W, Hendricks D, Rosenthal M (1991) Revascularization of an ischemic limb by use of a muscle pedicle flap: a rabbit model. J Vase Surg 13:85–390
Rudolph R (1983) Nonhealing leg and foot wounds resulting from correctable arterial occlusion. Plast Reconstr Surg 71:209–211
Sadove R, Kanter M (1993) Absent neovascularization in a lower extremity free flap: a case report. J Reconstr Microsurg 9,5–9
Sayers RD, Thompson MM, Hartshorne T (1994) Treatment and outcome of severe lower-limb ischaemia. Br J Surg 81:521–523
Searles J, Colen L (1991) Foot reconstruction in diabetes mellitus and peripheral vascular insufficiency. Clin Plast Surg 18:467–483
Serafin D, Shearin J, Georgiade N (1977) The vascularization of free flaps: a clinical and experimental correlation. Plast Reconstr Surg 60:233–241
Serletti J, Hurwitz S, Jones A (1993) Extension of limb salvage by combined vascular reconstruction and adjunctive free-tissue transfer. J Vase Surg 18:972–980
Shestak K, Fritz D, Newton E (1990) Expanding the horizons in treatment of severe peripheral vascular disease using microsurgical techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 85:406–411
Shestak K, Hendricks D, Webster M (1990) Indirect revascularization of the lower extremity by means of microvascular free-muscle flap — a preliminary report. J Vase Surg 12:581–585
Sonntag B, Murphy R, Chernofsky M (1995) Microvascular steal phenomenon in lower extremity reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 34:336–340
Stark B, Hong C, Futrell J (1988) Enhanced neovascularization of rat tubed pedicle flaps with low perfusion of the wound margin. Plast Reconstr Surg 80:814–824
Tyrell M, Grigg M, Wolfe J (1989) Is arterial reconstruction to the ankle worthwhile in the absence of autologous vein? Eur J Vase Surg 3:429–434
Ubbink D, Kitslaar P, Tordoir J (1993) Skin microcirculation in diabetic and non-diabetic patients at different stages of lower limb ischaemia. Eur J Vasc Surg 7:659–666
van Berge Henegouwen D, Stelzer G, Deutzenberg T (1987) Pedal and distal lower leg bypasses with a distal arteriovenous fistula. Eur J Vasc Surg 1:251–258
Vidal P (1994) Microsurgical management of extremity wounds in diabetics with peripheral vascular disease (letter). Plast Reconstr Surg 94:742–743
Vos G, Rauwerda J, van den Broek T (1989) The correlation of perioperative outflow resistance measurements with patency in 109 infrainguinal arterial reconstructions. Eur J Vasc Surg 3:539–542
The Vascular Surgical Society of Great-Brittain and Ireland (1995) Critical limb ischaemia: management and outcome. Report of a national survey. Eur J Vasc Surg 10:108–113
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Landuyt, K., Vermassen, F., Monstrey, S. et al. Single-stage revascularization and free flap coverage in the treatment of ischemic lower limb lesions. Eur J Plast Surg 19, 245–252 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171878
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171878