Abstract
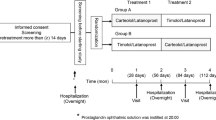
• Background: In this double-blind prospective trial the efficacy of lowering the intraocular pressure of l-moprolol given alone and in combination with dipivefrin was tested. a Methods: Twenty-seven patients with primary open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension were randomly assigned to receive twice-daily l-moprolol eye drops or dipivefrin eye drops for 4 weeks; in a second phase of the trial, the combination of the two drugs was administered for 4 weeks. • Results: The results of this study indicated that l-moprolol and dipivefrin had an equivalent effect in lowering the intraocular pressure. The association of the two drugs caused a further reduction of intraocular pressure which was significant only in the group previously treated with dipivefrin alone. • Conclusion: This trial demonstrated that the combination of l-moprolol and dipivefrin is an effective and safe treatment for elevated intraocular pressure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RC, Robin AL, Long D, et al. (1988) A combination of levobunolol and dipivefrin for the treatment of glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol 106:904–907
Demailly P (1991) Medical treatment of primary open-angle glaucoma. Proceedings, Fourth EUPO Course for Residents in Ophthalmology, 20–22 June, Turin, Italy, pp 135–154
Garofalo G, Grecchi G, Terrana M et al. (1987) Controllo delta pressione oculare mediante associazione l-moprololo e terapie antiglaucomatose tradizionali. Boll Ocul 66 (4):607–610
Goldberg I, Ashburn FS, Palmberg PF, et al. (1980) Timoptic and epinephrine. A clinical study of ocular interactions. Arch Ophthalmol 98:484–486
Higgins RG, Brubaker RF (1980) Acute effect of epinephrine on aqueous humor formation in the timclol treated normal eye as measured by fluorophotometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 19:420–423
Keates EU, Stone RA (1981) Safety and effectiveness of concomitant administration of dipivefrin and timolol maleate. Am J Ophthalmol 91:243–248
Korey MS, Hodapp E, Kass MA et al. (1982) Timolol and epinephrine. Long-term evaluation of concurrent administration. Arch Ophthalmol 100:742–745
Lison L (1961) Statistica applicate alla biologia sperimentale. Ambrosiana, Milan
Morrison JC, Robin AL (1989) Adjunctive glaucoma therapy. A comparison of apraclonidine to dipivefrin when added to timolol maleate. Ophthalmology 96:3–7
Ohrstrom A, Kattstrom O (1981) Interaction of timolol and adrenaline. Br J Ophthalmol 65:53–55
Parrow KA, Hong YJ, Shin DH et al. (1989) Is it worthwhile to add dipivefrin HCl 0.1% to topical betal-, beta2-blockert herapy? Ophthalmology 96:1338–1342
Pecori Giraldi J, Virno M, Ciarnella A et al. (1985) Le beta bloquant levomoprolol dans le treaement du glaucome. Bull Mem S F O 96:433–436
Pecori Giraldi J, Virno M, Ralli R et al. (1986) Long-term treatment of wide angle glaucoma with the betablocker levomoprolol: therapeutic efficiency without side effects. Fortschr Ophthalmol 83:564–566
Robuschi M, Barbieri P, Lodola E et al. (1990) Levomoprolol, a new beta-blocker for the treatment of glaucoma: effect on IOP and on pulmonary functions. Proceedings, Twenty-sixth ICO, Singapore
Thomas JV, Epstein DL (1981) Timolol and epinephrine in primary openangle glaucoma. Transient additive effect. Arch Ophthalmol 99:91–95
Tsoy EA, Meekins BB, Shields BM (1986) Comparison of two treatment schedules for combined timolol and dipivefrin therapy. Am J Ophthalmol 102:320–324
Virno M, Pecori Giraldi J, Taverniti L et al. (1983) Effetto ipotensivo endoculare del beta-bloccante l-moprololo nel glaucoma. Nota preliminare. Proceedings, Eighth Convegno della Societa' Oftalmologica Siciliana, Taormina-Giardini Naxos, pp 267-275
Virno M, Ciarnella A, Cozza R et al. (1984) 11 levomoprololo nel trattamento a lungo termine del glaucoma cronico semplice. Proceedings, sixty-fourth Congresso della Societa' Oftalmologica Italiana, Roma, pp 647–651
Virno M, Pecori Giraldi J, Garofalo G (1986) Topical levomoprolol in the treatment of glaucoma. Glaucoma 8:14–17
Weinreb RN, Ritch R, Kushner FH (1986) Effect of adding betaxolol to dipivefrin therapy. Am J Ophthalmol 101:196–198
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rossetti, L., Barbieri, P., Velati, P. et al. The efficacy of the combination of I-moprolol and dipivefrin in reducing the intraocular pressure in primary open-angle glaucoma or in ocular hypertension. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 232, 670–674 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171382
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171382