Abstract
Several gastric functions are modulated by the sympathetic nervous system, but local mechanisms involved in the control of noradrenaline release are largely unknown.
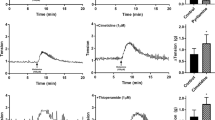
Overflow of endogenous noradrenaline was studied from isolated rat stomach incubated in Ussing chambers allowing the separate determination of mucosal and serosal overflow. Spontaneous noradrenaline overflow was similar at the mucosal and serosal side, but electrical field stimulation caused a frequency-dependent increase in noradrenaline overflow selectively at the serosal side. Evoked noradrenaline overflow was blocked by tetrodotoxin, not affected by indometacin and markedly enhanced (by about 250%) by yohimbine. In the presence of indometacin and yohimbine, sulprostone (an agonist at EP1/EP3 receptors) and misoprostol (an agonist at EP2/EP3 receptors) reduced the noradrenaline overflow evoked by stimulation at 3 Hz maximally by about 80% (EC50: 6 nmol/l and 11 nmol/l, respectively). The EP1 receptor selective antagonist AH 6809 (6-isopropoxy-9-oxoxanthene-2-carboxylic acid) did not antagonize the inhibition by sulprostone. Noradrenaline overflow evoked by stimulation at 1 Hz and 3 Hz was increased by scopolamine by about 50% and almost completely inhibited by oxotremorine. Neither, histamine nor the H3 receptor selective agonist (R)-α-methyl-histamine, nor the H1, H2 and H3 selective receptor antagonists mepyramine, cimetidine and thioperamide significantly affected noradrenaline overflow evoked by stimulation at 1 Hz or 3 Hz.
In conclusion, impulse-induced noradrenaline release in the rat stomach is controlled by multiple presynaptic mechanisms involving α2-adrenergic autoreceptors, EP3 prostanoid and muscarine heteroreceptors, whereas histaminergic mechanisms do not appear to be significant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrang JM, Garbarg M, Schwartz JC (1983) Auto-inhibition of histamine release mediated by a novel class (H3) of histamine receptors. Nature 302:832–837
Blair EL, Grund ER, Reed JD, Sanders DJ, Sanger G, Shaw B (1975) The effect of sympathetic nerve stimulation on serum gastrin, gastric acid secretion and mucosal blood flow responses to meat extract stimulation in anaesthetized cats. J Physiol (Lond) 253:493–504
Catterall WA (1980) Neurotoxins that act on voltage sensitive sodium channels in excitable membranes. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 20:15–43
Coleman RA, Smith WL, Narumiya S (1994) VIII. International union of pharmacology classification of prostanoid receptors: properties, distribution, and structure of receptors and their subtypes. Pharmacol Rev 46:205–229
Eglen RM, Whiting RL (1988) The action of prostanoid receptor agonists and antagonists on smooth muscle and platelets. Br J Pharmacol 94:591–601
Ekblad E, Ekelund M, Graffner H, Hakanson R, Sundler M (1985) Peptide containing nerve fibres in the stomach wall of rat and mouse. Gastroenterology 89:73–85
Fink K, Schlicker E, Neise A, Göthert M (1990) Involvement of presynaptic H3 receptors in the inhibitory effect of histamine on serotonin release in the rat brain cortex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 342:513–519
Fuder H, Muscholl E (1995) Heteroreceptor-mediated modulation of noradrenaline and acetylcholine release from peripheral nerves. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 126:265–412
Fuder H, Egenolf M, Torzewski M (1990) Inhibitory prejunctional histamine H3 receptors on noradrenergic nerves of guinea-pig atria. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 341:R87
Furness JB, Costa M (1974) The adrenergic innervation of the gastrointestinal tract. Ergeb Physiol 69:1–51
Furness JB, Costa M (1982) Identification of gastrointestinal neurotransmitters. In: Bertaccini G (ed) Mediators and drugs in gastrointestinal motility 1. (Handbook experimental pharmacology, vol 59/1.) Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp. 383–462
Hedqvist P (1977) Basic mechanisms of prostaglandin action on autonomic neurotransmission. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 17:259–279
Hew RWS, Hodgkinson CR, Hill SJ (1990) Characterization of histamine H3-receptors in guinea-pig ileum with H3-selective ligands. Br J Pharmacol 101:621–624
Hey C, Wessler I, Racké K (1995) Muscarinic inhibition of endogenous noradrenaline release from rabbit isolated trachea: receptor subtype and receptor reserve. Naunyn-Schmiedberg's Arch Pharmacol 350:464–472
Hill SJ (1990) Distribution, properties, and functional characteristics of three classes of histamine receptor. Pharmacol Rev 42:45–83
Holzer P, Livingston EH, Guth PH (1991a) Sensory neurons signal for an increase in rat gastric mucosal blood flow in face of pending acid injury. Gastroenterology 101:416–423
Holzer P, Livingston EH, Saria A, Guth PH (1991b) Sensory neurons mediate protective vasodilatation in rat gastric mucosa. Am J Physiol 260:G363-G370
Ishikawa S, Sperelakis N (1987) A novel class (H3) of histamine receptors on perivascular nerve terminals. Nature 327:158–160
Jansson G, Martinson J (1966) Studies on the ganglionic site of action of sympathetic outflow to the stomach. Acta Physiol Scand 68:184–192
Lee Y, Shiosaka S, Emson PC, Powell JF, Smith AD, Tohyama M (1985) Neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactive structure in the rat stomach with special reference to noradrenaline neuron system. Gastroenterology 89:118–126
Mantelli L, Amerini S, Rubio A, Ledda F (1991) Prejunctional prostanoid receptors on cardiac adrenergic terminals belong to the EP3 subtype. Br J Pharmacol 102:573–576
Miller TA (1983) Protective effects of prostaglandins against gastric mucosal damage: current knowledge and proposed mechanisms. Am J Physiol 245:601–623
Möhlig A, Reimann A, Bräutigam M, Racké K (1992) Release of endogenous noradrenaline from the rat stomach is inhibited via prostanoid receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 345:R63
Molderings G, Malinowska B, Schlicker E (1992) Inhibition of noradrenaline release in the rat vena cava via prostanoid receptors of the EP3-subtype. Br J Pharmacol 107:352–355
Muscholl E (1980) Peripheral muscarinic control of norepinephrine release in the cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol 239:H713-H720
Ohia SE, Jumblatt JE (1990) Prejunctional inhibitory effects of prostanoids on sympathetic neurotransmission in the rabbit irisciliary body. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1255:11–16
Okuma Y, Yokotani K, Osumi Y (1987) Sympatho-adrenomedullary system mediation of the bombesin-induced central inhibition of gastric acid secretion. Eur J Pharmacol 139:73–78
Racké K, Schwörer H (1994) Role of histamine H3 receptors in the control of neuro-humoral mechanisms in the gastro-intestinal tract. Z Gastroenterol 32 [Suppl. 2]:61–63
Racké K, Krupa H, Schröder H, Vollrath L (1989) In vitro synthesis of dopamine and noradrenaline in the isolated rat pineal gland. Day-night variations and effects of electrical stimulation. J Neurochem 53:354–361
Racké K, Bähring A, Brunn G, Elsner M, Wessler I (1991) Characterization of endogenous noradrenaline release from intact and epithelium-denuded rat isolated trachea. Br J Pharmacol 103:1213–1217
Racké K, Bähring J, Langer C, Bräutigam M, Wessler I (1992a) Prostanoids inhibit release of endogenous norepinephrine from rat isolated trachea. Am Rev Respir Dis 146:1182–1186
Racké K, Möhlig A, Reimann A, Bräutigam M (1992b) Release of endogenous noradrenaline from the rat stomach is inhibited via prostanoid receptors of the EP3 subtype. Pharmacol Res 26:318
Racké K, Brunn G, Elsner M, Wessler I (1993) Effects of indomethacin on muscarinic inhibition of endogenous noradrenaline release from rat isolated trachea. Naunyn-Schmiedberg's Arch Pharmacol 348:21–27
Rangachari PK (1992) Histamine — mercurial messenger in the gut. Am J Physiol 262:G1-G13
Reed JD, Sanders DJ (1971) Splanchnic nerve inhibition of gastric acid secretion and mucosal blood flow in anaesthetized cats. J Physiol (Lond) 219:555–570
Reimann A, Hering B (1992) Vascular pre-perfusion markedly affects the modulation by nicotine and muscarine receptors of intestinal serotonin release studied in Ussing chambers. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 345:R111
Reimann A, Bock C, Racké K (1993) Muscarinic M3 receptors mediate stimulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) release from isolated segments of the rabbit small intestine incubated in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 367:150P
Ries P, Fuder H (1992) Mast cell degranulation by different stimuli modulates evoked noradrenaline overflow from rat perfused heart differentially. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 346:R17
Roman C (1982) Nervous control of esophageal and gastric motility. In: Bertaccini G, (ed) Mediators and drugs in gastrointestinal motility I. (Handbook Experimental Pharmacology, vol 59/1) Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp. 223–278
Rump LC, Schollmeyer P (1989) Effects of endogenous and synthetic prostanoids, the thromboxane A2 receptor agonist U-46619 and arachidonic acid on [3H]-noradrenaline release and vascular tone in rat isolated kidney. Br J Pharmacol 97:819–828
Schlicker E, Betz R, Göthert M (1988) Histamine H3 receptor-mediated inhibition of serotonin release in the rat brain cortex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337:588–590
Schlicker E, Schunack W, Göthert M (1990) Histamine H3 receptor-mediated inhibition of noradrenaline release in the pig retina discs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 342:497–501
Sontag SJ (1986) Prostaglandins in peptic ulcer disease. An overview of current status and future directions. Drugs 32:445–457
Starke K, Göthert M, Kilbinger H (1989) Modulation of neurotransmitter release by presynaptic autoreceptors. Physiol Rev 69:864–989
Tallarida RJ, Murray RB (1998) Manual of pharmacological calculations. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Tepperman BL, Whittle BJR (1991) Comparison of the effects of neuropeptide Y and noradrenaline on rat gastric mucosal blood flow and integrity. Br J Pharmacol 102:95–100
Terano A, Ota S, Hiraishi H, Mutoh H (1993) Gastric cytoprotection — morphological perspectives. Acta Jpn 43:2–10
Whittle BJR (1989) The defensive role played by the gastric microcirculation. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 11 [Suppl. I]: 35–43
Yokotani K, Muramatsu I, Fujiwara M, Osumi Y (1983) Effects of the sympathoadrenal system on vagally induced gastric acid secretion and mucosal blood flow in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 224:436–442
Yokotani K, Muramatsu I, Fujiwara M (1984) α1- and α2-type adrenoceptors involved in the inhibitory effect of splanchnic nerves on parasympathetically stimulated gastric acid secretion in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 229:305–310
Yokotani K, Okuma Y, Osumi Y (1992) Release of endogenous noradrenaline from the vascularly perfused rat stomach in vitro —modulation by presynaptic and postsynaptic adrenoceptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 260:728–733
Yokotani K, Osumi Y (1993) Cholinergic M2 muscarinic receptor-mediated inhibition of endogenous noradrenaline release from the isolated vascularly perfused rat stomach. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:54–60
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Racké, K., Berrino, L., Möhlig, A. et al. Modulation of noradrenaline release in rat isolated stomach by prostanoids, but not by histaminergic mechanisms. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 352, 631–639 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171322
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171322